tensorflow的官方强化学习库agents的相关内容及一些注意事项
源代码地址:
https://github.com/tensorflow/agents
TensorFlow给出的官方文档说明:
https://tensorflow.google.cn/agents
相关视频:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7g7-Jzj9qo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tAOApRQAgpc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52DTXidSVWc&list=PLQY2H8rRoyvxWE6bWx8XiMvyZFgg_25Q_&index=2
-----------------------------------------------------------
框架实现的算法:
论文1:
论文3:
论文4:
论文5:
论文6:
论文7:
论文8:
论文9:
论文10:
====================================
1. gym的环境版本有要求,给出具体安装及Atari的安装:
pip install gym[atari]==0.23.0
pip install gym[accept-rom-license]
=====================================
2. 代码的逻辑bug
tf_agents/specs/array_spec.py 代码bug:
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
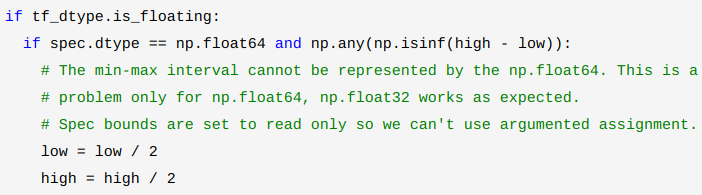
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 or spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
这个代码的意思就是在给定区间能进行均匀抽样,但是由于区间可能过大因此导致无法使用库函数抽样,因此需要对区间进行压缩。
当抽样的数据类型为np.float64时,由代码:
np.array(np.zeros(10), dtype=np.float64)+np.finfo(np.float64).max-np.finfo(np.float64).min

np.random.uniform(size=10, low=np.finfo(np.float64).min, high=np.finfo(np.float64).max)

可以知道,当类型为np.float64时,如果抽样区间过大会(超出数值表示范围)导致无法抽样,因此进行压缩区间:
当数据类型为np.float32时,虽然也会存在超出表示范围的问题:
np.array(np.zeros(10), dtype=np.float32)+np.finfo(np.float32).max-np.finfo(np.float32).min

但是由于函数 np.random.uniform 的计算中会把np.float32转为np.float64,因此不会出现报错,如下:
np.random.uniform(size=10, low=np.finfo(np.float32).min, high=np.finfo(np.float32).max)

---------------------------------------------------
当数值类型为int时,区间访问过大的检测代码为:
np.any(high - low < 0)
原因在意np.float类型数值超出表示范围会表示为infi变量,但是int类型则会以溢出形式表现,如:

但是在使用numpy.random.randint 函数时,即使范围为最大范围也没有报错:
np.random.randint(size=10000, low=tf.as_dtype(np.int64).min, high=tf.as_dtype(np.int64).max)

np.random.randint(size=10000, low=np.iinfo(np.int64).min, high=np.iinfo(np.int64).max)

而且即使由于high值是取开区间的,我们对high值加1以后也没有报错:
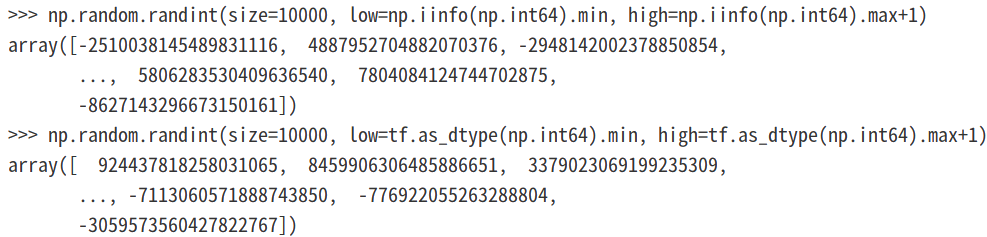
但是需要注意,此时传给np.random.randint函数中的low和high数值都为python数据类型int而不是numpy中的np.int64,下面我们看下numpy.float64类型是否会溢出:
当以数组形式传递最高high值并使其保持np.float64类型,发现使用high+1就会溢出:
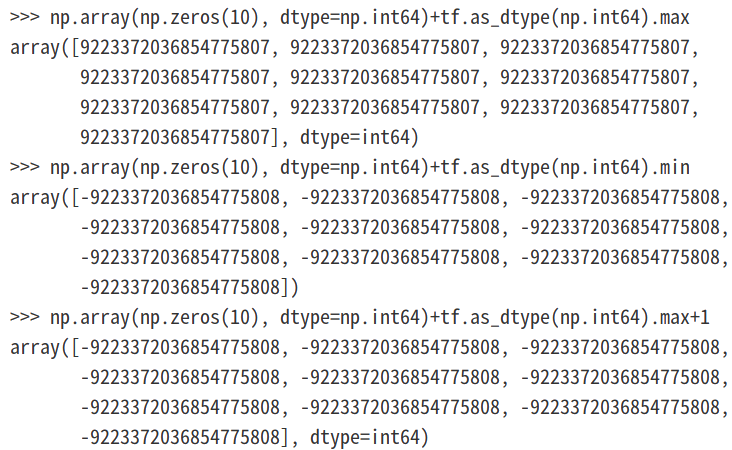
可以看到使用最大范围+1作为high值会导致报错:
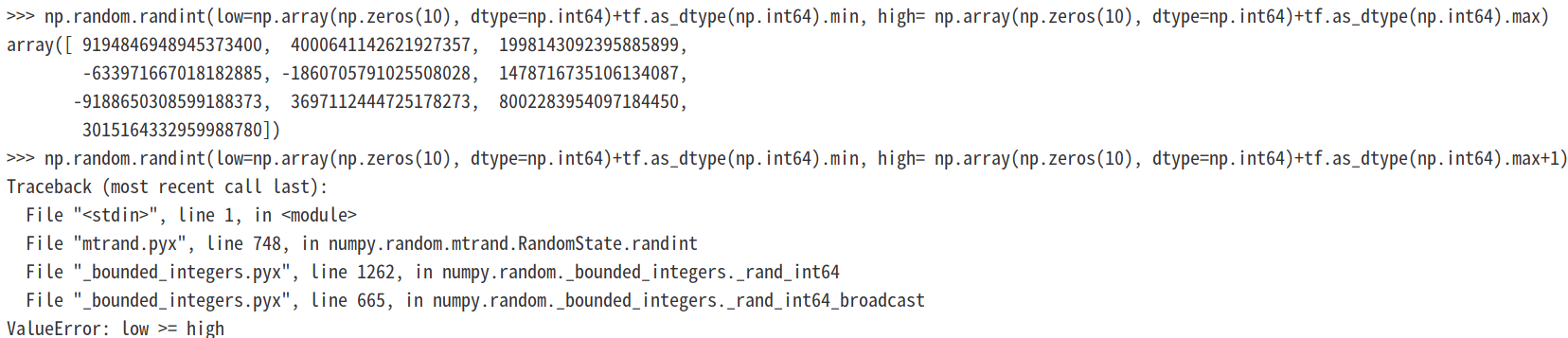
可以看到在使用numpy.random.randint时对上下限还是要注意的,虽然numpy.random.randint对上限是开区间,但是+1操作是很可能引起溢出错误的。
这也就是为什么 high+1操作之前要做判断了,如下:

