侯捷C++STL源码分析
STL六大部件
容器(Containers):放东西,需要占用内存。
分配器(Allocators):支持容器。
算法(Algorithms):操作容器里面的数据。
迭代器(Iterators):容器和算法之间的桥梁,泛化的指针。
适配器(A dapters)
仿函数(Functors)
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ia[6] = {27,210,12,47,109,83};
vector<int,allocator<int>> vi(ia,ia+6)//vector<类型,分配器(/*一般不会写*/)>
cout<<cout_if(vi.begin(),vi.end(),not1(bind2nd(less<int>(),40)));//其中cout_if为algorithm,not1为functionadapter(negator) bind2nd为functionadapter(binder) less<int>为functionobject
return 0;
}
复杂度 Complexity,Big-oh
O(1)或O(c)常数时间(constant time)
O(n):称为线性时间(linear time)
O(log2 n)称为二次线性时间(sub—linlear time)
O(n*n)称为平方时间(quadratic time)
O(nnn)称为立方时间(cubic time)
O(2的n次方)称为指数时间
O(nlog2 n):
前闭后开区间
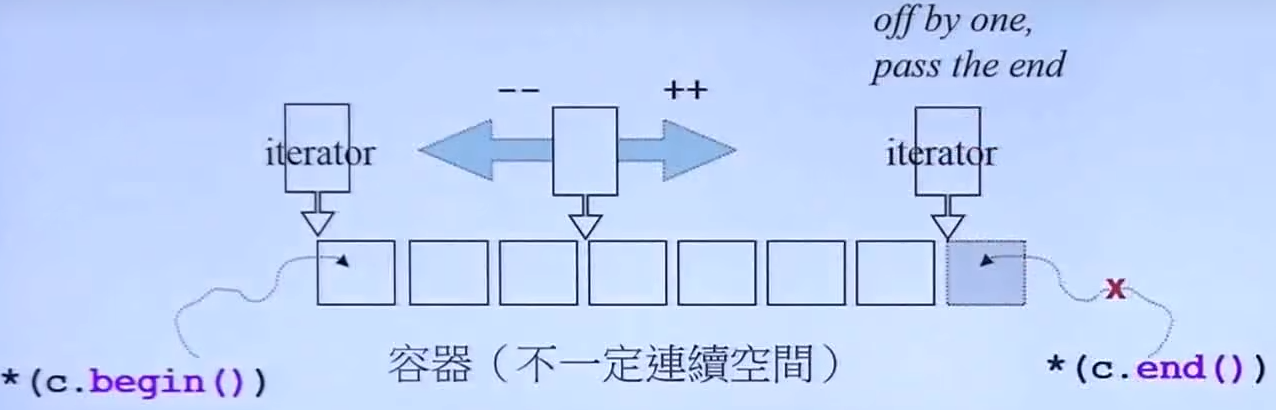
range-based for statement (since C++11)
for(decl:coll){
statement
}
for(int i :{2,3,57,9,13,17,19}){
std::cout<<i<<std::endl;
}
std::vector<double> vec;
...
for(auto elem:vec){
std::cout<<elem<<std::endl;
}
for(auto& elem:vec){
elem *= 3;
}
auto key
list<string> c;
list<string>::iterator ite;
ite = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);

list<string> c;
....
auto ite = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
容器——结构及分类
Sequence Contaioners(序列式容器)
Array:数组(c++11增加的,连续空间)

Vector:动态数组(分配器去处理)

Deque:双向队列(先进先出)

List:双向链表
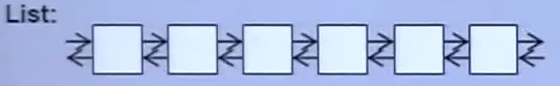
Forward-List:单向链表

Associative Containers(关联式容器)适合快速查找
Set/Multiset(红黑树是高度平衡二叉树,Set放的元素不能重复,Multiset放的元素可以重复)

Map/Multimap(key:value)

