Spring中BeanPostProcessor
Spring中BeanPostProcessor
前言:
本文旨在介绍Spring动态配置数据源的方式,即对一个DataSource的配置诸如jdbcUrl,user,password,driverClass都通过运行时指定,而非由xml静态配置定死。
Spring构造Context的参数一般只包含配置文件路径和类加载器,如果需要达到动态传入配置参数的目的,需要Spring在初始化数据源相关bean的时候能够对原有配置执行修改或替换,为方便处理,本文将定义一个名为DynamicDataSourceConfigHolder的公共类提供配置数据存储。
本文替换数据源为c3p0配置。
BeanPostProcessor简介:
Spring BeanPostProcesssor通常被称为Spring Bean回调处理器,它一般用于在实例化一个bean的前后增加一些附加操作,它会对全局的Spring bean配置生效。
Spring Bean的生命周期处理:
Spring Bean生命周期通常对应两种处理方式,一种是init-method &destroy-method, 另一种是InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()方法和DisposeBean的destroy()方法,BeanPostProcessor的出现使得批处理Spring bean定义有了可能。
BeanPostProcessor定义:
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,
* e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
*
* <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their
* bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created.
* Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors,
* applying to all beans created through this factory.
*
* <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces
* or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization},
* while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally
* implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 10.10.2003
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
* @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor
* @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor { /**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's <code>afterPropertiesSet</code>
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; if
* <code>null</code>, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; /**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's <code>afterPropertiesSet</code>
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding <code>bean instanceof FactoryBean</code> checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; if
* <code>null</code>, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
以上为Spring源代码,我们重点关注它和Spring bean初始化的关系,即postProcessBeforeInitialization将会在Spring 执行bean初始化钩子(init-method或者afterPropertiesSet)之前被调用。
DynamicDataSourceConfigHolder:
package org.wit.ff; import java.util.Map; /**
* 动态数据源配置存储.
* @author ff
*
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceConfigHolder { /**
* 定义本地变量,加入存在多个Spring Context连接多个不同的数据源时,可以共用此类。
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<String,String>> dynamicDataSourceConfigHolder = new ThreadLocal<Map<String,String>>(); public static void setDynamicConfig(Map<String,String> dynamicDataSourceConfig) {
dynamicDataSourceConfigHolder.set(dynamicDataSourceConfig);
} public static Map<String,String> getDynamicDataSourceConfig() {
return (dynamicDataSourceConfigHolder.get());
} public static void clear() {
dynamicDataSourceConfigHolder.remove();
} }
数据源配置文件:
1 db.driverClass=****
2 db.jdbcUrl=****
3 db.user=****
4 db.password=**** 自定义bean回调处理器:
package org.wit.ff; import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils; import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource; /**
* Bean回调处理器.
* @author ff
*
*/
public class ComboPooledDataSourceBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { private String dataSourceName; @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String paramString) throws BeansException {
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 限制数据源名称和类型.
if (bean instanceof ComboPooledDataSource && dataSourceName.equals(beanName)) {
final Map<String,String> methodMatchField = new HashMap<String,String>();
methodMatchField.put("setDriverClass", "db.driverClass");
methodMatchField.put("setJdbcUrl", "db.jdbcUrl");
methodMatchField.put("setUser", "db.user");
methodMatchField.put("setPassword", "db.password");
// 从公共存储区中加载.
final Map<String, String> config = DynamicDataSourceConfigHolder.getDynamicDataSourceConfig();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(bean.getClass(), new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method paramMethod) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if(methodMatchField.containsKey(paramMethod.getName())){
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(paramMethod, bean, config.get(methodMatchField.get(paramMethod.getName())));
}
}
});
}
return bean;
} public void setDataSourceName(String dataSourceName) {
this.dataSourceName = dataSourceName;
} }
Spring 配置文件dynamicDatasource/applicationContext.xml:
<!-- 加载properties配置文件 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<!-- 这里支持多种寻址方式:classpath和file -->
<value>classpath:dynamicDatasource/dbconfig.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 回调处理器.-->
<bean id="dynamicDataSourceBp" class="org.wit.ff.ComboPooledDataSourceBeanPostProcessor" >
<property name="dataSourceName" value="dataSource" />
</bean> <!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${db.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${db.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="user" value="${db.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</bean>
测试示例:
Map<String,String> dynamicDataSourceConfig = new HashMap<String,String>();
dynamicDataSourceConfig.put("db.driverClass", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dynamicDataSourceConfig.put("db.jdbcUrl", "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/menlo3?autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf-8");
