基于Open vSwitch搭建虚拟路由器
As part of my work in OpenDaylight, we are looking at creating a router using Open vSwitch... Why? Well OpenStack requires some limited L3 capabilities and we think that we can handle those in a distributed router.
Test Topology
My test topology looks like this:

We have a host in an external network 172.16.1.0/24, one host in an internal network 10.10.10.0/24 and two hosts in another internal network 10.10.20.0/24.
As such, The hosts in the 10.x.x.x range should be able to speak to each other, but should not be able to speak to external hosts.
The host 10.10.10.2 has a floating IP of 172.16.1.10 and should be reachable on this address from the external 172.16.1.0/24network. To do this, we'll use DNAT for traffic from 172.16.1.2 -> 172.16.1.10 and SNAT for traffic back from10.10.10.2 -> 172.16.1.2
If you'd like to recreate this topology you can checkout the OpenDaylight OVSDB project source on GitHub and:
vagrant up mininet
vagrant ssh mininet
cd /vagrant/resources/mininet
sudo mn --custom topo.py --topo l3
The Pipeline
Our router is implemented using the following pipeline:
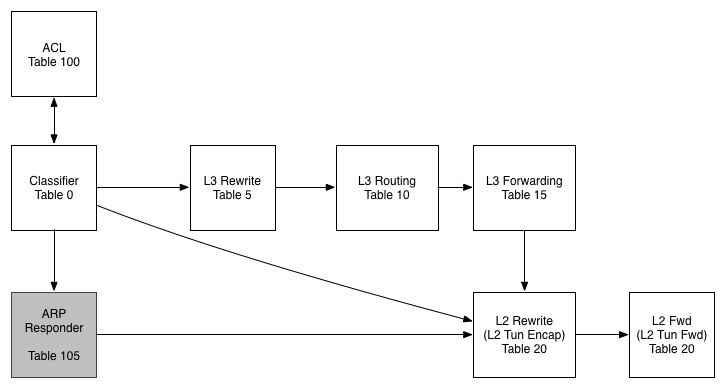
Table 0 - Classifier
In this table we work out what traffic is interesting for us before pushing it further along the pipeline
Table 100 - ACL
While we don't use this table today, the idea would be to filter traffic in this table (or series of tables) and to then resubmit to the classifier once we have scrubbed them.
Table 105 - ARP Responder
In this table we use some OVS-Jitsu to take an incoming ARP Request and turn it in to an ARP reply
Table 5 - L3 Rewrite
In this table, we make any L3 modifications we need to before a packet is routed
Table 10 - L3 Routing
The L3 routing table is where the routing magic happens. Here we modify the Source MAC address, Decrement the TTL and push to the L2 tables for forwarding
Table 15 - L3 Forwarding
In the L3 forwarding table we resolve a destination IP address to the correct MAC address for L2 forwarding.
Table 20 - L2 Rewrites
While we aren't using this table in this example, typically we would push/pop any L2 encapsulations here like a VLAN tag or a VXLAN/GRE Tunnel ID.
Table 25 - L2 Forwarding
In this table we do our L2 lookup and forward out the correct port. We also handle L2 BUM traffic here using OpenFlow Groups - no VLANs!
The Flows
To program the flows, paste the following in to mininet:
## Set Bridge to use OpenFlow 1.3
sh ovs-vsctl set Bridge s1 "protocols=OpenFlow13" ## Create Groups
sh ovs-ofctl add-group -OOpenFlow13 s1 group_id=,type=all,bucket=output:
sh ovs-ofctl add-group -OOpenFlow13 s1 group_id=,type=all,bucket=output:,
sh ovs-ofctl add-group -OOpenFlow13 s1 group_id=,type=all,bucket=output: ## Table - Classifier
# Send ARP to ARP Responder
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=0, priority=1000, dl_type=0x0806, actions=goto_table=105"
# Send L3 traffic to L3 Rewrite Table
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=0, priority=100, dl_dst=00:00:5E:00:02:01, action=goto_table=5"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=0, priority=100, dl_dst=00:00:5E:00:02:02, action=goto_table=5"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=0, priority=100, dl_dst=00:00:5E:00:02:03, action=goto_table=5"
# Send L3 to L2 Rewrite Table
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=0, priority=0, action=goto_table=20" ## Table - L3 Rewrites
# Exclude connected subnets
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=5, priority=65535, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.10.0/24 actions=goto_table=10"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=5, priority=65535, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.20.0/24 actions=goto_table=10"
# DNAT
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=5, priority=100, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=172.16.1.10 actions=mod_nw_dst=10.10.10.2, goto_table=10"
# SNAT
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=5, priority=100, dl_type=0x0800, nw_src=10.10.10.2, actions=mod_nw_src=172.16.1.10, goto_table=10"
# If no rewrite needed, continue to table
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=5, priority=0, actions=goto_table=10" ## Table - IPv4 Routing
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=10, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.10.0/24, actions=mod_dl_src=00:00:5E:00:02:01, dec_ttl, goto_table=15"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=10, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.20.0/24, actions=mod_dl_src=00:00:5E:00:02:02, dec_ttl, goto_table=15"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=10, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=172.16.1.0/24, actions=mod_dl_src=00:00:5E:00:02:03, dec_ttl, goto_table=15"
# Explicit drop if cannot route
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=10, priority=0, actions=output:0" ## Table - L3 Forwarding
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=15, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.10.2, actions=mod_dl_dst:00:00:00:00:00:01, goto_table=20"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=15, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.20.2, actions=mod_dl_dst:00:00:00:00:00:02, goto_table=20"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=15, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=10.10.20.4, actions=mod_dl_dst:00:00:00:00:00:04, goto_table=20"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=15, dl_type=0x0800, nw_dst=172.16.1.2, actions=mod_dl_dst:00:00:00:00:00:03, goto_table=20"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=15, priority=0, actions=goto_table=20" ## Table - L2 Rewrite
