DSU模板(树的启发式合并)
With dsu on tree we can answer queries of this type:
How many vertices in subtree of vertex v has some property in O(n lg n) time (for all of the queries).
For example:
Given a tree, every vertex has color. Query is how many vertices in subtree of vertex v are colored with color c?
要点:记录每棵子树的大小,启发式合并。
模板整理如下:
1. easy to code but 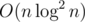
//O(nlognlogn)
map<int, int> *cnt[maxn];
void dfs(int v, int p){
int mx = -, bigChild = -;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p){
dfs(u, v);
if(sz[u] > mx)
mx = sz[u], bigChild = u;
}
if(bigChild != -)
cnt[v] = cnt[bigChild];
else
cnt[v] = new map<int, int> ();
(*cnt[v])[ col[v] ] ++;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild){
for(auto x : *cnt[u])
(*cnt[v])[x.first] += x.second;
}
//now (*cnt)[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily. }
2. easy to code and 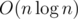
vector<int> *vec[maxn];
int cnt[maxn];
void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){
int mx = -, bigChild = -;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && sz[u] > mx)
mx = sz[u], bigChild = u;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild)
dfs(u, v, );
if(bigChild != -)
dfs(bigChild, v, ), vec[v] = vec[bigChild];
else
vec[v] = new vector<int> ();
vec[v]->push_back(v);
cnt[ col[v] ]++;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild)
for(auto x : *vec[u]){
cnt[ col[x] ]++;
vec[v] -> push_back(x);
}
//now (*cnt)[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily.
// note that in this step *vec[v] contains all of the subtree of vertex v.
if(keep == )
for(auto u : *vec[v])
cnt[ col[u] ]--;
}
3. heavy-light decomposition style 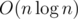
int cnt[maxn];
bool big[maxn];
void add(int v, int p, int x){
cnt[ col[v] ] += x;
for(auto u: g[v])
if(u != p && !big[u])
add(u, v, x)
}
void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){
int mx = -, bigChild = -;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && sz[u] > mx)
mx = sz[u], bigChild = u;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild)
dfs(u, v, ); // run a dfs on small childs and clear them from cnt
if(bigChild != -)
dfs(bigChild, v, ), big[bigChild] = ; // bigChild marked as big and not cleared from cnt
add(v, p, );
//now cnt[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily.
if(bigChild != -)
big[bigChild] = ;
if(keep == )
add(v, p, -);
}
4. My invented style 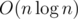
This implementation for "Dsu on tree" technique is new and invented by me. This implementation is easier to code than others. Let st[v] dfs starting time of vertex v, ft[v] be it's finishing time and ver[time] is the vertex which it's starting time is equal to time. int cnt[maxn];
void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){
int mx = -, bigChild = -;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && sz[u] > mx)
mx = sz[u], bigChild = u;
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild)
dfs(u, v, ); // run a dfs on small childs and clear them from cnt
if(bigChild != -)
dfs(bigChild, v, ); // bigChild marked as big and not cleared from cnt
for(auto u : g[v])
if(u != p && u != bigChild)
for(int p = st[u]; p < ft[u]; p++)
cnt[ col[ ver[p] ] ]++;
cnt[ col[v] ]++;
//now cnt[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily.
if(keep == )
for(int p = st[v]; p < ft[v]; p++)
cnt[ col[ ver[p] ] ]--;
}
时间复杂度分析
4. My invented style
考虑每个节点最多会被清零几次?
显然被清零的次数即为该节点到根节点的链上轻儿子的个数
联系树链剖分,任意一个节点到根节点的链最多被划分为O(logn)段重链,最多被清零O(logn)次.
故时间复杂度为O(nlogn).
2, 3, 4时间复杂度分析类似.
启发式合并算法复杂度总结
线段树合并 => O(nlogU), U为线段树权值域,从势能分析,合并的复杂度为O(总节点数减小的个数)
平衡树合并+树链剖分+单次插入删除O(logn) => O(nlognlogn)
平衡树合并+树链剖分+单次插入删除O(1) => O(nlogn)
set合并 => O(nlognlogn), 显然set合并复杂度不会高于multiset(平衡树)合并复杂度
DSU模板(树的启发式合并)的更多相关文章
- Problem E. TeaTree - HDU - 6430 (树的启发式合并)
题意 有一棵树,每个节点有一个权值. 任何两个不同的节点都会把他们权值的\(gcd\)告诉他们的\(LCA\)节点.问每个节点被告诉的最大的数. 题解 第一次接触到树的启发式合并. 用一个set维护每 ...
- dsu on tree 树上启发式合并 学习笔记
近几天跟着dreagonm大佬学习了\(dsu\ on\ tree\),来总结一下: \(dsu\ on\ tree\),也就是树上启发式合并,是用来处理一类离线的树上询问问题(比如子树内的颜色种数) ...