dynamicDataSourceConfig.put("db.user", "root");
dynamicDataSourceConfig.put("db.password", "root");
DynamicDataSourceConfigHolder.setDynamicConfig(dynamicDataSourceConfig);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"classpath:dynamicDatasource/applicationContext.xml"}); //执行一段操作数据库的逻辑验证即可. assertNotNull(applicationContext);
Spring提供了很多扩展接口,BeanPostProcessor接口和InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口就是其中两个。
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor接口作用是:如果我们需要在Spring容器完成Bean的实例化、配置和其他的初始化前后添加一些自己的逻辑处理,我们就可以定义一个或者多个BeanPostProcessor接口的实现,然后注册到容器中。
Spring中Bean的实例化过程图示:
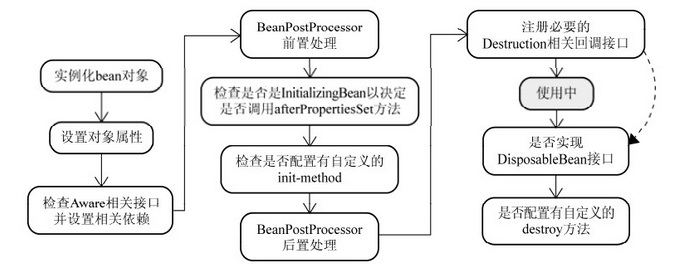
由上图可以看到,Spring中的BeanPostProcessor在实例化过程处于的位置,BeanPostProcessor接口有两个方法需要实现:postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization,
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor() {
super();
System.out.println("这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("bean处理器:bean创建之后..");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("bean处理器:bean创建之前..");
return bean;
}
}
由方法名字也可以看出,前者在实例化及依赖注入完成后、在任何初始化代码(比如配置文件中的init-method)调用之前调用;后者在初始化代码调用之后调用。
注意:
1、接口中的两个方法都要将传入的bean返回,而不能返回null,如果返回的是null那么我们通过getBean方法将得不到目标。
2、BeanFactory和ApplicationContext对待bean后置处理器稍有不同。ApplicationContext会自动检测在配置文件中实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的所有bean,并把它们注册为后置处理器,然后在容器创建bean的适当时候调用它,因此部署一个后置处理器同部署其他的bean并没有什么区别。而使用BeanFactory实现的时候,bean 后置处理器必须通过代码显式地去注册,在IoC容器继承体系中的ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中定义了注册方法
/**
* Add a new BeanPostProcessor that will get applied to beans created
* by this factory. To be invoked during factory configuration.
* <p>Note: Post-processors submitted here will be applied in the order of
* registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} interface will be ignored. Note
* that autodetected post-processors (e.g. as beans in an ApplicationContext)
* will always be applied after programmatically registered ones.
* @param beanPostProcessor the post-processor to register
*/
void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor);
另外,不要将BeanPostProcessor标记为延迟初始化。因为如果这样做,Spring容器将不会注册它们,自定义逻辑也就无法得到应用。假如你在<beans />元素的定义中使用了'default-lazy-init'属性,请确信你的各个BeanPostProcessor标记为'lazy-init="false"'。
Spring中BeanPostProcessor的更多相关文章
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(01)
在spring中beanPostProcessor绝对是开天辟地的产物,给了程序员很多自主权,beanPostProcessor即常说的bean后置处理器. 一.概览 先来说下Instantiatio ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之三:InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在<spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)>一文中,分析到在调用CommonAnnotationB ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之四:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在<spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)>中分析了CommonAnnotationBeanPos ...
- spring(三):spring中BeanPostProcessor的使用
spring中实现BeanPostProcessor的后置处理器 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 进入该实现类内部 可以看到:该类帮我们组建IOC容器,判断我们的be ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之二:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(01)
在上篇博客中分享了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口中的四个方法,分别对其进行了详细的介绍,在文末留下了一个问题,那就是postProcessPropertie ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(03)
前面介绍了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInstantiation和postProcessAfterInstant ...
- spring中BeanPostProcessor之一:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(02)
在上篇博客中写道了bean后置处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,只介绍了其中一个方法的作用及用法,现在来看postProcessBeforeInstanti ...
- 通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期
通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期及AOP原理 Spring源码解析(十一)Spring扩展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProces ...
- Spring点滴十一:Spring中BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor区别
Spring中BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor都是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点.两个接口从名字看起来很相似,但是作用及使用场景却不同 ...
随机推荐
- [Bhatia.Matrix Analysis.Solutions to Exercises and Problems]ExI.3.7
For every matrix $A$, the matrix $$\bex \sex{\ba{cc} I&A\\ 0&I \ea} \eex$$ is invertible and ...
- dll打包进需要发布的exe z
http://www.cnblogs.com/Jarvin/p/3721195.html 我们需要发布的exe文件很多时候都可能会依赖于一堆松散的dll,如果想在发布 的时候只提供exe文件,而不想把 ...
- Appium原理
Appium原理小结 Api接口调用selenium的接口,android底层用android的instrumentation(API2.3+ 通过绑定另外一个独立的selendroid项目来实现的) ...
- (转)Make命令简介与使用
转载自阮一峰的博客: http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/02/make.html 代码变成可执行文件,叫做编译(compile):先编译这个,还是先编译那个(即编 ...
- 进入IT行业,你后悔过吗?
问:你曾后悔进入 IT 行业吗?为什么? 也许你后悔做了IT,但是很希望你能用自己混IT界的惨痛经历给题主这样的后来人提个醒. 也许你庆幸做了IT,同样很希望能够看到同行朋友们的真诚交流. miao ...
- leetcode—Same Tree
1.题目描述 Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are equal or not. Two binary tree ...
- openstack api
1,Identity service generates authentication tokens that permit access to the openstack service REST ...
- yum 安装 PHP,apache,nginx,mysql
如果是Centos OS 64 位,首先更新 rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarc ...
- WIN7 如何关闭Aero
控制面板-性能信息和工具-调整视觉效果-视觉效果 里面选择 调整为最佳性能,这样就关闭了win7的Aero特效
- html标签应用
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
