mockito使用
mockito学习资料:
http://docs.mockito.googlecode.com/hg/org/mockito/Mockito.html
http://blog.csdn.net/sdyy321/article/details/38757135
1、验证行为是否发生
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Testpublic void mockedList(){ List mockedList = mock(List.class); mockedList.add("one"); mockedList.clear(); verify(mockedList).add("one"); verify(mockedList).clear();} |
验证add和clear是否执行。
2、验证返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Test public void two(){ //模拟创建一个List对象 LinkedList mockLinkedList = mock(LinkedList.class); //打桩,当LinkedList调用get(0)方法时,第一次返回zero,第二次n次返回nnnn when(mockLinkedList.get(0)).thenReturn("zero").thenReturn("nnnn"); //使用mock对象 System.out.println(mockLinkedList.get(0)); System.out.println(mockLinkedList.get(0)); System.out.println(mockLinkedList.get(0)); //验证行为get是否发生 verify(mockLinkedList).get(0); } |
这里注意所有的方法都会有返回值,如果没有设置返回值,那么就会返回null或者空集、适当的类型。 Stubbing可以被重写,也就是同一个参数方法可以放回不同的值,但是已最后一次设置的值为标准。一旦被 Stubbed,无论方法被调用多少次,都只会返回Stubbed value。最后一次最重要原则。
3、参数匹配
通过equals()来验证参数。
不同的参数返回不同的结果:
|
1
2
|
when(comparable.compareTo("Test")).thenReturn(1); when(comparable.compareTo("Omg")).thenReturn(2); |
一旦你使用了参数匹配器,那么所有的参数都必须由匹配器给出:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//stubbing using built-in anyInt() argument matcher when(mockedList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("element"); //stubbing using hamcrest (let's say isValid() returns your own hamcrest matcher): when(mockedList.contains(argThat(isValid()))).thenReturn("element"); //following prints "element" System.out.println(mockedList.get(999)); //you can also verify using an argument matcher verify(mockedList).get(anyInt()); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
verify(mock).someMethod(anyInt(), anyString(), eq("third argument")); //above is correct - eq() is also an argument matcher verify(mock).someMethod(anyInt(), anyString(), "third argument"); //above is incorrect - exception will be thrown because third argument is given without an argument matcher. |
4、验证调用次数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
@Test public void three(){ List mockedList = mock(List.class); mockedList.add(1); mockedList.add(2); mockedList.add(2); mockedList.add(3); mockedList.add(3); mockedList.add(3); //验证是否被调用一次,等效于下面的times(1),默认的,可以不写 verify(mockedList).add(1); verify(mockedList,times(1)).add(1); //验证是否被调用2次 verify(mockedList,times(2)).add(2); //验证是否被调用3次 verify(mockedList,times(3)).add(3); //验证是否从未被调用过 verify(mockedList,never()).add(4); //验证至少调用一次 verify(mockedList,atLeastOnce()).add(1); //验证至少调用2次 verify(mockedList,atLeast(2)).add(2); //验证至多调用3次 verify(mockedList,atMost(3)).add(3); } |
add(1)这个方法被调用了1次,add(2)这个被调用了2次。add(3)这个方法被调用了3次,如果将verify(mockedList,times(1)).add(3);运行后那么就会出现错误:
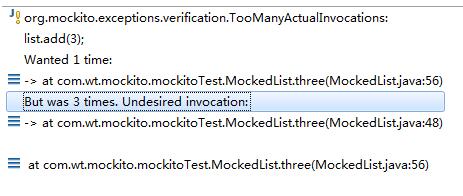
5、模拟方法体抛出异常
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
doThrow(new RuntimeException()).when(mockedList).clear(); //following throws RuntimeException:mockedList.clear();doThrow(new RuntimeException()).when(list).add(1); list.add(1); |
6、验证执行的顺序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@Test public void four(){ List firstList = mock(List.class); List secondList = mock(List.class); //using mocks firstList.add("was called first one mock"); secondList.add("was called second one mock"); //create inOrder object passing any mocks that need to be verified in order InOrder indOrder = inOrder(firstList,secondList); indOrder.verify(firstList).add("was called first one mock"); indOrder.verify(secondList).add("was called second one mock"); } |
如果将11,12调换,
indOrder.verify(secondList).add("was called second one mock");
indOrder.verify(firstList).add("was called first one mock");
会出现如下错误:
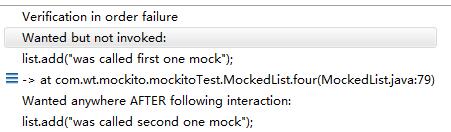
可是如果顺序如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
firstList.add("was called first one mock");secondList.add("was called second one mock");InOrder indOrder = inOrder(secondList,firstList);indOrder.verify(firstList).add("was called first one mock");indOrder.verify(secondList).add("was called second one mock"); |
