POJ - 1978 Hanafuda Shuffle
最初给牌编号时,编号的顺序是从下到上;洗牌时,认牌的顺序是从上到下。注意使用循环是尽量统一“i”的初始化值,都为“0”或者都为“1”,限界条件统一使用“<”或者“<=”。
POJ - 1978 Hanafuda Shuffle
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000KB 64bit IO Format: %I64d & %I64u
Description
There are a number of ways to shuffle a deck of cards. Hanafuda shuffling for Japanese card game 'Hanafuda' is one such example. The following is how to perform Hanafuda shuffling.
There is a deck of n cards. Starting from the p-th card from the top of the deck, c cards are pulled out and put on the top of the deck, as shown in Figure 1. This operation, called a cutting operation, is repeated.
Write a program that simulates Hanafuda shuffling and answers which card will be finally placed on the top of the deck.
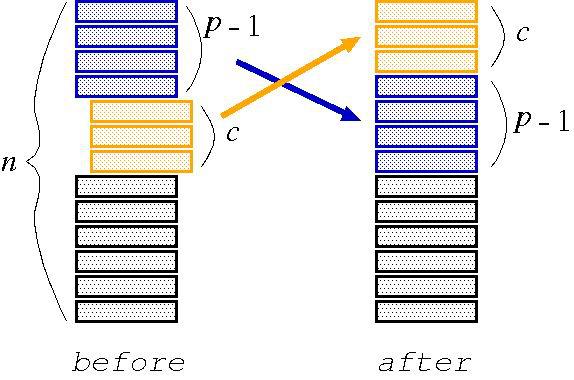
Figure 1: Cutting operation
Input
The input consists of multiple data sets. Each data set starts with a line containing two positive integers n (1 <= n <= 50) and r (1 <= r <= 50); n and r are the number of cards in the deck and the number of cutting operations, respectively.
There are r more lines in the data set, each of which represents a cutting operation. These cutting operations are performed in the listed order. Each line contains two positive integers p and c (p + c <= n + 1). Starting from the p-th card from the top of the deck, c cards should be pulled out and put on the top.
The end of the input is indicated by a line which contains two zeros.
Each input line contains exactly two integers separated by a space character. There are no other characters in the line.
Output
For each data set in the input, your program should write the number of the top card after the shuffle. Assume that at the beginning the cards are numbered from 1 to n, from the bottom to the top. Each number should be written in a separate line without any superfluous characters such as leading or following spaces.
Sample Input
5 2
3 1
3 1
10 3
1 10
10 1
8 3
0 0
Sample Output
4
4
Source
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h> struct card{
int i;
}; card cards[];
card t[]; int main()
{
int n = , r = , p = , c = ;
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &r)) {
if(!n && !r) break;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
cards[i].i = n-i+;
}
for(int i = ; i <= r; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &p, &c);
for(int j = ; j <= c; j++) { //抽牌
t[j] = cards[p+j-];
}
for(int j = p-; j >= ; j--) { //顶牌下落
cards[j+c] = cards[j];
}
for(int j = ; j <= c; j++) { //放顶牌
cards[j] = t[j];
}
}
printf("%d\n", cards[].i);
} return ;
}
POJ - 1978 Hanafuda Shuffle的更多相关文章
- POJ 3590 The shuffle Problem
Any case of shuffling of n cards can be described with a permutation of 1 to n. Thus there are total ...
- poj 3590 The shuffle Problem——DP+置换
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3590 bzoj 1025 的弱化版.大概一样的 dp . 输出方案的时候小的环靠前.不用担心 dp 时用 > 还是 >= 来转 ...
- 【POJ - 3087】Shuffle'm Up(模拟)
Shuffle'm Up 直接写中文了 Descriptions: 给定两个长度为len的字符串s1和s2, 接着给出一个长度为len*2的字符串s12. 将字符串s1和s2通过一定的变换变成s12, ...
- POJ 3087:Shuffle'm Up
Shuffle'm Up Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 7364 Accepted: 3408 Desc ...
- POJ 1978
#include <iostream> #define MAXN 55 using namespace std; int _m[MAXN]; int tem[MAXN]; void cop ...
- POJ 3590 The shuffle Problem [置换群 DP]
传送门 $1A$太爽了 从此$Candy?$完全理解了这种$DP$做法 和bzoj1025类似,不过是求最大的公倍数,并输出一个字典序最小的方案 依旧枚举质因子和次数,不足的划分成1 输出方案从循环长 ...
- POJ 题目分类(转载)
Log 2016-3-21 网上找的POJ分类,来源已经不清楚了.百度能百度到一大把.贴一份在博客上,鞭策自己刷题,不能偷懒!! 初期: 一.基本算法: (1)枚举. (poj1753,poj2965 ...
- (转)POJ题目分类
初期:一.基本算法: (1)枚举. (poj1753,poj2965) (2)贪心(poj1328,poj2109,poj2586) (3)递归和分治法. (4)递推. ...
- poj分类
初期: 一.基本算法: (1)枚举. (poj1753,poj2965) (2)贪心(poj1328,poj2109,poj2586) (3)递归和分治法. ( ...
随机推荐
- Oracle数据库合并行记录,WMSYS.WM_CONCAT 函數的用法
Sql代码 select t.rank, t.Name from t_menu_item t; 10 CLARK 10 KING 10 MILLER 20 ADAMS 20 F ...
- wego微购RSS、Sitemap、Ping、腾讯拍拍网购采集插件
和哥们研究淘宝客,找到微购这个程序觉得挺不错的,但是地图和RSS功能不是特别完善,于是小憩一下,做了下初级的拓展,分享给大家,开源精神嘛,大家也可以去我的网站我要购物平台去看看. 1.拓展后台seoA ...
- CSS3+HTML5实现块阴影与文字阴影
CSS 3 + HTML 5 是未来的 Web,它们都还没有正式到来,虽然不少浏览器已经开始对它们提供部分支持.本教程分5节介绍了 5 个 CSS3 技巧,可以帮你实现未来的 Web,不过,这些技术不 ...
- JavaScript:词法结构
1.字符集JavaScript程序是用Unicode字符集编写的. 1.1 区分大小写 JavaScript是区分大小写的语言.也就是说,关键字.变量.函数名和所有标识符(identifier)都必须 ...
- Js练笔——用循环和递归实现追踪对象深度(循环引用关系不考虑)
function reobs(obj){ //返回对象中对象属性组成的数组 var a=[]; var b=[]; for(it in obj){ a.push(it); } for(var i=0; ...
- java程序实现删除本地文件
import java.io.File; public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { Test t = new Te ...
- 想通过加HINT让其走全表扫描
一个SQL,通过SPM固定它的执行计划,可以通过DBMS_SPM.LOAD_PLANS_FROM_CURSOR_CACHE实现.也可以通地此功能在不修改原SQL的情况下对其加HINT来固定执行计划.D ...
- EmguCV+Win7+Visual C# 2012 配置
一.下载与安装OpenCV 安装包版本:OpenCV2.4.2 X86 下载地址:http://sourceforge.net/projects/opencvlibrary/files/opencv- ...
- Objective-c 代理模式(delegate)
Objective-c 代理模式(delegate) (2012-07-31 22:04:39) 转载▼ 标签: 杂谈 分类: iOS Objective-c 代理模式(delegate) 一 ...
- iOS开发UI篇—Quartz2D使用(绘制基本图形)
iOS开发UI篇—Quartz2D使用(绘制基本图形) 一.简单说明 图形上下文(Graphics Context):是一个CGContextRef类型的数据 图形上下文的作用:保存绘图信息.绘图状态 ...
