C++目录遍历:使用第三方库boost.filesystem等
1. opencv 目录文件遍历
注释:2014 0814 这个代码是基于java的,Java使用托管代码进行目录管理,C++就不那么跨平台了.
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/zxlstudio/article/details/10100345
在做图像处理的时候,可能进行一个文件夹的所有文件的遍历。
使用c 的文件夹遍历方式,代码太难理解,而且如果在windows中使用还需要使用wchar_t宽字符。
opencv本身就有目录遍历的类库,非常方便,我以前还一直傻傻的使用c的方式进行遍历。
示例代码:非常简单的操作
#include "iostream"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "opencv\cv.h"
#include "opencv\highgui.h"
#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp> using namespace std;
using namespace cv; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string dir_path = "C:/Users/zxl/Desktop/XOXO/New folder/";
Directory dir;
vector<string> fileNames = dir.GetListFiles(dir_path, "*.jpg", false); for(int i=0; i < fileNames.size(); i++)
{
string fileName = fileNames[i];
string fileFullName = dir_path + fileName;
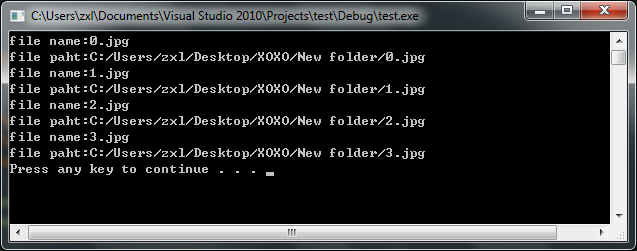
cout<<"file name:"<<fileName<<endl;
cout<<"file paht:"<<fileFullName<<endl;
} system("pause");
return 0;
}
效果:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-24462747-id-2980901.html
3..使用boost::filesystem实现目录遍历
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_48d4cf2d0100mx4o.html
下面的代码实现了深度优先和广度优先两种遍历方式,可以指定最大遍历深度,可以指定结果中是否包含子文件夹
======================================================================
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <utility>
#include<boost/filesystem/operations.hpp>
#include<boost/filesystem/path.hpp> class file_tool
{
public: enum traverse_order_t
{
DEPTH_FIRST = 1,
BREADTH_FIRST =2,
}; enum { UNLIMITED_DEPTH =-1}; static bool get_sub_files(conststd::string& path,std::vector<std::string>&files, int max_depth = UNLIMITED_DEPTH, bool include_sub_dirs =false, traverse_order_t order = BREADTH_FIRST)
{
using namespace std;
namespace fs =boost::filesystem;
typedefstd::pair<string,int> path_and_depth_t;
deque<path_and_depth_t> qu;
{
fs::path root(path);
if(!fs::exists(root) ||!fs::is_directory(root))
{
return false;
}
if(max_depth <= 0 &&max_depth != UNLIMITED_DEPTH)
{
return true;
}
fs::directory_iteratorend_iter;
for(fs::directory_iteratorfile_itr(root); file_itr != end_iter; ++file_itr)
{
qu.push_back(path_and_depth_t(fs::system_complete(*file_itr).native_directory_string(),1));
}
}
while (!qu.empty())
{
path_and_depth_t path_and_depth = (order == DEPTH_FIRST) ?qu.back() : qu.front();
string& file_str(path_and_depth.first);
int depth= path_and_depth.second;
if (order== DEPTH_FIRST)
{
qu.pop_back();
}
else
{
qu.pop_front();
}
fs::path file(file_str);
if(fs::exists(file))
{
if(fs::is_directory(file))
{
if (include_sub_dirs)
{
files.push_back(file_str);
}
if (depth <max_depth || max_depth == UNLIMITED_DEPTH)
{
intnext_depth = depth + 1;
fs::directory_iteratorend_iter;
for(fs::directory_iteratorfile_itr(file); file_itr != end_iter; ++file_itr)
{
qu.push_back(path_and_depth_t(fs::system_complete(*file_itr).native_directory_string(),next_depth));
}
}
}
else
{
files.push_back(file_str);
}
}
}
return true;
} };
4.使用boost filesystem递归遍历文件夹
原文链接:http://www.th7.cn/Program/cp/2012/02/21/60128.shtml
编译环境vc 9
#ifndef SCANALLFILES_H
#define SCANALLFILES_H
#include "boost/filesystem/operations.hpp"
#include "boost/filesystem/path.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; class ScanAllFiles{
public:
static const vector<string>& scanFiles(const string&,vector<string>&); //方法一,自己写递归,用filesystem里的directory_iterator
static const vector<string>& scanFilesUseRecursive(const string&,vector<string>&); //方法二,直接用boost的filesystem里的recursive_directory_iterator
};
//方法一,自己写递归
const vector<string>& ScanAllFiles::scanFiles(const string& rootPath,vector<string>& container=*(new vector<string>())){
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
fs::path fullpath (rootPath, fs::native);
vector<string> &ret = container; if(!fs::exists(fullpath)){return ret;}
fs::directory_iterator end_iter; /**无参构造函数是最后那个iterator的value 摘抄如下
*If the end of the directory elements is reached, the iterator becomes equal to the end iterator value. The constructor directory_iterator() with no arguments always constructs an end iterator object, which is the only legitimate iterator to be used for the end condition. The result of operator* on an end iterator is not defined. For any other iterator value a const directory_entry& is returned. The result ofoperator-> on an end iterator is not defined. For any other iterator value a const directory_entry* is returned.
