张高兴的 Raspberry Pi AI 开发指南:(二)使用 Python 进行目标检测
在上一篇博客中,探讨了使用 rpicam-apps 通过 JSON 文件配置并运行目标检测示例程序。虽然这种方法可以实现有效的检测,但它限制了开发者直接在代码中利用检测结果的能力。因此,在本篇博客中,将深入探讨如何借助 HailoRT Python API 调用神经处理单元(NPU),以实现在 Python 程序中的目标检测功能。
Python 环境配置
在上一篇博客中已经安装了 hailo-all,这其中包含了 Hailo NPU 的所有必要组件。然而,根据硬件和操作系统需求,可能需要单独安装或更新驱动程序。对于非 Raspberry Pi 设备或当遇到驱动版本不兼容的问题时,此时可以登录 Hailo 的网站 https://hailo.ai/developer-zone/software-downloads,并选择适合系统的驱动程序进行下载与安装。

例如,如果正在使用基于 arm64 架构的 Ubuntu 操作系统,并且需要 4.19.0 版本的驱动,那么可以下载相应的 PCIe 驱动包和 HailoRT 包,并执行以下命令完成安装:
sudo apt purge -y hailo-all # 卸载现有的整合包
sudo dpkg -i hailort-pcie-driver_4.19.0_all.deb # 安装新的驱动
sudo dpkg -i hailort_4.19.0_arm64.deb # 安装 HailoRT
为了能够在 Python 中调用 NPU,还需要安装 Python 相关库。同样地,在 Hailo 的官方网站中找到对应 Python 版本的 .whl 文件,并按照下面的步骤创建虚拟环境并安装必要的软件包:
conda create -n hailort python=3.10 # 创建虚拟环境
conda activate hailort # 激活虚拟环境
pip install hailort-4.19.0-cp310-cp310-linux_aarch64.whl # 安装 HailoRT Python 包
还需要安装 OpenCV 对图像进行处理。由于 OpenCV 无法读取 Raspberry Pi 的 CSI 摄像头,如果需要使用请额外安装 picamera2 和 rpi-libcamera。
pip install opencv-python
pip install picamera2 rpi-libcamera
实现 USB 摄像头的目标检测
为了让目标检测更加实用,需要将摄像头获取的实时视频流作为输入,并在每帧图像上应用深度学习模型来识别对象。无论是否使用 Hailo-8 进行目标检测,都需要遵循以下步骤来编写代码。
- 打开摄像头;
- 加载目标检测模型;
- 处理视频流,显示结果。
这里提供一个基本的代码框架,下面将逐步完成这个代码。
import cv2
# TODO: 加载模型
# 打开默认摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
# 读取帧
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# TODO: 进行推理
# 显示帧
cv2.imshow('Detections', frame)
# 按下 'q' 键退出循环
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# 释放摄像头并关闭窗口
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
首先来完成第一个 TODO 的内容 加载模型 。在代码的顶部引入 HailoRT 中必要的类。
import numpy as np
from hailo_platform import HEF, Device, VDevice, InputVStreamParams, OutputVStreamParams, FormatType, HailoStreamInterface, InferVStreams, ConfigureParams
在 Hailo NPU 上运行的是 .hef 的模型文件,Hailo 的 GitHub 仓库 https://github.com/hailo-ai/hailo_model_zoo 提供了大部分主流的预编译模型,可以直接下载使用。这里使用 YOLOv8s 作为测试。
# COCO 数据集的标签
class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush']
# 加载 YOLOv8s 模型
hef_path = 'yolov8s.hef'
hef = HEF(hef_path)
模型加载完成后,还需要对 Hailo 设备进行一些配置。
# 初始化 Hailo 设备
devices = Device.scan()
target = VDevice(device_ids=devices)
# 配置网络组
configure_params = ConfigureParams.create_from_hef(hef, interface=HailoStreamInterface.PCIe)
network_group = target.configure(hef, configure_params)[0]
network_group_params = network_group.create_params()
# 获取输入输出流信息
input_vstream_info = hef.get_input_vstream_infos()[0]
output_vstream_info = hef.get_output_vstream_infos()[0]
# 创建输入输出虚拟流参数
input_vstreams_params = InputVStreamParams.make_from_network_group(network_group, quantized=False, format_type=FormatType.FLOAT32)
output_vstreams_params = OutputVStreamParams.make_from_network_group(network_group, quantized=False, format_type=FormatType.FLOAT32)
到这里第一个 TODO 的内容已经完成,下面来完成第二个 TODO 的内容 进行推理 。在推理之前,需要对输入模型中的图像进行变换,调整为模型输入的大小。
# 对图像进行预处理
resized_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (input_vstream_info.shape[0], input_vstream_info.shape[1]))
