廖雪峰Java6IO编程-2input和output-1inputStream
1.InputStream
1.1InputStream是所有输入流的超类:
- int read()
* 读取下一个字节,并返回字节(0-255)
* 如果已读到末尾,返回-1
* read()方法是阻塞(blocking)的,必须等待read()方法返回才能执行下一行代码 - int read(byte[]):读取若干字节并填充到byte[]数组,返回读取的字节数
- int read(byte[], int off, int len):指定byte[]数组的偏移量和最大填充术数。
- void close():关闭输入流
- 使用try(resource)可以保证InputStream正确关闭
代码一,使用close关闭文件:如果运行时发生IO错误,文件不能正确关闭,资源不能得到及时的释放
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream input = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt");
int n;
while((n=input.read())!= -1){
System.out.println(n);
}
input.close();
}
}
代码二:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream input = null;
try{
input= new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt");
int n;
while((n=input.read())!= -1){
System.out.println(n);
}
}finally {
if (input != null) {
input.close();
}
}
}
}
代码三,使用try(resource)保证InputStream正确关闭,推荐
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(InputStream input = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt")){
int n;
while((n=input.read())!= -1){
System.out.println(n);
}
}//自动关闭InputStream
}
}
代码四,利用缓冲区一次读取多个字节
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(InputStream input = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt")){
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
int n;
while((n=input.read(buffer))!= -1){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
}
}
}
}
1.2常用InputStream
1.2.1 FileInputStream
FileInputStream是InputStream的实现类,可以从文件获取输入流。
try(InputStream input = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt")){
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
int n;
while((n=input.read(buffer))!= -1){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
}
1.2.2 ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayInputStream可以在内存中模拟一个InputStream。用的不多,可以测试的时候构造InputStream
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] data = {-26, -103, -82, -23, -128, -102, -27, -83, -105, -25,-84, -90, -28, -72, -78, 10, 99, 111, 109, 46,116, 101, 115, 116, 76, 105, 115, 116, 46, 77,97, 105, 110, 64, 50, 98, 49, 57, 51, 102,50, 100, 10, 64, 50, 98, 49, 57, 51, 102};
try(InputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(data)){
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
int n;
while((n=input.read(buffer))!= -1){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
}
}
}
}
1.3总结:
- InputStream定义了所有输入流的超类
- FileInputStream实现了文件输入
- ByteArrayInputStream在内存中模拟一个字节流输入
- 使用try(resource)保证InputStream正确关闭
2.OutputStream
2.1 java.io.OutPutStream是所有输出流的超类:
- abstract write(int b):写入一个字节
- void write(byte[] b):写入byte数组的所有字节
- void write(byte[] b, int off, int len):写入byte[]数组指定范围的字节
- write()方法是阻塞的,必须等待write方法执行完毕返回后才能执行下一行代码
- void close():关闭输出流
- 使用try(resource)可以保证OutputStream正确关闭
- void flush() :将缓冲区的内容输出
为什么需要flush呢?
