Axis in DataFrame
Axis in DataFrame
Optional parameter axis may appear in arithmetric between DataFrame and Series,the key point understanding the meaning of axis is match,by default the index of series shall match columns of DataFrame,broadcasting down the rows;And axis may also appear in apply(),max(),mean() or so kind of DataFrame object method,by default, axis='index',meaning find the max one among index,and that is to find the max one of every column.Please note that,apply() is not identical to applymap().apply(f) will perform f function on one-dimentional array(index or columns),by default,axis='index' while applymap(f) will perform f function on element-wise for DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
frame=pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(4,3),index=['Utah','Ohio','Texas','Oregon'],columns=list('bde'));frame
\3c pre>\3c code>.dataframe tbody tr th { vertical-align: top }
.dataframe thead th { text-align: right }
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -0.311649 | 0.252285 | -0.741715 |
| Ohio | 0.351583 | 1.287569 | 0.726872 |
| Texas | 0.605527 | -0.186660 | -0.993184 |
| Oregon | 1.577405 | 0.381833 | 1.607757 |
frame['b']
Utah -0.311649
Ohio 0.351583
Texas 0.605527
Oregon 1.577405
Name: b, dtype: float64
series1=frame.iloc[0];series1
b -0.311649
d 0.252285
e -0.741715
Name: Utah, dtype: float64
frame.sub(series1,axis='columns') # By default,arithmetic between DataFrame and Series matches the index of Series on the DataFrame's columns,broadcasting down the rows.
\3c pre>\3c code>.dataframe tbody tr th { vertical-align: top }
.dataframe thead th { text-align: right }
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Ohio | 0.663232 | 1.035284 | 1.468587 |
| Texas | 0.917176 | -0.438944 | -0.251470 |
| Oregon | 1.889054 | 0.129548 | 2.349471 |
frame.sub(series1,axis=1) # The same with above
\3c pre>\3c code>.dataframe tbody tr th { vertical-align: top }
.dataframe thead th { text-align: right }
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Ohio | 0.663232 | 1.035284 | 1.468587 |
| Texas | 0.917176 | -0.438944 | -0.251470 |
| Oregon | 1.889054 | 0.129548 | 2.349471 |
series2=frame['d'];series2
Utah 0.252285
Ohio 1.287569
Texas -0.186660
Oregon 0.381833
Name: d, dtype: float64
frame.sub(series2,axis='index') # Must set axis='index',so that broadcasts down on column.
\3c pre>\3c code>.dataframe tbody tr th { vertical-align: top }
.dataframe thead th { text-align: right }
| b | d | e | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utah | -0.563934 | 0.0 | -0.993999 |
| Ohio | -0.935986 | 0.0 | -0.560697 |
| Texas | 0.792186 | 0.0 | -0.806525 |
| Oregon | 1.195572 | 0.0 | 1.225924 |
frame.max(axis='index') # max() default to set axis='index',meaning find the max one among 'index',not every max one of every index.
b 1.577405
d 1.287569
e 1.607757
dtype: float64
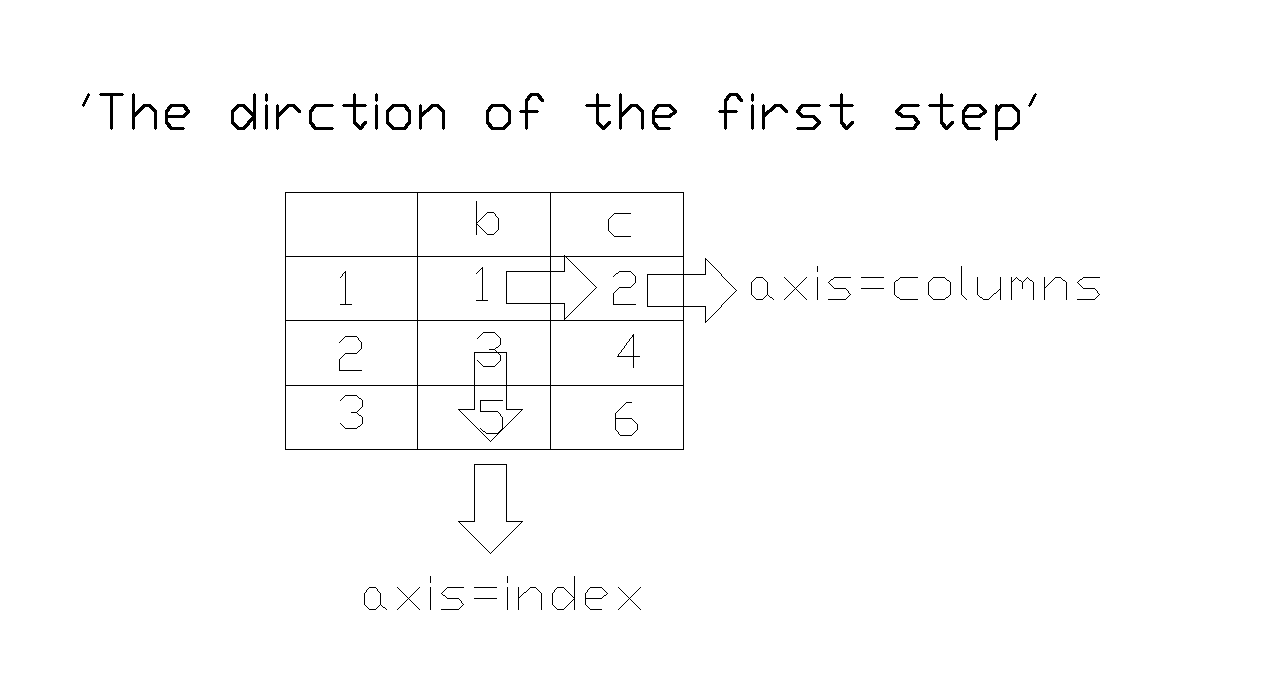
Summary:no matter arithmetic between df and series,and df object method, the operation steps can be divided into 2 setps,firstly, finding the direction of elementwise level operation,and then reapeating this process along the other direction.