不过如果数据类型不为np.int64,并且也不为np.uint64,那么我们依然可以把high值转为np.int64后在+1 ,但是上面的逻辑判断是有一定问题的,这些修正后如下:

总的修改后的代码为:
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 and spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
加入对np.uint64类型的判断:
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if spec.dtype == np.uint64 and np.any(high >= np.iinfo(np.int64).max):
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 and spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
===========================================
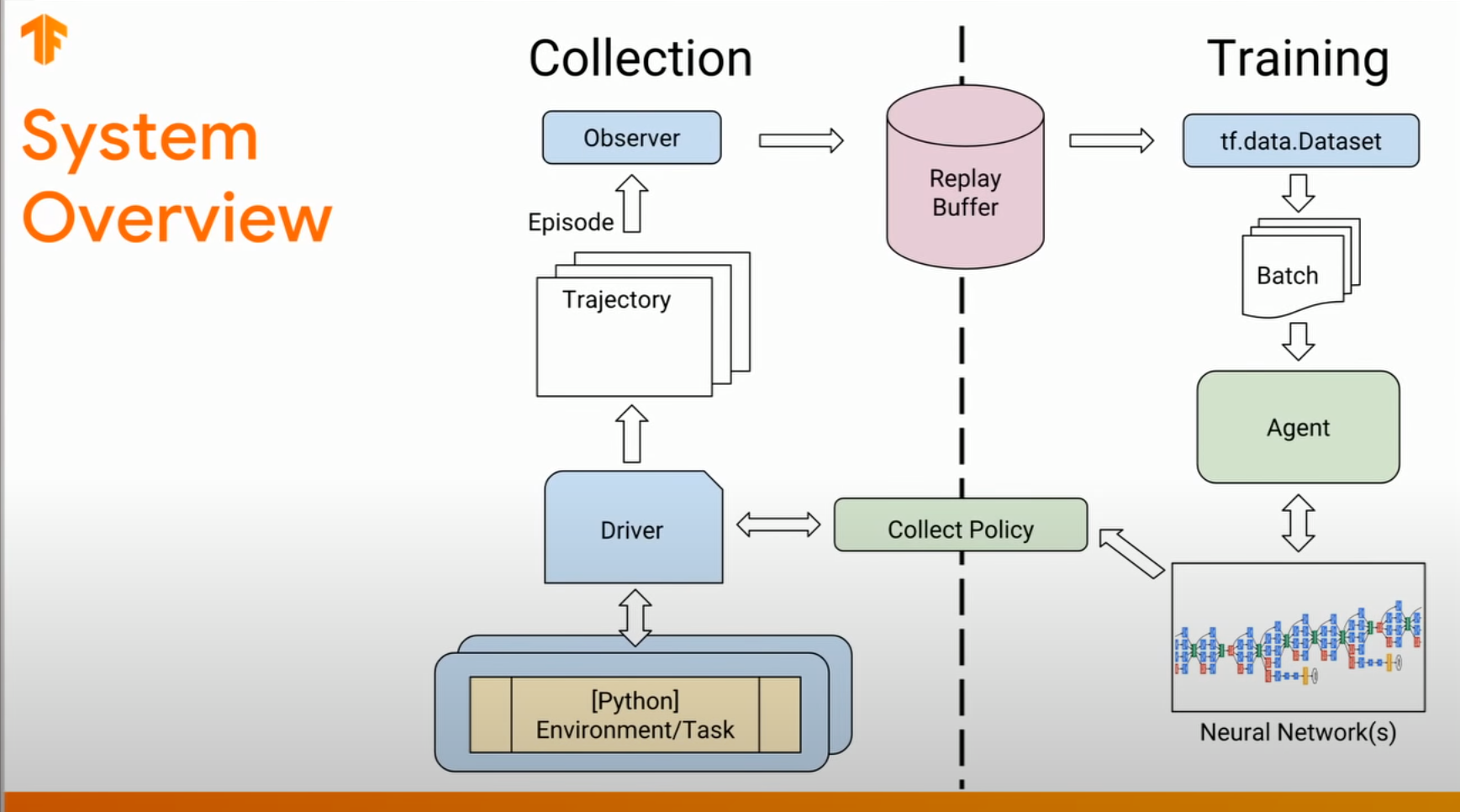
tf-agents框架的交互逻辑代码:
===========================================