# Go to next table
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=20, priority=0, actions=goto_table=25" ## Table - L2 Forwarding
# Use groups for BUM traffic
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, in_port=1, dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00, actions=group=1"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, in_port=2, dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00, actions=group=2"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, in_port=3, dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00, actions=group=3"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, in_port=4, dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00, actions=group=2"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:01,actions=output=1"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:02,actions=output=2"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:03,actions=output=3"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=25, dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:04,actions=output=4" ## Table - ARP Responder
# Respond to ARP for Router Addresses
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=105, dl_type=0x0806, nw_dst=10.10.10.1, actions=move:NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[]->NXM_OF_ETH_DST[], mod_dl_src:00:00:5E:00:02:01, load:0x2->NXM_OF_ARP_OP[], move:NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[]->NXM_NX_ARP_THA[], move:NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[]->NXM_OF_ARP_TPA[], load:0x00005e000201->NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[], load:0x0a0a0a01->NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[], in_port"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=105, dl_type=0x0806, nw_dst=10.10.20.1, actions=move:NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[]->NXM_OF_ETH_DST[], mod_dl_src:00:00:5E:00:02:02, load:0x2->NXM_OF_ARP_OP[], move:NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[]->NXM_NX_ARP_THA[], move:NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[]->NXM_OF_ARP_TPA[], load:0x00005e000202->NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[], load:0xa0a1401->NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[], in_port"
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=105, dl_type=0x0806, nw_dst=172.16.1.1, actions=move:NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[]->NXM_OF_ETH_DST[], mod_dl_src:00:00:5E:00:02:03, load:0x2->NXM_OF_ARP_OP[], move:NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[]->NXM_NX_ARP_THA[], move:NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[]->NXM_OF_ARP_TPA[], load:0x00005e000203->NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[], load:0xac100101->NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[], in_port"
# Proxy ARP for all floating IPs go below
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=105, dl_type=0x0806, nw_dst=172.16.1.10, actions=move:NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[]->NXM_OF_ETH_DST[], mod_dl_src:00:00:5E:00:02:03, load:0x2->NXM_OF_ARP_OP[], move:NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[]->NXM_NX_ARP_THA[], move:NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[]->NXM_OF_ARP_TPA[], load:0x00005e000203->NXM_NX_ARP_SHA[], load:0xac10010a->NXM_OF_ARP_SPA[], in_port"
# if we made it here, the arp packet is to be handled as any other regular L2 packet
sh ovs-ofctl add-flow -OOpenFlow13 s1 "table=105, priority=0, action=resubmit(,20)"
If you'd like to paste these in without comments, you can use this Gist
Testing
We can run a pingall to test this out:
mininet> pingall
*** Ping: testing ping reachability
h1 -> h2 h3 h4
h2 -> h1 X h4
h3 -> X X X
h4 -> h1 h2 X
*** Results: % dropped (/ received)
hosts 1,2 and 4 can speak to each other. Everything initiated by h3 is dropped (as expected) but h1 can speak to h3 (thanks to NAT). We can test our DNAT and Proxy ARP for Floating IP's using this command:
mininet> h3 ping 172.16.1.10
PING 172.16.1.10 (172.16.1.10) () bytes of data.
bytes from 172.16.1.10: icmp_seq= ttl= time=1.30 ms
bytes from 172.16.1.10: icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.043 ms
bytes from 172.16.1.10: icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.045 ms
bytes from 172.16.1.10: icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.050 ms
^C
--- 172.16.1.10 ping statistics ---
packets transmitted, received, % packet loss, time 2999ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.043/0.360/1.305/0.545 ms
Cool! It works!
Conclusion
So far we've implemented the nuts and bolts of routing, but we are missing one crucial piece - ICMP handling. Without this useful things like Path MTU Discovery won't work and neither will diagnostics tools like Ping and Traceroute. I think we can do this using a Open vSwitch but first we'll need to add some new NXM fields to ICMP Data and ICMP Checksum and to also make the existing OXM's writable through set_field. I'm going to start talking to the OVS community about this to see if it's possible so watch this space!