inorder中顺序调换后,上面程序居然没有出错?难道我理解错了。验证的顺序是按照inOrder中给出的,也就是second要在first前面,而在verify中明显second在first后验证了,应该出错啊。
7、模拟对象上没有相互关系
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//using mocks - only mockOne is interacted mockOne.add("one"); //ordinary verification verify(mockOne).add("one"); //verify that method was never called on a mock verify(mockOne, never()).add("two"); //verify that other mocks were not interacted verifyZeroInteractions(mockTwo, mockThree); |
8、找出多余的调用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
//using mocks mockedList.add("one"); mockedList.add("two"); verify(mockedList).add("one"); //following verification will fail 检查是否有未被验证的行为 verifyNoMoreInteractions(mockedList); verify(list,times(2)).add(anyInt()); //检查是否有未被验证的互动行为,因为add(1)和add(2)都会被上面的anyInt()验证到,所以下面的代码会通过 verifyNoMoreInteractions(list); |
mockedList还有add("two")没有验证,所以出错。
9、使用注解来mock
这里注意要在构造函数中初试化mock对象,否则mock对象为null。
也可以通过在类上使用注解:@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)
这样就不需要初始化mock了。
10、连续调用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@Test(expected = RuntimeException.class) public void consecutive_calls(){ List mockList = mock(List.class); //模拟连续调用返回期望值,如果分开,则只有最后一个有效 when(mockList.get(0)).thenReturn(0); when(mockList.get(0)).thenReturn(1); when(mockList.get(0)).thenReturn(2); when(mockList.get(1)).thenReturn(0).thenReturn(1).thenThrow(new RuntimeException()); assertEquals(2,mockList.get(0)); assertEquals(2,mockList.get(0)); assertEquals(0,mockList.get(1)); assertEquals(1,mockList.get(1)); //第三次或更多调用都会抛出异常 mockList.get(1); } |
11、使用回调来stub
通用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
when(mock.someMethod(anyString())).thenAnswer(new Answer() { Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) { Object[] args = invocation.getArguments(); Object mock = invocation.getMock(); return "called with arguments: " + args; } }); //Following prints "called with arguments: foo" System.out.println(mock.someMethod("foo")); |
使用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Test public void six(){ List mockList = mock(List.class); when(mockList.get(anyInt())).thenAnswer(new Answer<Object>() { public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable { Object[] args = invocation.getArguments(); return "hi:"+args[0]; } }); assertEquals("hi:0",mockList.get(0)); assertEquals("hi:1",mockList.get(1)); } |
12、对于void方法,有系列函数可以用来处理。
doThrow() doAnswer doNothing doReturn。当一个void的方法有异常抛出时可以使用doThrow()。
13、监控真实对象
当使用spy的时候真正的方法将会被调用,而不再是stub的对象了,这个和部分mock的思想是一样的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@Test public void seven(){ List list = new LinkedList(); List spy = spy(list); //optionally, you can stub out some methods: when(spy.size()).thenReturn(100); //using the spy calls real methods spy.add("one"); spy.add("two"); //prints "one" - the first element of a list System.out.println(spy.get(0)); //size() method was stubbed - 100 is printed System.out.println(spy.size()); //optionally, you can verify verify(spy).add("one"); verify(spy).add("two"); } |
使用spy的时候需要注意一点:有时候是不能使用when语句的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
List list = new LinkedList(); List spy = spy(list); //Impossible: real method is called so spy.get(0) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException (the list is yet empty) when(spy.get(0)).thenReturn("foo"); //You have to use doReturn() for stubbing doReturn("foo").when(spy).get(0); |
14、设置未stub的调用的默认值
对于没有stub方法的调用,我们一般返回null,或者是默认类型。也可以修改使其返回你指定的值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
@Test public void eight(){ //mock对象使用Answer来对未预设的调用返回默认期望值 List mocklist = mock(List.class,new Answer(){ public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable { return 999; } }); //下面的get(1)没有预设,通常情况下会返回NULL,但是使用了Answer改变了默认期望值 assertEquals(999, mocklist.get(1)); //下面的size()没有预设,通常情况下会返回0,但是使用了Answer改变了默认期望值 assertEquals(999,mocklist.size()); }
|
mockito使用的更多相关文章
- Junit mockito 测试Controller层方法有Pageable异常
1.问题 在使用MockMVC+Mockito模拟Service层返回的时候,当我们在Controller层中参数方法调用有Pageable对象的时候,我们会发现,我们没办法生成一个Pageable的 ...