因为像磁盘、网络写入数据的时候,出于效率的考虑,很多时候,并不是输出1个字节就立即写入。而是先把输出的字节放在内存缓冲区里,等到缓冲区满了之后,再一次性写入。对于很多设备来说,一次写入1个字节和写入1000个字节话费的时间是一样的。所以Output Stream有一个flush方法,能够强制把缓冲区的内容输出。通常情况下,我们不需要调用这个方法,因为缓冲区在满的时候,会自动调用flush。我们在调用close方法关闭OutputStream时,也会调用flush方法。
代码一:如果写入过程中发生IO错误,OutputStream不能正常关闭
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/output.txt");
output.write(72);//1次写入1个字节
output.write(101);
output.write(108);
output.write(108);
output.write(111);
output.close();
}
}
代码二:通过try(resource)自动关闭文件
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/output.txt")){
output.write(72);
output.write(101);
output.write(108);
output.write(108);
output.write(111);
}
}
}
代码三:一次传入多个字节
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/output.txt")){
byte[] b = "hello,张三".getBytes("UTF-8");
output.write(b,3,9);
}
}
}
代码四:一次性写入
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/output.txt")){
byte[] b = "hello,张三".getBytes("UTF-8");
output.write(b);
}
}
}
2.2 常用OutPutStream:
2.2.1 FileOutStream
FileOutStream可以输出到文件
2.2.2 ByteArrayOutPutStream
ByteArrayOutputStream可以在内存中模拟一个OutputStream
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream()){
output.write("Hello".getBytes("utf-8"));
output.write("world!".getBytes("utf-8"));
byte[] data = output.toByteArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
}
2.3 总结
- OutputStream定义了所有输出流的超类
- FileOutputStream实现了文件流输出
- ByteArrayOutputStream在内存中模拟一个字节流的输出
- 使用try(resource)保证OutputStream正确关闭
3.Input/OutPut练习
FileInputStream可以从文件读取数据,FileOutputStream可以把数据写入文件。
如果我们一边从一个文件读取数据,一边把数据写入到另一个文件,就完成了文件的拷贝。
请编写一个程序,接收两个命令行参数,分别表示源文件和目标文件,然后用InputSream/OutputStream把源文件复制到目标文件。
复制后,请检查源文件和目标文件是否相同(文件长度相同,内容相同),分别用文本文件、图片文件和zip文件测试。
使用FileInputStream读取文件
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.java");
System.out.println(f.length());
//创建字节输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.java");
//创建竹筒
byte[] bbuf = new byte[100];
//保存实际读取的字节数
int hasRead = 0;
//使用循环重复取水过程
while((hasRead = fis.read(bbuf))>0){
//取出竹筒中的水滴即字节,将字节数组转换成字符串输入
System.out.println(new String(bbuf,0,hasRead));
}
//关闭字节流
fis.close();
}
}
使用FileReader读取文件
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.java");
System.out.println(f.length());
try(
//创建字符输入流
FileReader fr = new FileReader("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.java")
){
//创建一个长度为100的竹筒
char[] cbuf = new char[100];
//hasRead用于保存实际读取的字符数
int hasRead = 0;
while((hasRead =fr.read(cbuf))>0){//使用循环重复取水过程
//取出竹筒中的水滴即字符,将字符数组转换为字符串输入
System.out.println(new String(cbuf,0,hasRead));
}
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
//创建字节输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.java");
//创建字节输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt")
){
byte[] bbuf = new byte[300];
int hasRead = 0;
//循环从输入流中取出数据
while ((hasRead = fis.read(bbuf))>0){
//取出1次,写入1次
fos.write(bbuf,0,hasRead);
}
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
//创建字节输出流
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt")
){
fw.write("于易水送人 - 骆宾王\r\n");
fw.write("此地别燕丹,壮士发冲冠。\r\n");
fw.write("昔时人已没,今日水犹寒。\r\n");