input_data = {input_vstream_info.name: np.expand_dims(np.asarray(resized_frame), axis=0).astype(np.float32)}
图像调整完成后,使用 infer() 方法进行推理。tf_nms_format 参数控制结果的输出形式,默认为 False,输出 Hailo 格式的数据,一个 numpy.ndarray 列表,每个元素代表类的检测结果,其格式为 [number_of_detections,BBOX_PARAMS];值为 True 时输出 TensorFlow 格式的数据,numpy.ndarray 类型的值,其格式为 [class_count, BBOX_PARAMS, detections_count]。
# 创建输入输出虚拟流并推理
with InferVStreams(network_group, input_vstreams_params, output_vstreams_params, tf_nms_format = True) as infer_pipeline:
with network_group.activate(network_group_params):
output_data = infer_pipeline.infer(input_data)
推理后需要对结果进行解析,不论是哪种类型的格式,BBOX_PARAMS 都是归一化后的值。因此需要计算原始图像和输入图像的比例,将结果逆归一化,然后再画出检测框。
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(class_names), 3))
# 根据坐标画出检测框
def draw_bboxes(image, bboxes, confidences, class_ids, class_names, colors):
for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
label = f'{class_names[class_ids[i]]}: {confidences[i]:.2f}'
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# 图像缩放比例
scale_x = frame.shape[1] / input_vstream_info.shape[1]
scale_y = frame.shape[0] / input_vstream_info.shape[0]
# 提取检测框坐标、类别等信息,并在原始帧上绘制
for key in output_data.keys():
num_classes, bbox_params, num_detections = output_data[key][0].shape
boxes = []
confidences = []
class_ids = []
for class_id in range(num_classes):
for detection_id in range(num_detections):
bbox = output_data[key][0][class_id, :, detection_id]
if bbox[4] > 0.5:
x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence = bbox[:5]
x1 = int(x1 * input_vstream_info.shape[0] * scale_x)
y1 = int(y1 * input_vstream_info.shape[1] * scale_y)
x2 = int(x2 * input_vstream_info.shape[0] * scale_x)
y2 = int(y2 * input_vstream_info.shape[1] * scale_y)
print(f'{class_names[class_id]}: {[x1, y1, x2, y2]} {bbox[:5]}')
boxes.append([x1, y1, x2, y2])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
draw_bboxes(frame, boxes, confidences, class_ids, class_names, colors)
到此,第二个 TODO 的内容也已实现,完整的程序如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from hailo_platform import HEF, Device, VDevice, InputVStreamParams, OutputVStreamParams, FormatType, HailoStreamInterface, InferVStreams, ConfigureParams
class_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush']
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(class_names), 3))
# 根据坐标画出检测框
def draw_bboxes(image, bboxes, confidences, class_ids, class_names, colors):
for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
label = f'{class_names[class_ids[i]]}: {confidences[i]:.2f}'
color = colors[class_ids[i]]
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# 加载YOLOv8模型
hef_path = 'yolov8s.hef'
hef = HEF(hef_path)
# 初始化Hailo设备
devices = Device.scan()
target = VDevice(device_ids=devices)
# 配置网络组
configure_params = ConfigureParams.create_from_hef(hef, interface=HailoStreamInterface.PCIe)
network_group = target.configure(hef, configure_params)[0]
network_group_params = network_group.create_params()
