mybatis源码-原来resultMap解析完是这样
@
在 select 语句中查询得到的是一张二维表, 水平方向上看是一个个字段, 垂直方向上看是一条条记录。
作为面向对象的语言, Java 中的的对象是根据类定义创建的。 类之间的引用关系可以认为是嵌套的关系。
在 mybatis 中, resultMap 节点定义了结果集和结果对象(JavaBean)之间的映射规则。
本文主要讲解的是 resultMap 的解析。
1 两个基础类
在阅读本文之前, 最好能对这两个类有相应的理解。
1.1 列映射类ResultMapping
ResultMapping 对象记录了结果集中一列与队友JavaBean中一个属性的对应关系。
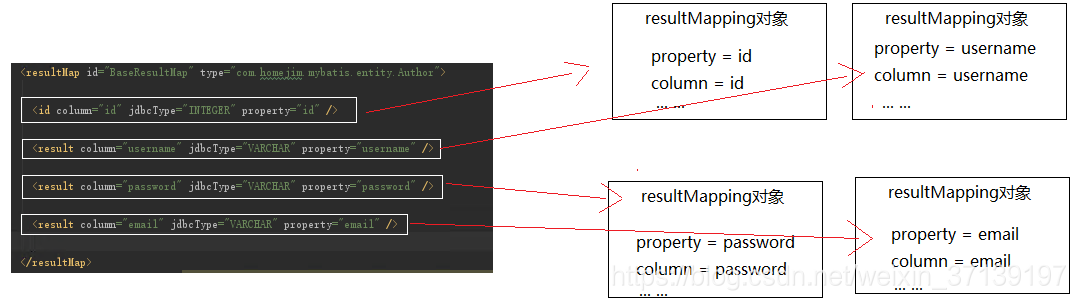
更多详情, 请参考mybatis百科-列映射类ResultMapping
1.2 结果集映射类ResultMap
ResultMap 对应的是结果集 <resultMap>中的一个结果集。 其基本组成部分中, 含有 ResultMapping 对象。
其组成大致如下:
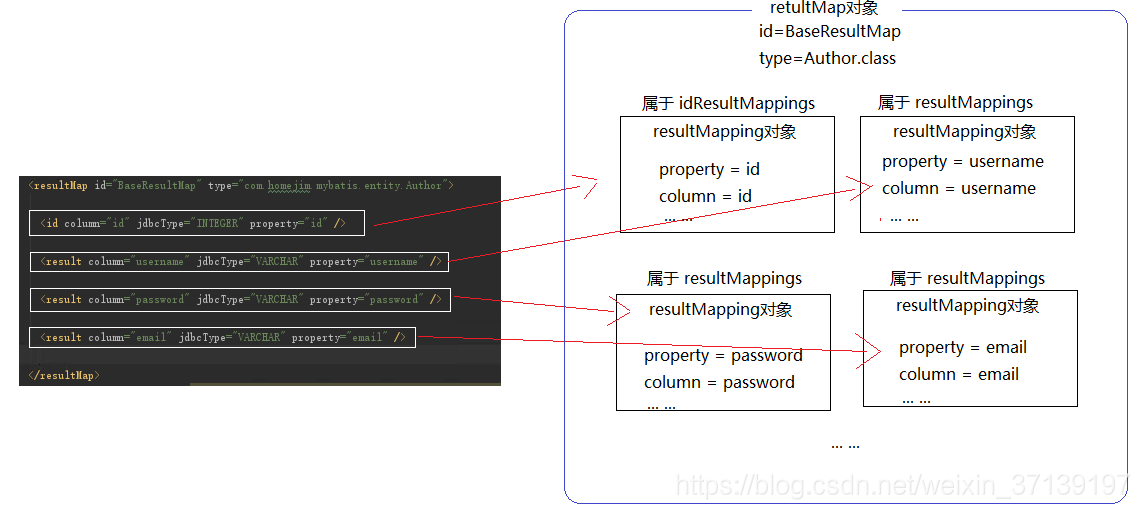
更多详情, 请参考mybatis百科-结果集映射类ResultMap
2. 解析
2.1 入口函数
resultMap 是 mapper.xml 文件下的, 因此其是解析 Mapper 的一个环节。
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
解析<resultMap>, 由于<resultMap>是可以有多个的, 因此, context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap")返回的是一个 List。
private void resultMapElements(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
// 遍历, 解析
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
}
2.2 解析流程
整个过程就是 resultMapElement 这个函数。其流程大体如下

对应的代码
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode) throws Exception {
return resultMapElement(resultMapNode, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList());
}
/**
* 处理 <resultMap> 节点, 将节点解析成 ResultMap 对象, 下面包含有 ResultMapping 对象组成的列表
* @param resultMapNode resultMap 节点
* @param additionalResultMappings 另外的 ResultMapping 列
* @return ResultMap 对象
* @throws Exception
*/
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取 ID , 默认值会拼装所有父节点的 id 或 value 或 property
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取 type 属性, 表示结果集将被映射为 type 指定类型的对象
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 获取 extends 属性, 其表示结果集的继承
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
// 自动映射属性。 将列名自动映射为属性
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 解析 type, 获取其类型
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
Discriminator discriminator = null;
// 记录解析的结果
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// 处理子节点
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
// 处理 constructor 节点
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析构造函数元素,其下的没每一个子节点都会生产一个 ResultMapping 对象
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
// 处理 discriminator 节点
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
// 处理其余节点, 如 id, result, assosation d等
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 创建 resultMapping 对象, 并添加到 resultMappings 中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