- dsu on tree[树上启发式合并学习笔记]
dsu on tree 本质上是一个 启发式合并 复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\) 不支持修改 只能支持子树统计 不能支持链上统计- 先跑一遍树剖的dfs1 搞出来轻重儿子- 求每个节点的子树上有 ...
- dsu on tree (树上启发式合并) 详解
一直都没出过算法详解,昨天心血来潮想写一篇,于是 dsu on tree 它来了 1.前置技能 1.链式前向星(vector 建图) 2.dfs 建树 3.剖分轻重链,轻重儿子 重儿子 一个结点的所有 ...
- 【BZOJ3123】森林(主席树,启发式合并)
题意:一个带点权的森林,要求维护以下操作: 1.询问路径上的点权K大值 2.两点之间连边 n,m<=80000 思路:如果树的结构不发生变化只需要维护DFS序 现在因为树的结构发生变化,要将两棵 ...
- bzoj2733 永无乡 splay树的启发式合并
https://vjudge.net/problem/HYSBZ-2733 给一些带权点,有些点是互相连通的, 然后给出2种操作,在两点间加一条边,或者询问一个点所在的连通块内的第k小值的编号 并查集 ...
- BZOJ3123[Sdoi2013]森林——主席树+LCA+启发式合并
题目描述 输入 第一行包含一个正整数testcase,表示当前测试数据的测试点编号.保证1≤testcase≤20. 第二行包含三个整数N,M,T,分别表示节点数.初始边数.操作数.第三行包含N个非负 ...
- bzoj 2809 左偏树\平衡树启发式合并
首先我们对于一颗树,要选取最多的节点使得代价和不超过m,那么我们可以对于每一个节点维护一个平衡树,平衡树维护代价以及代价的和,那么我们可以在logn的时间内求出这个子树最多选取的节点数,然后对于一个节 ...
- 【CF778C】Peterson Polyglot(Trie树,启发式合并)
题意:有一棵n个结点的只由小写字母组成的Trie树,给定它的具体形态,问删除哪一层后剩下Trie树的结点数最少 n<=3e5 思路:先建出原Trie树,对于每一层的每一个结点计算删除后对答案的贡 ...
随机推荐
- GoLang入门(一)
1.Go语言的简述 Go语言可能大家对它并不是很了解,因为它相对其他语言来说实在是太年轻了,从创建到现在仅仅十年,09年,谷歌团队初设该想法,到实现也就是10年时间,对于go语言,它不是万能的,每种语 ...
- linux镜像(持续更新)
Linux系统历史衍生图:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/1b/Linux_Distribution_Timeline.svg ubu ...
- myeclipse激活后server不能用问题
一般是由于激活失败造成的,这种问题就卸了重新安装吧,目前还没有找到合理的方法解决,这个还真的看哥们的运气了,我是装了不下5遍才激活成功的,一般情况下,在激活的时候 出现下图的情况,Usercode写好 ...
- oracle数据库之rownum和rowid用法
Rownum 和 Rowid是Oracle数据库所特有的,通过他们可以查询到指定行数范围内的数据记录. 以下通过例子讲解: -- 为了方便,首先,查找dept表中的所有. select deptn ...
- Lwip:原生态的Linux socket应用如何移植到Lwip上
lwIP - A Lightweight TCP/IP stack 在上一篇中,我们了解到在OpenFastPath上如何移植原生态的Linux Socket应用程序,那么,对于另外一个老牌的小型TC ...
- 【神经网络】自编码聚类算法--DEC (Deep Embedded Clustering)
1.算法描述 最近在做AutoEncoder的一些探索,看到2016年的一篇论文,虽然不是最新的,但是思路和方法值得学习.论文原文链接 http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48 ...
- git ssh密钥配置添加
1. 初次安装git配置用户名和邮箱 $ git config --global user.name "xxx" $ git config --global user.email ...
- 凡事不求甚解,遇事必定抓瞎——PHP开发Apache服务器配置备忘录
照此配置流程,绝对一路畅通,可保无虞. 昨天弄了个PHP小程序,想在本地跑一下测试,可是工作电脑没有安装环境,于是下载了一个wamp,一路畅通,Apache.Mysql.PHP就全有了.启动wamp服 ...
- web12 使用map型的request、session、application
电影网站:www.aikan66.com 项目网站:www.aikan66.com 游戏网站:www.aikan66.com 图片网站:www.aikan66.com 书籍网站:www.aikan66 ...
- 1001 A+B
代码链接 PDF链接 首先要说的是这道题的难点是如何把数字输出加入逗号,毕竟数据范围并没有超过Long.当然这个难点也不是问题,将数字转为字符串,C中就有这样的函数,然后再用 %3==0 这样来控制输 ...