# 获取输入输出流信息
input_vstream_info = hef.get_input_vstream_infos()[0]
output_vstream_info = hef.get_output_vstream_infos()[0]
# 创建输入输出虚拟流参数
input_vstreams_params = InputVStreamParams.make_from_network_group(network_group, quantized=False, format_type=FormatType.FLOAT32)
output_vstreams_params = OutputVStreamParams.make_from_network_group(network_group, quantized=False, format_type=FormatType.FLOAT32)
# 使用摄像头0作为视频源
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 对图像进行预处理
resized_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (input_vstream_info.shape[0], input_vstream_info.shape[1]))
input_data = {input_vstream_info.name: np.expand_dims(np.asarray(resized_frame), axis=0).astype(np.float32)}
# 创建输入输出虚拟流并推理
with InferVStreams(network_group, input_vstreams_params, output_vstreams_params, tf_nms_format = True) as infer_pipeline:
with network_group.activate(network_group_params):
output_data = infer_pipeline.infer(input_data)
# 图像缩放比例
scale_x = frame.shape[1] / input_vstream_info.shape[1]
scale_y = frame.shape[0] / input_vstream_info.shape[0]
# 提取边界框、类别等信息,并在原始帧上绘制
for key in output_data.keys():
num_classes, bbox_params, num_detections = output_data[key][0].shape
boxes = []
confidences = []
class_ids = []
for class_id in range(num_classes):
for detection_id in range(num_detections):
bbox = output_data[key][0][class_id, :, detection_id]
if bbox[4] > 0.5:
x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence = bbox[:5]
x1 = int(x1 * input_vstream_info.shape[0] * scale_x)
y1 = int(y1 * input_vstream_info.shape[1] * scale_y)
x2 = int(x2 * input_vstream_info.shape[0] * scale_x)
y2 = int(y2 * input_vstream_info.shape[1] * scale_y)
print(f'{class_names[class_id]}: {[x1, y1, x2, y2]} {bbox[:5]}')
boxes.append([x1, y1, x2, y2])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
class_ids.append(class_id)
draw_bboxes(frame, boxes, confidences, class_ids, class_names, colors)
cv2.imshow('Detection', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# 释放资源
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
程序效果如下:
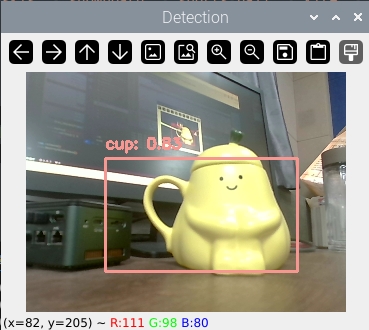
Hailo 的 GitHub 仓库中也提供了其他类型的应用,更多用法请查看 https://github.com/hailo-ai/Hailo-Application-Code-Examples 以及官方文档。
参考
- Hailo Documentation:https://hailo.ai/developer-zone/documentation/
- Hailo Application Code Examples:https://github.com/hailo-ai/Hailo-Application-Code-Examples
张高兴的 Raspberry Pi AI 开发指南:(二)使用 Python 进行目标检测的更多相关文章
- [Lua游戏AI开发指南] 笔记零 - 框架搭建
一.图书详情 <Lua游戏AI开发指南>,原作名: Learning Game AI Programming with Lua. 豆瓣:https://book.douban.com/su ...
- 树莓派(raspberry pi)系统开发
[树莓派(raspberry pi)] 01.在linux环境下给树莓派安装系统及入门各种资料 [树莓派(raspberry pi)] 02.PI3安装openCV开发环境做图像识别(详细版) 出处: ...
- Spark Streaming和Kafka整合开发指南(二)
在本博客的<Spark Streaming和Kafka整合开发指南(一)>文章中介绍了如何使用基于Receiver的方法使用Spark Streaming从Kafka中接收数据.本文将介绍 ...
- 利用raspberry pi搭建typecho笔记(二) sqlite和typecho部署
sqlite概述 typecho可以支持MYSQL和Sqlite两种数据库,因为Sqlite更为轻量,并且不需要额外的进程,而是直接对数据库文件进行读取,所以配置相对于MySQL也更为简单,仅需指定数 ...