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./src/main/java/com/testList/Person.txt");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos)
){
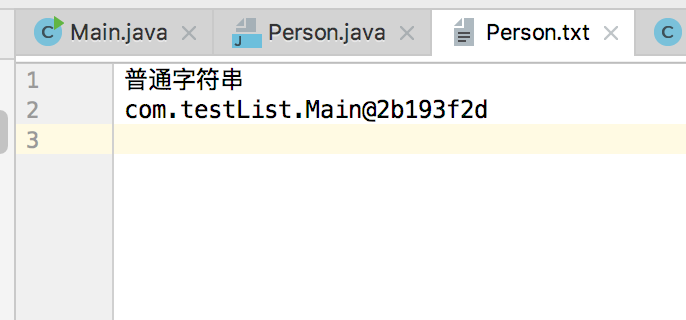
ps.println("普通字符串");
ps.println(new Main());
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
廖雪峰Java6IO编程-2input和output-1inputStream的更多相关文章
- 廖雪峰Java6IO编程-1IO基础-1IO简介
1.IO简介 IO是指Input/Output,即输入和输出: Input指从外部读取数据到内存,例如从磁盘读取,从网络读取. * 为什么要把数据读到内存才能处理这些数据呢? * 因为代码是在内存中运 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-3JDBC接口-5JDBC连接池
1. JDBC连接池 1.1 JDBC连接池简介 线程池可以复用一个线程,这样大量的小任务通过线程池的线程执行,就可以避免反复创建线程带来的开销. 同样JDBC可以复用一个JDBC连接 JDBC的连接 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-3JDBC接口-4JDBC事务
1 数据库事务:Transaction 1.1 定义 若干SQL语句构成的一个操作序列 要么全部执行成功 要么全部执行不成功 1.2 数据库事务具有ACID特性: Atomicity:原子性 一个事务 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-3JDBC接口-3JDBC更新
使用update语句的时候,需要通过JDBC实现update语句的执行,这个时候仍然通过PreparedStatement对象来使用,直接传入update语句,然后通过setObject传入占位符的值 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-3JDBC接口-2JDBC查询
我们可以使用JDBC查询来执行select语句. 1. Statement try(Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(JDBC_URL, JD ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-3JDBC接口-1JDBC简介
JDBC:Java DataBase Connectivity Java程序访问数据库的标准接口 使用Java程序访问数据库的时候,Java代码并不是直接通过TCP连接去访问数据库,而是通过JDBC接 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-2SQL入门-2insert/select/update/delete
1. INSERT用于向数据库的表中插入1条记录 insert into 表名 (字段1,字段2,...) values (数据1,数据2,数据3...) 示例 -- 如果表存在,就删除 drop t ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-2SQL入门-1SQL介绍
1.SQL:结构化查询语言 Structured Query Language 针对关系数据库设计 各种数据库基本一致 允许用户通过SQL查询数据而不关心数据库底层存储结构 1.1 SQL使用: 可以 ...
- 廖雪峰Java15JDBC编程-1关系数据库基础-1关系数据库简介
1.数据库 1.1 定义 数据库是按照数据结构来组合.存储和管理数据的软件. 1.2 数据库模型 数据库有层次模型.网状模型.关系模型三种模型. 2 关系数据库 关系数据库是建立在关系模型上的数据库, ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu下安装JDK图文教程详解 jdk-java6-30 .bin 的处理方法
Ubuntu下安装JDK图文教程详解 jdk-java6-30 .bin 的处理方法: https://blog.csdn.net/mingjie1212/article/details/485250 ...
- python数据类型及字符编码
一.python数据类型,按特征划分 1.数字类型 整型:布尔型(True,False).长整型(L),会自动帮你转换成长整型.标准整型 2.序列类型 字符串(str).元组(tuple).列表(li ...
- CH3B04 Xiao 9*大战朱最学
题意 3B04 Xiao 9*大战朱最学 0x3B「数学知识」练习 背景 Xiao 9*.朱最学.小全同属LOI,朱某某同学由于学习认真得到了小全的仰慕~~送其外号---朱最学.最学想:神牛我当不成难 ...
- centos7配置openldap服务器
参考链接 https://www.cnblogs.com/bigbrotherer/p/7251372.html 上面这篇参考文件在最后登录是有问题的 vi /etc/openldap/sldap.c ...
- Java(命令行)打印库存清单
public class demo{ public static void main(String[] args){ //1 顶部 System.out.println("--------- ...
- tailor 基础模版的使用
对于需要实现共享的html 内容,tailor 提供了基础模版的概念,我们需要操作的就是添加slots ,以及使用slots 做为占位符 环境准备 使用现有的仓库代码 https://github.c ...
- mysql-sql语言参考
字段去重查询 select distinct style from music 批量修改某字段 update music set style = "ost" where styl ...
- 我发起并创立了一个 VMBC 的 子项目 D#
大家好, 我发起并创立了一个 VMBC 的 子项目 D# . 有关 VMBC , 请参考 <我发起了一个 用 C 语言 作为 中间语言 的 编译器 项目 VMBC> https ...
- 访问者模式-Visitor Pattern
1.主要优点 访问者模式的主要优点如下: (1) 增加新的访问操作很方便.使用访问者模式,增加新的访问操作就意味着增加一个新的具体访问者类,实现简单,无须修改源代码,符合“开闭原则”. (2) 将有关 ...
- URL编码规则
一.问题的由来 问题:当url地址中包含&.+.%等特殊字符(主要是传递参数时,参数的内容中包含这些字符)时,地址无效.比如http://10.190.0.0:108/doc/test+des ...
