学习小记: Kaggle Learn - Machine Learning Explainability
| Method | Feature(s) | Sample(s) | Result Value/Feature |
| Permutation Importance | 1 | all validation samples | Single Scale |
| Partial Dependence Plots | 1~2 | all validation samples | Vector(reasults vs feature) |
| SHAP Values | N | individual sample | 每个feature对当前结果的贡献(相对于baseline) |
| Advanced Uses of SHAP Values- Summary Plots | N | all | 绘制每个feature在每个样本预测结果中的贡献(相对于baseline) |
| Advanced Uses of SHAP Values- SHAP Dependence Contribution Plots | 2 | all | 绘制2个feature在所有样本也测结果中的贡献(相对于baseline) |
参考: https://www.kaggle.com/learn/machine-learning-explainability
这个课程将讲解如何从复杂的机器学习模型中解释这些发现。
- 模型认为数据中的哪些特征是最重要的?
- 对于来自模型的任何单个预测,数据中的每个特性如何影响该特定预测
- 每个特性如何影响模型的整体预测(当考虑大量可能的预测时,它的典型影响是什么?)
- 调试,理解模型所发现的模式将帮助您识别那些与您对真实世界的认识不一致的地方
- 为特征工程提供信息
- 指导未来的数据收集
- 为人的决策提供信息
- 建立信任,提高产品在用户中的接受度。
Permutation Importance置换重要性
统计每个feature的重要程度,训具体步骤如下:
- 正常训练完模型。
- 对原始validation数据,依次shuffle每个feature的原始数据。
- 根据得到的模型参数,对shuffle后的数据进行预测,计算性能(准确度)下降程度。
- 对每个feature重复2-3,最后得出每个feature的重要程度(shuffle它后性能下降程度)
用eli5库实现的置换重要性计算
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier data = pd.read_csv('../input/fifa-2018-match-statistics/FIFA 2018 Statistics.csv')
y = (data['Man of the Match'] == "Yes") # Convert from string "Yes"/"No" to binary
feature_names = [i for i in data.columns if data[i].dtype in [np.int64]]
X = data[feature_names]
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=1)
my_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0).fit(train_X, train_y)
import eli5
from eli5.sklearn import PermutationImportance
perm = PermutationImportance(my_model, random_state=1).fit(val_X, val_y)
eli5.show_weights(perm, feature_names = val_X.columns.tolist())
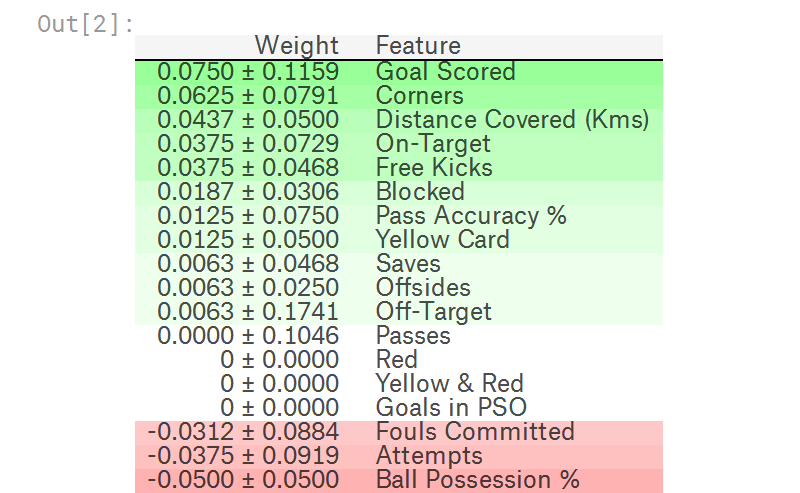