- 【转】Polymer API开发指南 (二)(翻译)
原文转自:http://segmentfault.com/blog/windwhinny/1190000000596258 公开 property 当你公开一个 Polymer 元素的 propert ...
- Polymer API开发指南 (二)(翻译)
公开 property 当你公开一个 Polymer 元素的 property 名字时,就等于把这个 property 设置为公开API了.公开 property 会有如下的特性: 支持声明数据双向绑 ...
- Python自动化运维开发实战 二、Python基本用法
导语: Python编程博大精深,知识点众多,需要先整体上了解python的一些基本用法之后再去对每一个知识点细细研究,这样学习的速度会快很多.所以下面就先看一些python事先需要知道的基本知识. ...
- 2014年基于Raspberry Pi的5大项目
2014年基于Raspberry Pi的5大项目 Raspberry Pi(即树莓派)是一款基于Linux系统(Debian.ArchLinux)的单板机计算机,它只有一张信用卡大小,可用于电子表 ...
- 树莓派(Raspberry Pi)上手小记
引言 本日志中有不少软广告,博主并没有收他们任何好处,完全是给想入手的小伙伴们指条路而已.不喜勿看,不喜勿闻,不喜勿喷. 介绍 之前两三个月突然听说了这么个东西,也没有留意,某天突然在一个微信公众号上 ...
- 2019 年在 Raspberry Pi 「树莓派」上运行的 10 个操作系统推荐
原文:2019 年在 Raspberry Pi 「树莓派」上运行的 10 个操作系统推荐 image Raspberry Pi** 是一款基于 ARM 的单板计算机,默认运行一款称为 Raspbian ...
随机推荐
- CSS & JS Effect – Blue Tick Avatar
效果 难点 难题只有一个, 那就是如何把 blue tick image 定位当 avatar 的右下角. HTML <div class="avatar-wrapper"& ...
- Azure 入门系列 (第三篇 Publish Web Application to VM)
本系列 这个系列会介绍从 0 到 1 搭建一个 Web Application 的 Server. 间中还会带上一些真实开发常用的功能. 一共 6 篇 1. Virtual Machine (VM) ...
- C++ cout打印输出 (解决输出乱码)
cout打印输出 输出单份内容 // 输出单份内容 cout << "Hello World!" << endl; cout << 10 < ...
- Nuxt Kit 实用工具的使用示例
title: Nuxt Kit 实用工具的使用示例 date: 2024/9/25 updated: 2024/9/25 author: cmdragon excerpt: 摘要:本文介绍了Nuxt ...
- 【USB3.0协议学习】Topic1·USB3.0Hub的一些机制
一.USB3.0 Hub的单播(非广播)机制 Hub通过解析下行packet header中的Route String字段识别packet要传递的终点,其中4'b0000代表hub本身,4'b0001 ...
- 分布式缓存 - 缓存服务器 - redis
如果一般的缓存可以解决问题,就不必使用分布式缓存 : 一般使用分布式缓存 都是使用 redis : 使用教程: 1. 安装包 Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.StackExc ...
- document.designMode 设计模式
document.designMode 的默认值是 off 关闭: 在控制台输入 document.designMode = 'on' 就可以编辑页面内容:
- 洛谷P1381单词背诵
单词背诵 题目描述 灵梦有 \(n\) 个单词想要背,但她想通过一篇文章中的一段来记住这些单词. 文章由 \(m\) 个单词构成,她想在文章中找出连续的一段,其中包含最多的她想要背的单词(重复的只算一 ...
- 一图为你揭秘云数据库GaussDB管理平台亮点
云数据库GaussDB管理平台(TPOPS)是一款即开即用.稳定可靠.管理便捷的数据库运维管理平台.通过该平台,用户可以快速部署安装GauSSDB,实现智能化运维,大幅度提升运维和管理效率.一图带你揭 ...
- 异常处理、逻辑与(&)在条件结束判定的应用
例子:求1+2+-+n的和,要求不能使用乘除法.for.while.if.else.switch.case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)(注 题目来自力扣) (1)boolean和逻辑与(&am ...