*
**/
for(fs::directory_iterator iter(fullpath);iter!=end_iter;iter++){
try{
if (fs::is_directory( *iter ) ){
std::cout<<*iter << "is dir.whose parent path is " << iter->path().branch_path() << std::endl;
ret.push_back(iter->path().string()); //递归前push_back进去一个
ScanAllFiles::scanFiles(iter->path().string(),ret);//递归,把vector也传进去
}else{
ret.push_back(iter->path().string());
std::cout << *iter << " is a file" << std::endl;
}
} catch ( const std::exception & ex ){
std::cerr << ex.what() << std::endl;
continue;
}
}
return ret;
}
//方法二,直接用boost的filesystem里的recursive_directory_iterator
const vector<string>& ScanAllFiles::scanFilesUseRecursive(const string& rootPath,vector<string>& container=*(new vector<string>())){
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
fs::path fullpath (rootPath, fs::native);
vector<string> &ret = container; if(!fs::exists(fullpath)){return ret;}
fs::recursive_directory_iterator end_iter;
for(fs::recursive_directory_iterator iter(fullpath);iter!=end_iter;iter++){
try{
if (fs::is_directory( *iter ) ){
std::cout<<*iter << "is dir" << std::endl;
ret.push_back(iter->path().string());
//ScanAllFiles::scanFiles(iter->path().string(),ret);
}else{
ret.push_back(iter->path().string());
std::cout << *iter << " is a file" << std::endl;
}
} catch ( const std::exception & ex ){
std::cerr << ex.what() << std::endl;
continue;
}
}
return ret;
}
#endif
5.我的代码:......
bool CCvMLP::loadFileList(const boost::filesystem::path &base_dir, const std::string &extension,
std::vector<std::string> &FileList)
{
if (!boost::filesystem::exists (base_dir) && !boost::filesystem::is_directory (base_dir))
return true; boost::filesystem::directory_iterator it(base_dir); for (;
it != boost::filesystem::directory_iterator ();
++it)
{
if (boost::filesystem::is_directory (it->status ()))
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << it->path ();
loadFileList (it->path (), extension, FileList);
}
if (boost::filesystem::is_regular_file (it->status ()) && boost::filesystem::extension (it->path ()) == extension)
{
std::string Path;
Path =base_dir.string();
Path.append("/");
Path.append(it->path().filename().string());
FileList.push_back (Path);
}
}
return (true);
}
6.我的代码-第二个版本
int loadFilelist(std::string folder, const std::string extension, std::vector<std::string> &Filelist)
{
//std::vector<std::string> Filelist(0);
Filelist.resize(0);
Traverse(folder.c_str(), extension.c_str(), Filelist);
//for ( auto ptr = Filelist.begin(); ptr != Filelist.end(); ++ptr )
//{
//}
if (Filelist.size() > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < Filelist.size(); ++i){
std::string T = Filelist[i];
std::string tF(folder);
tF.append(T);
Filelist[i] = tF;
}
} //return int32_t(1);
return (1);
} void Traverse( const char *pszPath, const char *extension, std::vector<std::string>& vctFileName )
{
char szFind[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
char szFile[MAX_PATH] = { 0 }; WIN32_FIND_DATAA FindFileData; //strcpy(szFind, pszPath);
//strcpy_s(szFind, strlen(pszPath), pszPath);
strcpy_s(szFind, 200, pszPath);
//strcat(szFind, "//*.bmp");
if (0){
strcat_s(szFind, sizeof(szFind), "//*.bmp");
}
else{
strcat_s(szFind, sizeof(szFind), "//*");
strcat_s(szFind, sizeof(szFind), extension);
} HANDLE hFind = ::FindFirstFileA(szFind, &FindFileData);
if (INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE == hFind) {
return;
} while (TRUE) {
if (FindFileData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY) {
//if(FindFileData.cFileName[0]!='.')