tensorflow的官方强化学习库agents的相关内容及一些注意事项的更多相关文章
- 学习笔记之html5相关内容
写一下昨天学习的html5的相关内容,首先谈下初次接触html5的感受.以前总是听说html5是如何的强大,如何的将要改变世界.总是充满了神秘感.首先来谈一下我接触的第一个属性是 input的里面的 ...
- 强化学习之四:基于策略的Agents (Policy-based Agents)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之三:双臂赌博机(Two-armed Bandit)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- DQN 强化学习
pytorch比tenserflow简单. 所以我们模仿用tensorflow写的强化学习. 学习资料: 本节的全部代码 Tensorflow 的 100行 DQN 代码 我制作的 DQN 动画简介 ...
- 强化学习之七:Visualizing an Agent’s Thoughts and Actions
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之六:Deep Q-Network and Beyond
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之五:基于模型的强化学习(Model-based RL)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之三点五:上下文赌博机(Contextual Bandits)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之二:Q-Learning原理及表与神经网络的实现(Q-Learning with Tables and Neural Networks)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译.(This article is my personal translation for the tutor ...
- 深度强化学习(DRL)专栏(一)
目录: 1. 引言 专栏知识结构 从AlphaGo看深度强化学习 2. 强化学习基础知识 强化学习问题 马尔科夫决策过程 最优价值函数和贝尔曼方程 3. 有模型的强化学习方法 价值迭代 策略迭代 4. ...
随机推荐
- jsp和servlet的区别、共同点、各自应用的范围?
JSP是Servlet技术的扩展,本质上就是Servlet的简易方式.JSP编译后是"类servlet".Servlet和JSP最主要的不同点在于: Servlet的应用逻辑是在J ...
- flutter 环境搭配 (一)
首先下载flutter SDK Flutter中文网 官网 (p2hp.com 选择下载 SDK 解压后 ,添加到环境变量中. 配置国内镜像, PUB_HOSTED_URL=https://pub.f ...
- ACPI Table 与 Device Tree
背景 在分析Linux内核驱动的时候,有时候会看到一些acpi字样的接口. 之前一直没搞明白ACPI是什么,现在知道了. Reference : https://www.cnblogs.com/jun ...
- Linux 特权 SUID/SGID 的详解
导航 0 前言 1 权限匹配流程 2 五种身份变化 3 有效用户/组 4 特权对 Shell 脚本无效 5 Sudo 与 SUID/SGID 的优先级 6 SUID.SGID.Sticky 各自的功能 ...
- 基于wxpython的时钟小工具
前言 基于python3.10 + wxpython 的时钟小工具 代码由chatgpt3.5生成,作者自己调试.留作后续参考. 正文 timer_ok.py import wx import tim ...
- c语言生成随机数
记录示例,留作自用 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) ...
- linux scp自动填充密码脚本
在linux上使用scp命令传输文件时,每传输一次,都要填写目标服务器的登录密码,十分麻烦. 配置系统密钥又比较复杂,于是想到的使用expect写一个自动填充密码的脚本,脚本内容如下: scp.sh ...
- SpringBoot集成MQTT
MQTT介绍 MQTT 是基于 Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅) 模式的物联网通信协议,凭借简单易实现.支持 QoS.报文小等特点. 其具有协议简洁.⼩巧.可扩展性强.省流量.省电等优 ...
- koa web框架入门
1.在hello-koa这个目录下创建一个package.json,这个文件描述了我们的hello-koa工程会用到哪些包.完整的文件内容如下: { "name": "h ...
- 运行前端React框架出现node Error: bind EADDRINUSE null的解决方法
运行前端React代码时,出现这样的错误: node Error: bind EADDRINUSE null 后来发现端口号冲突,换个端口号后问题就可以解决了.
