Python日志模块logging简介
日志处理是项目的必备功能,配置合理的日志,可以帮助我们了解系统的运行状况、定位位置,辅助数据分析技术,还可以挖掘出一些额外的系统信息。
本文介绍Python内置的日志处理模块logging的常见用法。
1,日志等级
日志是分等级的,这点不难理解,任何信息都有轻重缓急之分,通过分级,我们可以方便的对日志进行刷选过滤,提高分析效率。
简单说,日志有以下等级:
DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR,CRITICAL
其重要性依次增强。一般的,这五个等级就足够我们日常使用了。
2,日志格式
日志本质上记录某一事件的发生,那么它应当包括但不限于以下信息:
事件等级,发生时间,地点(代码位置),错误信息

3,logging模块的四大组件
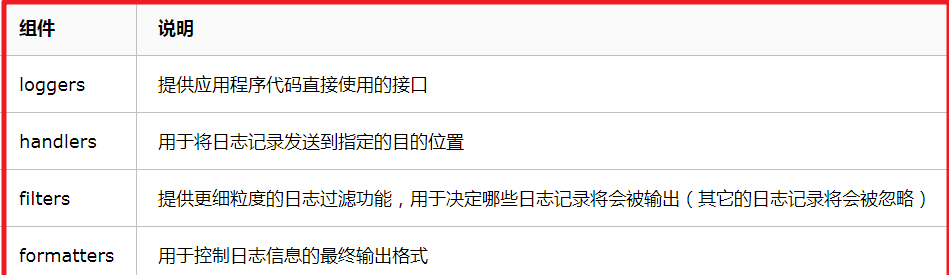
通过这四大组件,我们便可以自由配置自己的日志格式。
4,案例展示
在实际应用中,一般会按照时间或者预置的大小对日志进行定期备份和分割,我们下面就按照这两点分别进行介绍:
4-1,按照预置的文件大小配置日志,并自动分割备份
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import logging.handlers
import os def get_logger():
log_path = "./logs" if not os.path.isdir(log_path):
os.mkdir(log_path)
os.chmod(log_path, 0777) all_log = log_path + os.path.sep + "all.log"
error_log = log_path + os.path.sep + "error.log" if not os.path.isfile(all_log):
os.mknod(all_log)
os.chmod(all_log, 0777) if not os.path.isfile(error_log):
os.mknod(error_log)
os.chmod(error_log, 0777) log_format = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s") # get logger object
my_logger = logging.getLogger("my_logger")
my_logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # auto split log file by interval specified(every minute), record debug message and above.
rf_handler = logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(all_log, when='M', interval=1, backupCount=3)
rf_handler.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
rf_handler.setFormatter(log_format) # don't split log file, only record error message and above.
f_handler = logging.FileHandler(error_log)
f_handler.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
f_handler.setFormatter(log_format) my_logger.addHandler(rf_handler)
my_logger.addHandler(f_handler) return my_logger def test():
msg = {"debug": "This is a debug log",
"info": "This is a info log",
"warning": "This is a warning log",
"error": "This is a error log",
"critical": "This is a critical log"} for k, v in msg.items():
if k == "debug":
logger.debug(v)
elif k == "info":
logger.info(v)
elif k == "warning":
logger.warning(v)
elif k == "error":
logger.error(v)
elif k == "critical":
logger.critical(v) if __name__ == '__main__':
index = 1
logger = get_logger() while True:
test()
print(index)
index = index + 1
实际效果:
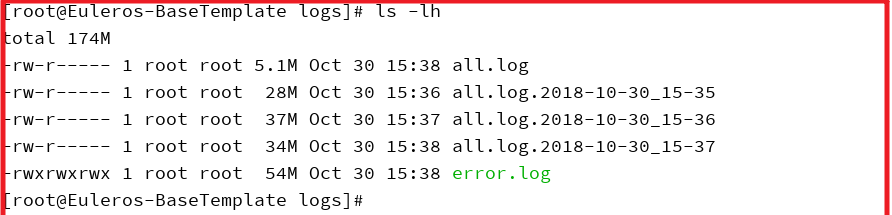
all.log保存最新的日志,历史副本按照时间后缀进行保存,最多留存三个。
4-2,按照预置的文件大小配置日志,并自动分割备份
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import logging
from logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler import os def test():
msg = {"debug": "This is a debug log",
"info": "This is a info log",
"warning": "This is a warning log",
"error": "This is a error log",
"critical": "This is a critical log"} for k, v in msg.items():
if k == "debug":
logger.debug(v)
elif k == "info":
logger.info(v)
elif k == "warning":
logger.warning(v)
elif k == "error":
logger.error(v)
elif k == "critical":
logger.critical(v) def get_logger():
dir_path = "./logs"
file_name = "rotating_log"
if not os.path.isdir(dir_path):
os.mkdir(dir_path)
os.chmod(dir_path, 0777) file_path = dir_path + "/" + file_name
if not os.path.isfile(file_path):
os.mknod(file_path)
os.chmod(file_path, 0777) my_logger = logging.getLogger("rotating_log")
my_logger.setLevel(level=logging.INFO) # auto split log file at max size of 4MB
r_handler = RotatingFileHandler(file_path, maxBytes=4*1024*1024, backupCount=3)
r_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO) formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
r_handler.setFormatter(formatter) my_logger.addHandler(r_handler) return my_logger if __name__ == '__main__':
logger = get_logger()
index = 1
while True:
test()
print(index)
index = index + 1
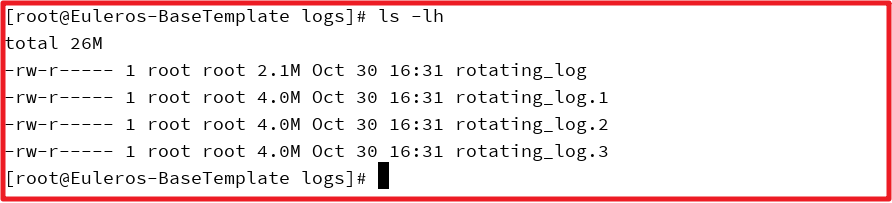
最终效果:
Python日志模块logging简介的更多相关文章
- python日志模块logging
python日志模块logging 1. 基础用法 python提供了一个标准的日志接口,就是logging模块.日志级别有DEBUG.INFO.WARNING.ERROR.CRITICAL五种( ...
