Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 1) D. Dividing Kingdom II 并查集求奇偶元环
Long time ago, there was a great kingdom and it was being ruled by The Great Arya and Pari The Great. These two had some problems about the numbers they like, so they decided to divide the great kingdom between themselves.
The great kingdom consisted of n cities numbered from 1 to n and m bidirectional roads between these cities, numbered from 1 to m. The i-th road had length equal to wi. The Great Arya and Pari The Great were discussing about destructing some prefix (all road with numbers less than some x) and suffix (all roads with numbers greater than some x) of the roads so there will remain only the roads with numbers l, l + 1, ..., r - 1 and r.
After that they will divide the great kingdom into two pieces (with each city belonging to exactly one piece) such that the hardness of the division is minimized. The hardness of a division is the maximum length of a road such that its both endpoints are in the same piece of the kingdom. In case there is no such road, the hardness of the division is considered to be equal to - 1.
Historians found the map of the great kingdom, and they have q guesses about the l and r chosen by those great rulers. Given these data, for each guess li and ri print the minimum possible hardness of the division of the kingdom.
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 1000, 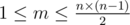 ) — the number of cities and roads in the great kingdom, and the number of guesses, respectively.
) — the number of cities and roads in the great kingdom, and the number of guesses, respectively.
The i-th line of the following m lines contains three integers ui, vi and wi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, 0 ≤ wi ≤ 109), denoting the road number iconnects cities ui and vi and its length is equal wi. It's guaranteed that no road connects the city to itself and no pair of cities is connected by more than one road.
Each of the next q lines contains a pair of integers li and ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ m) — a guess from the historians about the remaining roads in the kingdom.
For each guess print the minimum possible hardness of the division in described scenario.
5 6 5
5 4 86
5 1 0
1 3 38
2 1 33
2 4 28
2 3 40
3 5
2 6
1 3
2 3
1 6
-1
33
-1
-1
33 题意:
给你一个m边n点的无向有权图,q个询问,每次询问给你l,r求序号问l到r的边构成的图的hardness值
hardness值定义为:你可以任意选图中点划分为两点集合,取一个集合中任意相连两点的边权值的最大,取两个集合的max输出
当任意集合没有相连的两点为-1
题解:
画图.
奇元环必有一个非-1值
偶元环-1;
询问一次的话,按权值从大到小排序,按照并查集求奇偶环就好了
多次询问,q*m还是可以接受
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6+, inf = 2e9, mod = 1e9+; int n,m,q,fa[N];
struct ss{int u,v,w,id;}p[N];
bool cmp(ss s1,ss s2){return s1.w>s2.w;}
void init(){for(int i=;i<=n*;i++)fa[i]=i;}
int finds(int x) {return x==fa[x]?x:fa[x]=finds(fa[x]);} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&p[i].u,&p[i].v,&p[i].w);
p[i].id=i;
}
sort(p+,p+m+,cmp);
while(q--)
{
int f=,l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
init();
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
if(p[i].id>=l&&p[i].id<=r)
{
int fx=finds(p[i].u),fy=finds(p[i].v);
if(fx==fy)
{
f=;
printf("%d\n",p[i].w);
break;
}
else
{
fa[fx]=finds(p[i].v+n);
fa[fy)]=finds(p[i].u+n);
}
}
}
if(!f) printf("%d\n",-);
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 1) D. Dividing Kingdom II 并查集求奇偶元环的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 1) D. Dividing Kingdom II 暴力并查集
D. Dividing Kingdom II 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/687/problem/D Description Long time a ...
- Codeforces Round #181 (Div. 2) B. Coach 带权并查集
B. Coach 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/300/problem/A Description A programming coach has n ...
- Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 1) C. Table Compression dp+并查集
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/650/C C. Table Compression time limit per test4 secon ...
- Codeforces Round #346 (Div. 2) F. Polycarp and Hay 并查集 bfs
F. Polycarp and Hay 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/659/problem/F Description The farmer Pol ...
- Codeforces Round #375 (Div. 2) D. Lakes in Berland 并查集
http://codeforces.com/contest/723/problem/D 这题是只能把小河填了,题目那里有写,其实如果读懂题这题是挺简单的,预处理出每一块的大小,排好序,从小到大填就行了 ...
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree —— 并查集
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/699/problem/D D. Fix a Tree time limit per test 2 seconds memory ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) D. Secret Passwords(并查集)
链接: https://codeforces.com/contest/1263/problem/D 题意: One unknown hacker wants to get the admin's pa ...
- Codeforces Round #346 (Div. 2) F. Polycarp and Hay 并查集
题目链接: 题目 F. Polycarp and Hay time limit per test: 4 seconds memory limit per test: 512 megabytes inp ...
- codeforces Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 1) C. Table Compression 排序+并查集
C. Table Compression Little Petya is now fond of data compression algorithms. He has already studied ...
随机推荐
- Visual Studio Online Integrations-Sync and migration
原文:http://www.visualstudio.com/zh-cn/explore/vso-integrations-directory-vs
- 360双击ctrl搜索可能会与firefox快捷键冲突
最近使用火狐浏览器时有好几次要在网页上的对话框输入文字时出现问题,按下字母键直接跳出了firefox菜单选项,用鼠标重新定位到输入位置再打还是不行,照样会弹出菜单提示,如下图,这可能是有什么快捷键冲突 ...
- 入门必看--JavaScript基础
JavaScript他是一种描述性语言,其实他并不难学,只要用心学,一定会学好,我相信大家在看这篇文章的时候,一定也学过HTML吧,使用JavaScript就是为了能和网页有更好的交互,下面切入主题. ...
- NGUI 学习笔记实战——制作商城UI界面
http://www.cnblogs.com/chongxin/p/3876575.html Unity3D的uGUI听说最近4.6即将推出,但是目前NGUI等UI插件大行其道并且已经非常成熟,所以我 ...
- 经典sql语句
经典SQL语句大全 一.基础 1.说明:创建数据库CREATE DATABASE database-name 2.说明:删除数据库drop database dbname3.说明:备份sql serv ...
- scp 命令
复制文件: (1)将本地文件拷贝到远程 scp 文件名 用户名@计算机IP或者计算机名称:远程路径 (2)从远程将文件拷回本地 ...
- 一个csrf实例漏洞挖掘带你了解什么是csrf
[-]CSRF是个什么鬼? |___简单的理解: |----攻击者盗用了你的身份,以你的名义进行某些非法操作.CSRF能够使用你的账户发送邮件,获取你的敏感信息,甚至盗走你的财产. |___CSRF攻 ...
- NGINX userid 分析、解码
NGINX userid 分析.解码 生成userid的代码在 http/modules/ngx_http_userid_filter_module.c 大概550行左右. uid_set 是4个ui ...
- 架设基于StrongSwan的L2tp/IPSec VPN服务器
架设基于StrongSwan的L2tp/IPSec VPN服务器 参考: http://agit8.turbulent.ca/bwp/2011/01/setting-up-a-vpn-server-w ...
- 【leetcode】Palindrome Partitioning II
Palindrome Partitioning II Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition ...