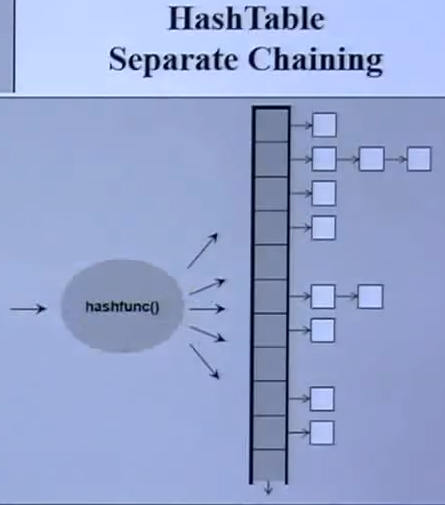
Unordered Containers(HashTable)
一次测试程序之辅助函数
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0 ;
cout<<"target 0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0 ;
char buf[10];
cout <<"target (0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):"
cin>> target;
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",target);//把后面的字符串赋值给buf,长度为min(10,后面那个字符串长度)-1
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a,const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
使用容器array
#include<array>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>//qsort bsearch NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_arry()
{
cout<<"\ntest_array()............\n";
array<long,ASIZE> c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0 ; i<ASIZE;++i){
c[i] = rand();
}
cout<<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart<<endl;
cout<<"array.size()="<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"array.front()="<<c.front()<<endl;
cout<<"array.back()="<<c.back()<<endl;
cout<<"array.data()="<<c.data()<<endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
qsort(c.data(),ASIZE,sizeof(long),compareLongs);
long* pItem = (long*)bsearch(&target,(c.data()),ASIZE,siezeof(long), compareLongs);
cout<<"qsort()+bsearch(),milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;//要使用二分查找之前,数据一定要排序
if(pItem != NULL)
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found"<<endl;
}
}
使用容器Vector
#include<vector>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
namespace jj02
{
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout<"\ntest_vector()..........\n";
vector<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0; i<value;++i)
{
try{
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}catch(exception& p){
cout<<"i="<<i<<""<<p.what()<<endl;
//曾经最高i=58389486 then std::dac_alloc
abort();
}
}
cout <<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
cout <<"vector.size():"<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.front():"<<c.front<<endl;
cout<<"vector.back():"<<c.back()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.data():"<<c.data()<<endl;
cout<<"vector.capacity()="<<c.capacity()<<endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem=::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
//find模板函数跟普通函数是一样的。其中双冒号是一个全局的东西
if(pItem != c.end())
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found!" <<endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin,c,end())
string* pItem = (string*) bsearch(&target,(c.data()),c.size(),sizeof(string)),compareLongs);
cout<<"sort()+bsearch(),milli-seconds:"<<(clock-timeStart);
if(pItem != NULL)
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found" <<endl;
}
}
}
//总结:不一定排序+二分查找 查找速度就快。
使用容器list
#include<vector>
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
namespace jj03
{
void test_list(long& value)
{
cout<<"\ntest_list()....................\n"
list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i = 0; i< value;++i)
{
try{
snprintf(buf,10,"%d",rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}catch(exception& p){
cout<<"i="<<i""<<p.what()<<endl;
abort();
}
}
cout<<"milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