官方例程输出如下,其中排在前面的是更重要的feature,排在后面的是不那么重要的feature,最后偶然出现负数,也是正常现象。
毕竟是shuffle feature data,对一些不太重要的feature,偶尔出现shuffle后比shuffle前更准确也时有发生。
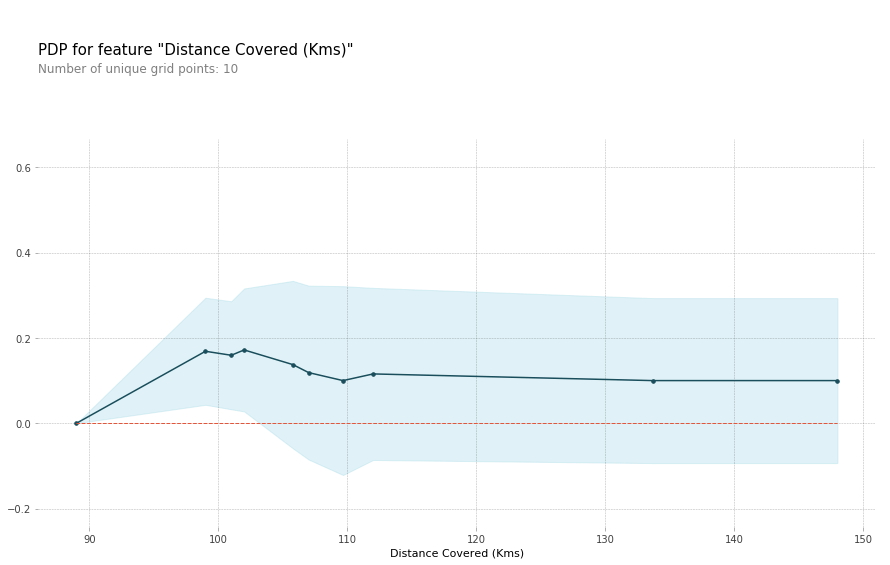
Partial Dependence Plots
用于统计feature(s)如何影响predictions,用pdpbox库
单个feature的影响
# Build Random Forest model
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=0).fit(train_X, train_y) pdp_dist = pdp.pdp_isolate(model=rf_model, dataset=val_X, model_features=feature_names, feature=feature_to_plot) pdp.pdp_plot(pdp_dist, feature_to_plot)
plt.show()
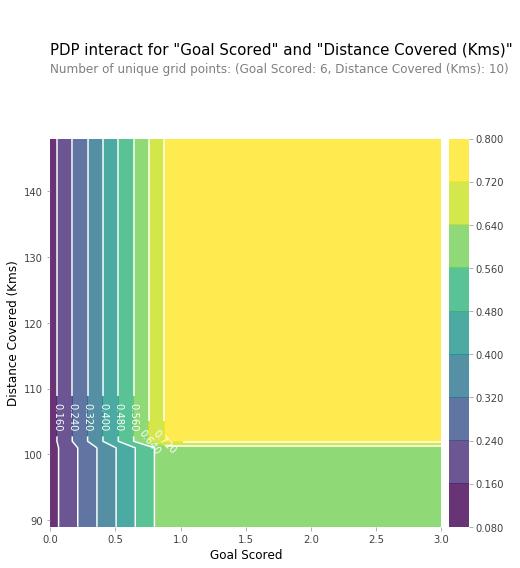
两个features的组合影响
# Similar to previous PDP plot except we use pdp_interact instead of pdp_isolate and pdp_interact_plot instead of pdp_isolate_plot
features_to_plot = ['Goal Scored', 'Distance Covered (Kms)']
inter1 = pdp.pdp_interact(model=tree_model, dataset=val_X, model_features=feature_names, features=features_to_plot) pdp.pdp_interact_plot(pdp_interact_out=inter1, feature_names=features_to_plot, plot_type='contour')
plt.show()
SHAP Values, SHapley Additive exPlanations
对于特定sample的预测,解释每个feature在其中的影响,正负都有。
可用于:
- 一个模型说银行不应该借钱给别人,法律要求银行解释每笔贷款被拒的原因。
- 医疗服务提供者想要确定,是什么因素导致了每个病人患某些疾病的风险,这样他们就可以通过有针对性的健康干预,直接解决这些风险因素
使用shap库,代码片段如下,其中KernelExplainer 结果和TreeExplainer不完全一样,但是比较接近,结果中表达的意思相同。
import shap # package used to calculate Shap values # Create object that can calculate shap values
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(my_model) # Calculate Shap values
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(data_for_prediction) shap.initjs()
shap.force_plot(explainer.expected_value[1], shap_values[1], data_for_prediction) # use Kernel SHAP to explain test set predictions
k_explainer = shap.KernelExplainer(my_model.predict_proba, train_X)