- Junit mockito解耦合测试
Mock测试是单元测试的重要方法之一. 1.相关网址 官网:http://mockito.org/ 项目源码:https://github.com/mockito/mockito api:http:/ ...
- Android 单元测试(junit、mockito、robolectric)
1.运用JUnit4 进行单元测试 首先在工程的 src 文件夹内创建 test 和 test/java 文件夹. 打开工程的 build.gradle(Module:app)文件,添加JUnit4依 ...
- Mockito Hello World
Mockito Hello World 项目配置 IDE是Intellij IDEA,用gradle配置项目. 新建一个Java项目,gradle中需要有这个: repositories { jc ...
- mockito使用心得
前提:pom引用<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifact ...
- Mock之easymock, powermock, and mockito
easymock, powermock, and mockito Easymock Class Mocking Limitations To be coherent with interface mo ...
- 用Mockito mock普通的方法
上面的例子是很理想化的状态,但是在实际的开发中,我们需要经常调用一些依赖特定环境的函数或者调用同事写的代码,而同事仅提供了接口.这个时候就需要利用Mockito来协助我们完成测试. 当然,你可以选择e ...
- mock测试框架Mockito
无论是敏捷开发.持续交付,还是测试驱动开发(TDD)都把单元测试作为实现的基石.随着这些先进的编程开发模式日益深入人心,单元测试如今显得越来越重要了.在敏捷开发.持续交付中要求单元测试一定要快(不能访 ...
- Mockito自定义verify参数Matcher
在TDD开发中,也许我们会遇见对一些重要的无返回值的行为测试,比如在用户的积分DB中增加用户的积分,这个行为对于我们的业务具有重要的价值,所以我们也希望能测试覆盖这部分业务价值.这个时候我们就得使用m ...
- Mockito学习资料
官网:http://mockito.org/ https://dzone.com/refcardz/mockito
随机推荐
- Oracle 同一个字段的两值进行加减计算
如 病人ID 入院日期 出院日期 00001 2016-09-01 2016-09-10 00001 2016-09-15 ...
- Hive基础之Hive的存储类型
Hive常用的存储类型有: 1.TextFile: Hive默认的存储类型:文件大占用空间大,未压缩,查询慢: 2.Sequence File:将属于以<KEY,VALUE>的形式序列化到 ...
- 自定义ExtJS插件
http://cache.baiducontent.com/c?m=9f65cb4a8c8507ed4fece763105392230e54f73b6f93834c28c3933fc239045647 ...
- 小朋友学Java(2):Win 7安装JDK
1 打开命令行窗口,输入java -version. 若提示不认识java命令,说明没有java环境. 1.png 2 从甲骨文网站(http://www.oracle.com/technetwo ...
- Axure8.1.0.3372 注册码
Axure8.1.0.3372 注册码 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/cslucifer/article/details/79355007 Koshy wTADPqxn3KChzJx ...
- C语言键盘按键无阻塞侦测:kbhit()
http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0414/09/1317564_203474440.shtml kbhit in c kbhit in c: kbhit functi ...
- docker 简单入门(一)
本篇目录 写在最前面的话 docker概念介绍 镜像的概念.容器的概念 docker的安装介绍 写在最前面的话 大家好,首先跟大家说声对不起,我班门弄斧了,我本身是做系统开发,使用的语言是C#和JAV ...
- springVC + logback
为什么用logback,而不是log4j? springmvc log只输出到console,不输出到文件 Spring MVC集成slf4j-logback springMVC如何配置logback ...
- 多媒体基础知识之PCM数据
1.什么是PCM音频数据 PCM(Pulse Code Modulation)也被称为脉冲编码调制.PCM音频数据是未经压缩的音频采样数据裸流,它是由模拟信号经过采样.量化.编码转换成的标准的数字音频 ...
- WP8.1 在默认浏览器中打开url
Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync(new Uri("http://www.google.com")); PS: This is for ...
