cf #365b 巧妙的统计
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Little Mishka is a great traveller and she visited many countries. After thinking about where to travel this time, she chose XXX — beautiful, but little-known northern country.
Here are some interesting facts about XXX:
- XXX consists of n cities, k of whose (just imagine!) are capital cities.
- All of cities in the country are beautiful, but each is beautiful in its own way. Beauty value of i-th city equals to ci.
- All the cities are consecutively connected by the roads, including 1-st and n-th city, forming a cyclic route 1 — 2 — ... — n — 1. Formally, for every 1 ≤ i < n there is a road between i-th and i + 1-th city, and another one between 1-st and n-th city.
- Each capital city is connected with each other city directly by the roads. Formally, if city x is a capital city, then for every1 ≤ i ≤ n, i ≠ x, there is a road between cities x and i.
- There is at most one road between any two cities.
- Price of passing a road directly depends on beauty values of cities it connects. Thus if there is a road between cities i and j, price of passing it equals ci·cj.
Mishka started to gather her things for a trip, but didn't still decide which route to follow and thus she asked you to help her determine summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX. Formally, for every pair of cities a and b (a < b), such that there is a road betweena and b you are to find sum of products ca·cb. Will you help her?
The first line of the input contains two integers n and k (3 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of cities in XXX and the number of capital cities among them.
The second line of the input contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 10 000) — beauty values of the cities.
The third line of the input contains k distinct integers id1, id2, ..., idk (1 ≤ idi ≤ n) — indices of capital cities. Indices are given in ascending order.
Print the only integer — summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX.
4 1
2 3 1 2
3
17
5 2
3 5 2 2 4
1 4
71
This image describes first sample case:
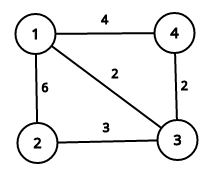
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 17.
This image describes second sample case:
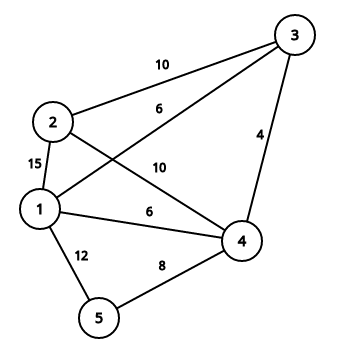
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 71.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxx = ;
int city[maxx];
bool cap[maxx];
int cap_city[maxx];
long long val_total;
long long total_cap;
int main()
{
int n,k;
val_total=;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",city+i);
val_total+=city[i];
}
total_cap=;
for(int i=;i<k;i++)
{
int tmp;
scanf("%d",&tmp);
cap[tmp]=true;
cap_city[i]=tmp;
total_cap+=city[tmp];
}
city[]=city[n];
cap[]=cap[n];
long long ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(cap[i])
{
ans+=*(city[i]*1LL*(val_total-city[i])*1LL);
if(!cap[(i-)%n])
{
ans-=city[i]*city[(i-)%n];
}
if(!cap[(i+)%n])
{
ans-=city[i]*city[(i+)%n];
}
}
else
ans+=(city[i]*city[i-]+city[i]*city[(i+)%n]);
}
for(int i=;i<k;i++)
{
ans-=(city[cap_city[i]]*(total_cap-city[cap_city[i]])*1LL); }
printf("%I64d\n",ans/);
return ;
}
简单统计所有边的代价是很简单的,但是因为点数较多,这样是会超时的。可以预先统计出所有点的总代价,所有关键点的总代价。计算时,将所有边统计两遍,其中非关键点较好处理,只要向两边连边,而关键点向所有点连两倍边,关键点之间会有四条边,要后期减去,而关键点和不是相邻的非关键点之间就是两倍边,而关键点和相邻的非关键点(如果是的话)是三倍边,要减去一次。最后,统计完之后,将总代价除以2,即为所求。
cf #365b 巧妙的统计的更多相关文章
- TTTTTTTTTTTTT CF#365 div2 B 统计点
B. Mishka and trip time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- 51nod 1042数字0-9的数量
1042 数字0-9的数量 基准时间限制:1 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 10 难度:2级算法题 收藏 关注 给出一段区间a-b,统计这个区间内0-9出现的次数. 比如 10-19 ...
- 2018 - 2019 CTU Open Contest E. Locker Room 【后缀数组】
任意门:http://codeforces.com/gym/101954/problem/E E. Locker Room time limit per test 2.0 s memory limit ...
- Self-Driving Database
最近一直在做 ML in Database 相关的工作.偶然发现CMU 19spring的15-721课程竟然专门安排了这个专题,不禁欣喜若狂,赶紧去学习了一下. Andy提出了self-drivin ...
- matplotlib补充知识及数据清理方法
今日内容概要 数据操作 数据清洗理论 数据清洗实操 数据操作 read_csv read_excel read_hdf read_html read_json read_msgpack read_sq ...
- 巧妙的运用group,count,order有利于统计
$aAwardMem = $this->dao_raward->getAwardAndMem($where,array('award_cat asc','award_level asc') ...
- ORA-00494: enqueue [CF] held for too long (more than 900 seconds) by 'inst 1, osid 5166'
凌晨收到同事电话,反馈应用程序访问Oracle数据库时报错,当时现场现象确认: 1. 应用程序访问不了数据库,使用SQL Developer测试发现访问不了数据库.报ORA-12570 TNS:pac ...
- [Recommendation System] 推荐系统之协同过滤(CF)算法详解和实现
1 集体智慧和协同过滤 1.1 什么是集体智慧(社会计算)? 集体智慧 (Collective Intelligence) 并不是 Web2.0 时代特有的,只是在 Web2.0 时代,大家在 Web ...
- CF 484E - Sign on Fence
E. Sign on Fence time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发学习网站汇总
*本文转自CocoaChina 原文:11 Insanely Great iOS Developers Sites永不止步地向他人学习 我相信,要想从一个"还不错"的人变成一个卓越 ...
- suse linux 10 下配置vpn服务器(pptp)
一.安装所需的软件包: pptpd-*.rpm ppp-*.rpm pptp-*.rpm 一般情况下系统已经将pptp和ppp包安装好了,所以只需安装pptpd ...
- Oracle 修改现有列的数据类型
如果表中有数据,Oracle是不能修改其数据类型的.但可以通过新建一个临时列,将要修改列的数据复制到临时列中,删除原列再修改临时列的名字.这样说好像有点拗口,分步解说一下. 表AC_REG中有列:is ...
- mybatis setting配置
Mybatis配置报错元素类型为 "configuration" 的内容必须匹配 "(properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHan ...
- 【leetcode】Reverse Linked List(easy)
Reverse a singly linked list. 思路:没啥好说的.秒... ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode * rList ...
- ios安装cocoaPods
1. 安装 a. 查看源 i. gem sources -l b. 删除源 i. sudo gem sources -r https://rubygems.org/ c. 设置源 i. s ...
- IIS服务的部署
1.安装 C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319 aspnet_regiis -i2.添加应用程序,选择Asp.net4.03.应用目录 IIS_U ...
- NYOJ之三个数从小到大排序
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAsoAAAGvCAIAAADNJWRjAAAgAElEQVR4nO3dPXLqSrs24DMJcgbi1A
- 实现QQ在线咨询(需先添加好友)
实现效果如图: 点击客服专员一.二.三之后提示添加qq好友,进行聊天. 代码如下: <div class="attachLeft"> <img src=" ...
- windows 远程桌面命令 mstsc
win+R------>mstsc: 弹出: 目标机必开远程