k_shap_values = k_explainer.shap_values(data_for_prediction)
shap.force_plot(k_explainer.expected_value[1], k_shap_values[1], data_for_prediction)
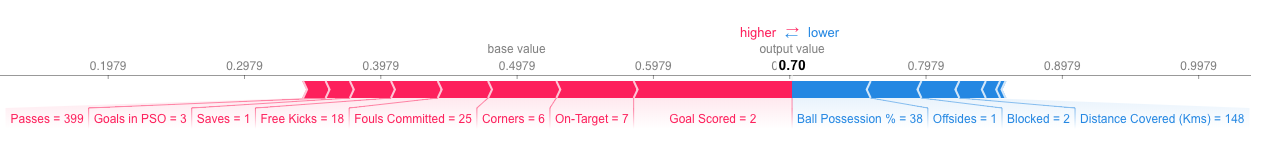
运行结果的图表类似如下图形,
- 其中左边(红色)代表当前样本相对于baseline增加的预测值
- 右边(蓝色)代表当前样本相对于baseline减少的预测值
- 左边(红色) - 右边(蓝色) => output_value - base_value
Advanced Uses of SHAP Values
Summary Plots
import shap # package used to calculate Shap values # Create object that can calculate shap values
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(my_model) # calculate shap values. This is what we will plot.
# Calculate shap_values for all of val_X rather than a single row, to have more data for plot.
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(val_X) # Make plot. Index of [1] is explained in text below.
shap.summary_plot(shap_values[1], val_X)
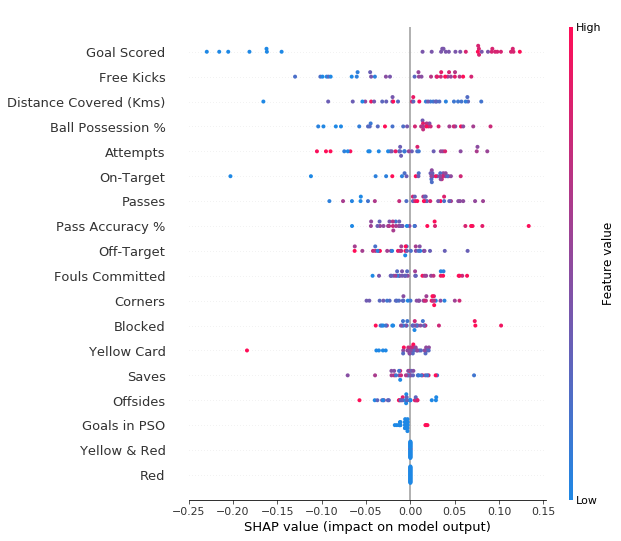
结果如下图所示:
- 每个点代表一个sample
- 垂直方向是特征
- 水平方向是该特征对应的SHAP Value
- 颜色代表该特征的数值大小
SHAP Dependence Contribution Plots
import shap # package used to calculate Shap values # Create object that can calculate shap values
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(my_model) # calculate shap values. This is what we will plot.
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X) # make plot.
shap.dependence_plot('Ball Possession %', shap_values[1], X, interaction_index="Goal Scored")
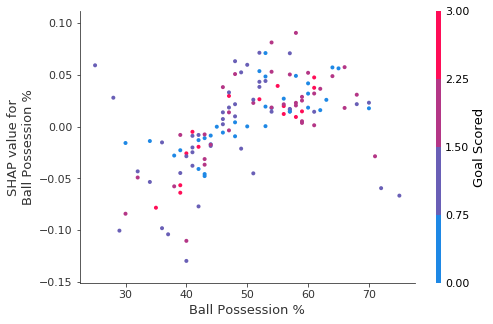
运行结果图简介:
- 横坐标表示Ball Possession %特征的值
- 纵坐标表示SHAP Value值
- 颜色(如右边注释)表示Goal Scored特征的值
学习小记: Kaggle Learn - Machine Learning Explainability的更多相关文章
- How do I learn machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-machine-learning-1?redirected_qid=6578644 How Can I Learn X? ...
- ML Lecture 0-2: Why we need to learn machine learning?