df1=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4));df1
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 2 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
df1.sub(df1.loc[1],axis=1)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -4 | -4 | -4 | -4 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
df1.sub(df1[1],axis=0)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
df1.max(axis=0)
0 8
1 9
2 10
3 11
dtype: int32
df1.max(axis=1)
0 3
1 7
2 11
dtype: int32
The same rule can also be applied to np.concatenate() and pd.concat(),pd.DataFrame.any(),pd.DataFrame.all()
Signature: pd.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=False, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, copy=True)
Docstring:
Concatenate pandas objects along a particular axis with optional set logic
along the other axes. Can also add a layer of hierarchical indexing on the
concatenation axis, which may be useful if the labels are the same (or
overlapping) on the passed axis number
Parameters
objs : a sequence or mapping of Series, DataFrame, or Panel objects
If a dict is passed, the sorted keys will be used as the keys
argument, unless it is passed, in which case the values will be
selected (see below). Any None objects will be dropped silently unless
they are all None in which case a ValueError will be raised
axis : {0/'index', 1/'columns'}, default 0
The axis to concatenate along
join : {'inner', 'outer'}, default 'outer'
How to handle indexes on other axis(es)
join_axes : list of Index objects
Specific indexes to use for the other n - 1 axes instead of performing
inner/outer set logic
ignore_index : boolean, default False
If True, do not use the index values along the concatenation axis. The
resulting axis will be labeled 0, ..., n - 1. This is useful if you are
concatenating objects where the concatenation axis does not have
meaningful indexing information. Note the index values on the other
axes are still respected in the join.
keys : sequence, default None
If multiple levels passed, should contain tuples. Construct
hierarchical index using the passed keys as the outermost level
levels : list of sequences, default None
Specific levels (unique values) to use for constructing a
MultiIndex. Otherwise they will be inferred from the keys
names : list, default None
Names for the levels in the resulting hierarchical index
verify_integrity : boolean, default False
Check whether the new concatenated axis contains duplicates. This can
be very expensive relative to the actual data concatenation
copy : boolean, default True
If False, do not copy data unnecessarily
Notes
The keys, levels, and names arguments are all optional
Returns
concatenated : type of objects
File: e:\software\anaconda\lib\site-packages\pandas\tools\merge.py
Type: function
Axis in DataFrame的更多相关文章
- 数据类型-DataFrame
数据类型-DataFrame DataFrame是由多个Series数据列组成的表格数据类型,每行Series值都增加了一个共用的索引 既有行索引,又有列索引 行索引,表明不同行,横向索引,叫inde ...
- pandas dataframe.apply() 实现对某一行/列进行处理获得一个新行/新列
重点:dataframe.apply(function,axis)对一行或一列做出一些操作(axis=1则为对某一列进行操作,此时,apply函数每次将dataframe的一行传给function,然 ...