//{
// strcpy(szFile,lpPath);
// strcat(szFile,"//");
// strcat(szFile,FindFileData.cFileName);
// Traverse(szFile);
//}
}
else{
//cout<<FindFileData.cFileName<<endl;
vctFileName.push_back(FindFileData.cFileName);
}
if (!FindNextFileA(hFind, &FindFileData)){
break;
}
}
FindClose(hFind);
}
#include <windows.h>
C++目录遍历:使用第三方库boost.filesystem等的更多相关文章
- Dev-C++安装第三方库boost
Dev-C++安装第三方库boost 转 https://www.jianshu.com/p/111571e4d6f5?utm_source=oschina-app 之前鉴于codeblocks界面 ...
- [boost][filesystem] 扫描给定目录下所有项
Intro. Boost的filesystem可以用来扫描给定目录下的所有项. 实现 具体实现代码如下: 需要包含的头文件和使用的命名空间: #include <boost/filesystem ...
- boost::filesystem总结
boost::filesystem是Boost C++ Libraries中的一个模块,主要作用是处理文件(Files)和目录(Directories).该模块提供的类boost::filesyste ...
- Laravel composer自定义命令空间,方便引用第三方库
第一步:自定义目录 在app文件夹下新建Library目录,做为第三方库的目录 第二步: 修改composer.json文件 autoload节点下的psr-4自定义命名空间 规则: key: 命名空 ...
- CMAKE编译时如何自动下载第三方库并解压、安装到指定目录
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. 导语 在日常开发过程中难免会使用到第三方库或者需要将部分库分离另外存储,如果将库与代码放在一起难免会造成工程庞大,此时就可 ...
- Boost::filesystem 使用小笔记
今天拿起手要用C++写个小工具,从指定的目录递归遍历文件,然后做一下处理.又翻了一下boost的filesystem库.小结一下,希望能加深印象,免得下次又要查看文档. 1. path对象就是一个跨平 ...
- 基于QT开发的第三方库
基于Qt开发的第三方库 分类: Qt2014-02-12 11:34 1738人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 QT第三方库 目录(?)[+] 文章来源:http://blog.csdn.net ...
- boost::filesystem经常使用使用方法具体解释
提示: filesystem库提供了两个头文件,一个是<boost/filesystem.hpp>,这个头文件包括基本的库内容.它提供了对文件系统的重要操作. 同一时候它定义了一个类pat ...
- 【Python基础】安装python第三方库
pip命令行安装(推荐) 打开cmd命令行 安装需要的第三方库如:pip install numpy 在安装python的相关模块和库时,我们一般使用“pip install 模块名”或者“pyth ...
随机推荐
- java链接linux服务器,命令操作
1.本地读取linux文件,即在Windows上链接外部linux package com.common.utils; import java.io.BufferedReader; import ja ...
- composer 安装教程
https://getcomposer.org/download/ 邓士鹏 1.先检查php.ini是否开启ssl ;extension=php_openssl.dll 2. php -r &qu ...
- hdu 1568关于斐波那契数列的公式及其思维技巧
先看对数的性质,loga(b^c)=c*loga(b),loga(b*c)=loga(b)+loga(c); 假设给出一个数10234432,那么log10(10234432)=log10(1.023 ...
- poj 1734 floyd求最小环,可得到环上的每个点
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define inf 100000000 #define N 110 #define min(a, ...
- C#--in逆变-out协变
MSDN上的解释 协变保留兼容性,逆变与之相反 in的使用 个人理解:就是表明泛型就是可以逆变的(逆变就是大变小) // Contravariant interface. interface ICon ...
- POJ 3678
这道题唯一一个注意的地方是,如出现X\/Y=0这种关系时,X=0,Y=0.已经是可以肯定的关系了,所以可以连边X->-X. 我也错了上面这地方.看来,还不够.以后要细心才好. #include ...
- BS程序怎样通过浏览器了解点击响应时间
原创作品,出自 "深蓝的blog" 博客.欢迎转载,转载时请务必注明出处,否则有权追究版权法律责任. 深蓝的blog:http://blog.csdn.net/huangyanlo ...
- Noip2011瑞士轮题解
题目背景 在双人对决的竞技性比赛.如乒乓球.羽毛球.国际象棋中.最常见的赛制是淘汰赛和循环赛.前者的特点是比赛场数少.每场都紧张刺激,但偶然性较高.后者的特点是较为公平,偶然性较低,但比赛过程往往十分 ...
- bootstrap模态框通过传值解决重复提交问题
自己通过模态框确认是否提交的功能时,总是重复提价上次的请求. 原因:重复的原因是jquery通过id绑定了确定按钮的onclick事件,所以每次提交都会增加 一次绑定(没有清除上次的绑定),才造成了重 ...
- php连接符
php连接符 很多时候我们需要将几个字符串连接起来显示,在PHP中,字符串之间使用 “点” 来连接,也就是英文中的半角句号 " . " ." . " 是字符串连 ...