在Github上也po了这个系列学习笔记(MachineLearningCourseNote),觉得写的不错的小伙伴欢迎来给项目点个赞哦~~ ML Lecture 0-2: Why we need t ...
- kaggle _Titanic: Machine Learning from Disaster
A Data Science Framework: To Achieve 99% Accuracy https://www.kaggle.com/ldfreeman3/a-data-science-f ...
- Kaggle:Titanic: Machine Learning from Disaster
一直想着抓取股票的变化,偶然的机会在看股票数据抓取的博客看到了kaggle,然后看了看里面的题,感觉挺新颖的,就试了试. 题目如图:给了一个train.csv,现在预测test.csv里面的Passa ...
- 李宏毅老师机器学习课程笔记_ML Lecture 0-2: Why we need to learn machine learning?
引言: 最近开始学习"机器学习",早就听说祖国宝岛的李宏毅老师的大名,一直没有时间看他的系列课程.今天听了一课,感觉非常棒,通俗易懂,而又能够抓住重点,中间还能加上一些很有趣的例子 ...
- 机器学习案例学习【每周一例】之 Titanic: Machine Learning from Disaster
下面一文章就总结几点关键: 1.要学会观察,尤其是输入数据的特征提取时,看各输入数据和输出的关系,用绘图看! 2.训练后,看测试数据和训练数据误差,确定是否过拟合还是欠拟合: 3.欠拟合的话,说明模 ...
- How do I learn mathematics for machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-mathematics-for-machine-learning How do I learn mathematics f ...
- 【机器学习Machine Learning】资料大全
昨天总结了深度学习的资料,今天把机器学习的资料也总结一下(友情提示:有些网站需要"科学上网"^_^) 推荐几本好书: 1.Pattern Recognition and Machi ...
- In machine learning, is more data always better than better algorithms?
In machine learning, is more data always better than better algorithms? No. There are times when mor ...
随机推荐
- 在Vue中echarts可视化组件的使用
echarts组件官网地址:https://echarts.apache.org/examples/zh/index.html 1.找到脚手架项目所在地址,执行cnpm install echarts ...
- P2015
二叉苹果树 1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include< ...
- mysqli_fetch_row()函数返回结果的理解
在PHP处理对数据库查询返回的结果集,即mysqli_query()函数返回的结果集,我们可以把它处理为数组形式以便于处理. 我们一般会用下面四个函数: 1.array mysqli_fetch_ar ...
- java高级编程笔记(四)
java的Object类: 1.Object 类位于 java.lang 包中,编译时会自动导入:Java 的所有类都继承了 Object,子类可以使用 Object 的所有方法. 2.Object ...
- Pelles C 五光十色中的一抹经典
我只是一个程序员,没有多少文化修养,根本不会组织出多么精彩动人的辞藻,所以废话不多说,开整. 前段时间,我开始了自己的毕业设计项目,项目的主题和内容是围绕数码防伪追溯原理制作一个识别装置,而这个装置并 ...
- 从零开始的Java RASP实现(一)
目录 0 从零开始的Java RASP实现(一) 1 javaagent 1.1 Main方法启动前 概念介绍: 如何使用 创建agent 创建main 1.2 JVM启动后 attach机制 启动一 ...
- 斐波那契数列——Python实现
# 功能:求斐波那契数列第 n 个数的值 # 在此设置 n n = 30 print('\n');print('n = ',n) # 代码生成 Fibonacci 序列,存于数组A A = [0] ...
- C# JSON学习之序列化与反序列化
在我的个人计划中,学习制作c#下的曲线平台属于下半年的重点.关于前后端的数据传递-json数据的学习很有必要,通过一个例子来加深自己的理解. 新建一个console控制台程序,通过导入NewstonS ...
- 获取不到自定义的request的header属性
java获取headers的代码如下: // 获取http-header里面对应的签名信息 Enumeration<?> headerNames = request.getHeaderNa ...
- DC-2 靶机渗透测试
DC-2 靶机渗透测试 冲冲冲,好好学习. 本靶机核心内容"受限shell提权",知识点在另一篇文章中总结归纳了. 攻击机:kali 靶 机:DC-2 准备:在使用前需要在操作机的 ...