@dave_tucker
Helpful Links and Further Reading
ovs-ofctl Man Page Neutron ARP Responder Write Up Address Resolution Protocol OpenFlow 1.3.1 Spec
本文转自http://dtucker.co.uk/hack/building-a-router-with-openvswitch.html
基于Open vSwitch搭建虚拟路由器的更多相关文章
- K8S学习心得 == 安装虚拟路由器RouterOS
使用RouterOS, 搭建虚拟路由器,并且配置多个网关互通.配置步骤如下. 基础配置 1. RouterOS 服务器,设置如下 2. VM 不同网段的设置 == 192. ...
- OVS-----CentOS7上搭建基于Open vSwitch的VxLAN隧道实验
一.关于VXLAN VXLAN 是 Virtual eXtensible LANs 的缩写,它是对 VLAN 的一个扩展,是非常新的一个 tunnel 技术,在Open vSwitch中应用也非常多. ...
- 【Nginx】如何基于主从模式搭建Nginx+Keepalived双机热备环境?这是最全的一篇了!!
写在前面 最近出版了<海量数据处理与大数据技术实战>,详情可以关注 冰河技术 微信公众号,查看<我的<海量数据处理与大数据技术实战>出版啦!>一文. 也有不少小伙伴 ...
- 基于Open vSwitch的OpenFlow实践
Open vSwitch(下面简称为 OVS)是由 Nicira Networks 主导的,运行在虚拟化平台(例如 KVM,Xen)上的虚拟交换机.在虚拟化平台上,OVS 可以为动态变化的端点提供 2 ...
- 基于VMware Workstation搭建开发服务器
基于VMware Workstation搭建开发服务器 文章为本人原创,转载请联系作者并注明出处.晓松 源URL: https://www.jianshu.com/p/e62ab7de0124 我 ...
- 基于 Azure IaaS 搭建企业官网的规划和实践
本课程主要介绍了基于 Azure IaaS 搭建企业官网的案例分析和实践,实践讲解如何使用 Azure 门户创建虚拟机, 创建虚拟网络, 创建存储账户等. 具体包括项目背景介绍, 项目架构, 准备和实 ...
- 基于S7-PLCSIM Advanced搭建S7通信仿真环境
写在前面: 之前有专门讲过一期如何搭建西门子PLC的S7通信仿真环境,感兴趣的可以点击查看:戳↓ 1.基于TIA搭建西门子PLC仿真环境及通信方案-联合出品 2.手把手教你搭建西门子PLC仿真环境 那 ...
- VRRP(Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) 虚拟路由器冗余协议简介
因工作中使用Keepalived配置Nginx代理和MySQL代理的高可用,而Keepalived是VRRP协议在linux上的软件实现.因此了解了下VRRP的基础. 1. VRRP技术的引入 随着I ...
- VRRP虚拟路由器冗余协议
VRRP(VirtualRouterRedundancyProtocol,虚拟路由冗余协议)是一种容错协议.通常,一个网络内的所有主机都设置一条缺省路由,这样,主机发出的目的地址不在本网段的报文将被通 ...
随机推荐
- Aptana STUDIO 3 使用(续)
1 使用Aptana studio 3 浏览ruby代码 2 设置gbk编码.打开Aptanna Studio,选择Windows->Preferences->General->Co ...
- oracle 11g 空表也导出
查询空表 并导出修改空表语句 select 'alter table '||table_name||' allocate extent;' from user_tables where num_row ...
- eval解析非标准json
以前一直在用,但是不知道原理,惭愧啊,今天把自己想法加上. eval("{a:1}"); eval("{a:,b:1}"); 第一眼的感觉是都会得到一个对象,其 ...
- echart------属性详细介绍
theme = { // 全图默认背景 // backgroundColor: 'rgba(0,0,0,0)', // 默认色板 color: ['#ff7f50','#87cefa','#da70d ...
- web.xml的初始化参数
web.xml的初始化参数 ---------首先声明,这里所介绍的是web中context-param,init-param参数的初始化配置---------- ------------------ ...
- 递归问题==优化 还有数据库sqlreader
reader尽量不要用获取列名方式 用索引比较好. int i= reader.GetOrdinal("<#=c.ColumnName#>"); reader[i ...
- 记录一些容易忘记的属性 -- UIScrollView
UIScrollView * sv = [[UIScrollView alloc] init]; //设置是否显示水平滚动条 sv.showsHorizontalScrollIndicator ...
- servlet jsp 客户端服务端跳转
jsp 客户端:href jsp 服务端:forward servlet 客户端:response.sendredirect(); servlet 服务器:request.getRequestDisp ...
- 关于jquery中的事件绑定bind()和live()
live可以说是bind是方法的变种. 二者的主要区别就是live方法的作用机理是事件委托,live方法的作用机理是将事件绑定DOM的根节点上. live方法的处理机制就是把事件绑定在DOM树的根节点 ...
- 判断CAD版本
使用命令: ACADVER ACADVER = "17.2s (LMS Tech)" (只读) CAD2016 ACADVER = "20.1s (LMS Tech)&q ...