- 【python】【logging】python日志模块logging常用功能
logging模块:应用程序的灵活事件日志系统,可以打印并自定义日志内容 logging.getLogger 创建一个log对象 >>> log1=logging.getLogger ...
- Python 日志模块logging
logging模块: logging是一个日志记录模块,可以记录我们日常的操作. logging日志文件写入默认是gbk编码格式的,所以在查看时需要使用gbk的解码方式打开. logging日志等级: ...
- Python日志模块logging用法
1.日志级别 日志一共分成5个等级,从低到高分别是:DEBUG INFO WARNING ERROR CRITICAL. DEBUG:详细的信息,通常只出现在诊断问题上 INFO:确认一切按预期运行 ...
- python日志模块logging学习
介绍 Python本身带有logging模块,其默认支持直接输出到控制台(屏幕),或者通过配置输出到文件中.同时支持TCP.HTTP.GET/POST.SMTP.Socket等协议,将日志信息发送到网 ...
- Python 日志模块 logging通过配置文件方式使用
vim logger_config.ini[loggers]keys=root,infoLogger,errorlogger [logger_root]level=DEBUGhandlers=info ...
- Python日志模块logging&JSON
日志模块的用法 json部分 先开一段测试代码:注意 str可以直接处理字典 eval可以直接将字符串转成字典的形式 dic={'key1':'value1','key2':'value2'} ...
- 『无为则无心』Python日志 — 64、Python日志模块logging介绍
目录 1.日志的作用 2.为什么需要写日志 3.Python中的日志处理 (1)logging模块介绍 (2)logging模块的四大组件 (3)logging日志级别 1.日志的作用 从事与软件相关 ...
- python日志模块---logging
1.将日志打印到屏幕 import logging logging.debug('This is debug message---by liu-ke') logging.info('This is i ...
随机推荐
- 代码审计-dedecms任意文件名修改拿shell
0x01 漏洞分析 漏洞文件: dede/file_manage_control.php ,$fmdo 开始时赋值,所以我们可以使fmdo=rename ,使其进入 if语句 ,调用 FileMana ...
- DNS记录类型
A 记录: A (Address) 记录是用来指定主机名(或域名)对应的IP地址记录.用户可以将该域名下的网站服务器指向到自己的web server上.同时也可以设置您域名的子域名.通俗来说A记录就是 ...
- vue+element 实现商品sku效果
在网上搜索了很久,没有发现合适sku编辑的文章,只能自己写一个vue+element 的sku编辑功能.实现的效果如下图 除成本.售价.库存.货号这几个写死的属性外,可自行添加/删除商品属性,自行添加 ...
- [JOYOI1510] 专家复仇 - Floyd
题目限制 时间限制 内存限制 评测方式 题目来源 1000ms 131072KiB 标准比较器 Local 题目背景 外星人完成对S国的考察后,准备返回,可他们的飞碟已经没燃料了……S国的专家暗自窃喜 ...
- Hello World ! 节日快乐!
节日快乐! 世界你好,Hello World Java public class HelloWorld{ public static void main(String[] args) { System ...
- .htaccess文件上传利用
一般.htaccess可以用来留后门和针对黑名单绕过 创建一个txt写入 AddType application/x-httpd-php .png 打开另存为 保存类型为所有文件 上传.htacces ...
- Vue学习系列(三)——基本指令
前言 在上一篇中,我们已经对组件有了更加进一步的认识,从组件的创建构造器到组件的组成,进而到组件的使用,.从组件的基本使用.组件属性,以及自定义事件实现父子通讯和巧妙运用插槽slot分发内容,进一步的 ...
- ArcGIS Engine专题地图渲染器的实现(入门版)
专题地图(Thematic Map)是着重表示一种或数种自然要素特征或社会经济现象的地图 专题地图的内容由两部分构成: 1.专题内容——图上突出表示的自然或社会经济现象及其有关特征 2.地理基础——用 ...
- CPU爆满后的无助感
告警 晚七点刚好上地铁,握在手里的手机震动了好几下,根据震动这几下的手感已经判断出这是钉钉在告警了,十有八九就是线上的问题,通过Zabbix监控的一台线上服务器已经五分钟不可达,这应该不会是网络网络问 ...
- SpringBoot系列之YAML配置用法
1.全局配置 SpringBoot的全局配置文件有两种: application.properties application.yml 配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值,主要是 ...