cout<<"list.size():"<<c.size()<<endl;
cout<<"list.max_size()"<<c.max_size()<<endl;
cout<<"list.front()"<<c.front<<endl;
cout<<"list.back()"<<c.back()<<endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = ::find(c.begin,c.end(),target);
cout<<"::find(),milli-seconds"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
if(pItem != c.end())
cout<<"found,"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not found"<<endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout<<"c.sort,milli-seconds:"<<(clock()-timeStart)<<endl;
}
}
侯捷C++STL源码分析的更多相关文章
- STL源码分析《4》----Traits技术
在 STL 源码中,到处可见 Traits 的身影,其实 Traits 不是一种语法,更确切地说是一种技术. STL库中,有一个函数叫做 advance, 用来将某个迭代器(具有指针行为的一种 cla ...
- STL 源码分析《1》---- list 归并排序的 迭代版本, 神奇的 STL list sort
最近在看 侯捷的 STL源码分析,发现了以下的这个list 排序算法,乍眼看去,实在难以看出它是归并排序. 平常大家写归并排序,通常写的是 递归版本..为了效率的考虑,STL库 给出了如下的 归并排序 ...
- STL源码分析《3》----辅助空间不足时,如何进行归并排序
两个连在一起的序列 [first, middle) 和 [middle, last) 都已经排序, 归并排序最核心的算法就是 将 [first, middle) 和 [middle, last) 在 ...
- STL源码分析读书笔记--第二章--空间配置器(allocator)
声明:侯捷先生的STL源码剖析第二章个人感觉讲得蛮乱的,而且跟第三章有关,建议看完第三章再看第二章,网上有人上传了一篇读书笔记,觉得这个读书笔记的内容和编排还不错,我的这篇总结基本就延续了该读书笔记的 ...
- stl源码分析之allocator
allocator封装了stl标准程序库的内存管理系统,标准库的string,容器,算法和部分iostream都是通过allocator分配和释放内存的.标准库的组件有一个参数指定使用的allocat ...
- STL 源码分析六大组件-allocator
1. allocator 基本介绍 分配器(allocator))是C ++标准库的一个组件, 主要用来处理所有给定容器(vector,list,map等)内存的分配和释放.C ++标准库提供了默认使 ...
- STL 源码分析《2》----nth_element() 使用与源码分析
Select 问题: 在一个无序的数组中 找到第 n 大的元素. 思路 1: 排序,O(NlgN) 思路 2: 利用快排的 RandomizedPartition(), 平均复杂度是 O(N) 思路 ...
- STL源码分析与实现-stl_list容器
1. stl_list 介绍 今天我们来总结一下stl_List, 通过之前介绍单链表的文章,其实对链表的基本操作已经十分熟悉了,那对于stl_list,无非就是链表结构不一样,至于其中的增删改查的细 ...
- STL源码分析之迭代器
前言 迭代器是将算法和容器两个独立的泛型进行调和的一个接口. 使我们不需要关系中间的转化是怎么样的就都能直接使用迭代器进行数据访问. 而迭代器最重要的就是对operator *和operator-&g ...
- STL 源码分析 (SGI版本, 侯捷著)
前言 源码之前,了无秘密 algorithm的重要性 效率的重要性 采用Cygnus C++ 2.91 for windows cygwin-b20.1-full2.exe 下载地址:http://d ...
随机推荐
- Kubernetes集群调度增强之超容量扩容
作者:京东科技 徐宪章 1 什么是超容量扩容 超容量扩容功能,是指预先调度一定数量的工作节点,当业务高峰期或者集群整体负载较高时,可以使应用不必等待集群工作节点扩容,从而迅速完成应用横向扩容.通常情况 ...
- ROS机器人SLAM创建地图
ROS机器人SLAM创建地图 连接小车 ssh clbrobot@clbrobot 激活树莓派 roslaunch clbrobot bringup.launch 开启雷达 打开另一个终端输入: ss ...
- 26-code split
第一种:多入口 const { resolve } = require('path'); const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin' ...
- Java全栈开发/API
2023/4/16 记录我学习的网站 前端 vuejs axios异步请求 微信开发者文档 uniapp开发文档 快速参考备忘清单 免费前端接口 读取json vant4UI cubeUI mintU ...
- 笔记:C++学习之旅---指针
笔记:C++学习之旅---指针 为什么要使用指针 因为在操作大型数据和类时,由于指针可以通过内存地址直接访问数据,从而避免在程序中赋值大量的代码,因此指针的效率最高,一般来说,指针会有三大用途: 1: ...
- Django笔记三十三之缓存操作
本文首发于公众号:Hunter后端 原文链接:Django笔记三十三之缓存操作 这一节介绍一下如何在 Django 中使用 redis 做缓存操作. 在 Django 中可以有很多种方式做缓存,比如数 ...
- P2482 [SDOI2010] 猪国杀
方法论 这是一道复杂的模拟题.由于游戏规则的条目很多,我们需要仔细考虑程序的组织.否则,在编写程序的过程中极容易陷入停滞的状态(不知道下一步应该怎么做),或在发现程序出问题时,难以快速定位到错误点,对 ...
- 【由浅入深学MySQL】- MySQL连接查询详解
本系列为:MySQL数据库详解,为千锋教育资深Java教学老师独家创作 致力于为大家讲解清晰MySQL数据库相关知识点,含有丰富的代码案例及讲解.如果感觉对大家有帮助的话,可以[点个关注]持续追更~ ...
- 2023-04-16:给定一个长度为N的数组,值一定在0~N-1范围,且每个值不重复 比如,arr = [4, 2, 0, 3, 1] 0 1 2 3 4 把0想象成洞
2023-04-16:给定一个长度为N的数组,值一定在0~N-1范围,且每个值不重复 比如,arr = [4, 2, 0, 3, 1] 0 1 2 3 4 把0想象成洞,任何非0数字都可以来到这个洞里 ...
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'flask_sqlalchemy'
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'flask_sqlalchemy' 解决: pip install flask_sqlalchemy