- Pandas 之 DataFrame 常用操作
import numpy as np import pandas as pd This section will walk you(引导你) through the fundamental(基本的) ...
- [数据分析工具] Pandas 功能介绍(二)
条件过滤 我们需要看第一季度的数据是怎样的,就需要使用条件过滤 体感的舒适适湿度是40-70,我们试着过滤出体感舒适湿度的数据 最后整合上面两种条件,在一季度体感湿度比较舒适的数据 列排序 数据按照某 ...
- 数据分析之pandas教程------数据处理
目录 1 数据合并 1.1 实现数据库表join功能 1.2 实现union功能 2 数据转换 2.1 轴旋转 2.2 数据转换 2.2.1 去重 2.2.2 对某一列运用函数 2.2 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析——pandas入门
利用Python进行数据分析--pandas入门 基于NumPy建立的 from pandas importSeries,DataFrame,import pandas as pd 一.两种数据结构 ...
- pandas知识点
1.选择对象 1.选择特定列和行的数据 a['x'] 那么将会返回columns为x的列,注意这种方式一次只能返回一个列.a.x与a['x']意思一样. 取行数据,通过切片[]来选择 如:a[0:3] ...
- python数据分析及展示(三)
一.Pandas库入门 1. Pandas库的介绍 http://pandas.pydata.org Pandas是Python第三方库,提供高性能易用数据类型和分析工具 import pandas ...
- pandas 基础操作 更新
创建一个Series,同时让pandas自动生成索引列 创建一个DataFrame数据框 查看数据 数据的简单统计 数据的排序 选择数据(类似于数据库中sql语句) 另外可以使用标签来选择 通过位置获 ...
- pandas 数据结构基础与转换
pandas 最常用的三种基本数据结构: 1.dataFrame: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.Data ...
随机推荐
- C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 27 期(2025年2.17-2.23)
前言 C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊,你的每周技术指南针!记录.追踪C#/.NET/.NET Core领域.生态的每周最新.最实用.最有价值的技术文章.社区动态.优质项目和学习资源等. ...
- abaqus建模时突发意外,软件闪退怎么才能找回操作?
abaqus/CAE 建模的时候可能经常由于各种各样的原因闪退(中断.卡住.未响应等等.) 这是很让人崩溃的时候,一个良好的习惯就是经常Ctrl+S,并且操作的时候不要太急,否则abaqus容易反应不 ...
- DBeaver连接mysql时Public Key Retrieval is not allowed错误
前言 DBeaver 连接 mysql 时,报错:Public Key Retrieval is not allowed 解决 在新建连接的时候,驱动属性里设置 allowPublicKeyRetri ...
- 实验一:Tableau数据可视化入门
实验目的: 1.熟悉TableauDesktop使用方法. 2.通过Tableau软件来实现Excel中数据的基本可视化. 实验原理: Tableau是新一代商业智能工具软件,它将数据连接.运算.分析 ...
- 项目实战 TS
项目实战 TS 通用技巧 新手先 any 再填坑,老手先定义数据结构写逻辑 遇到新场景,没把握快速,先用 any 再填坑,填坑的过程也是 TS 技能满满提升的过程. TS 发现潜在问题 1)复杂逻辑, ...
- BUUCTF---萌萌哒的八戒(猪圈密码)
1. 问题 2.知识点 猪圈密码 3.解题 对应解题,套上flag{whenthepigwanttoeat}
- DVWA靶场实战(十三)——CSP Bypass
DVWA靶场实战(十三) 十三.CSP Bypass: 1.漏洞原理: CSP Bypass全称是Content-Security-Policy,中文叫做绕过内容安全策略.Content-Securi ...
- 使用 gitee 托管你的 go 模块
前言 实话实说, github 作为这个球上顶级的代码托管平台, 公司/企业/开发者的认可和参与度是非常高的. 但是因为某些原因 特色墙, 国内使用 github 的体验不是非常好 速度慢 不靠谱同学 ...
- Windows Terminal 调整默认终端
Windows Terminal 打开时默认的是 PowerShell, 如下图: 但是, 我希望默认的是更轻快的 cmd... 打开设置 调整 defaultProfile 为 cmd.exe 配置 ...
- Docker 初始镜像 scratch
初识 scratch 有那么一天,我们在这里邂逅了镜像scratch... 先来搜索下这个镜像 docker search scratch NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIA ...