// 创建 ResultMapResolver 对象, 该对象可以生成 ResultMap 对象
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 如果无法创建 ResultMap 对象, 则将该结果添加到 incompleteResultMaps 集合中
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
2.3 获取 id
id 对于 resultMap 来说是很重要的, 它是一个身份标识。 具有唯一性
// 获取 ID , 默认值会拼装所有父节点的 id 或 value 或 property。
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id", resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
这里涉及到 XNode 对象中的两个函数
public String getStringAttribute(String name, String def) {
String value = attributes.getProperty(name);
if (value == null) {
return def;
} else {
return value;
}
}
该函数是获取 XNode 对象对应 XML 节点的 name 属性值, 如果该属性不存在, 则返回传入的默认值 def。
而在获取 id 的过程中, 默认值是下面这个函数
/**
* 生成元素节点的基础 id
* @return
*/
public String getValueBasedIdentifier() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
XNode current = this;
// 当前的节点不为空
while (current != null) {
// 如果节点不等于 this, 则在0之前插入 _ 符号, 因为是不断的获取父节点的, 因此是插在前面
if (current != this) {
builder.insert(0, "_");
}
// 获取 id, id不存在则获取value, value不存在则获取 property。
String value = current.getStringAttribute("id",
current.getStringAttribute("value",
current.getStringAttribute("property", null)));
// value 非空, 则将.替换为_, 并将value的值加上 []
if (value != null) {
value = value.replace('.', '_');
builder.insert(0, "]");
builder.insert(0,
value);
builder.insert(0, "[");
}
// 不管 value 是否存在, 前面都添加上节点的名称
builder.insert(0, current.getName());
// 获取父节点
current = current.getParent();
}
return builder.toString();
}
该函数是生成元素节点的id, 如果是这样子的 XML。
<employee id="${id_var}">
<blah something="that"/>
<first_name>Jim</first_name>
<last_name>Smith</last_name>
<birth_date>
<year>1970</year>
<month>6</month>
<day>15</day>
</birth_date>
<height units="ft">5.8</height>
<weight units="lbs">200</weight>
<active>true</active>
</employee>
我们调用
XNode node = parser.evalNode("/employee/height");
node.getValueBasedIdentifier();
则, 返回值应该是
employee[${id_var}]_height
2.4 解析结果集的类型
结果集的类型, 对应的是一个 JavaBean 对象。 通过反射来获得该类型。
// 获取type, type 不存在则获取 ofType, ofType
// 不存在则获取 resultType, resultType 不存在则获取 javaType
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// ... ...
// 获取 type 对应的 Class 对象
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
看源码, 有很多个 def 值, 也就是说, 我们在配置结果集的类型的时候都是有优先级的。 但是, 这里有一个奇怪的地方, 我源代码版本(3.5.0-SNAPSHOT)的 <resultMap> 的属性, 只有 type, 没有 ofType/resultType/javaType。 以下为相应的 DTD 约束:
<!ELEMENT resultMap (constructor?,id*,result*,association*,collection*, discriminator?)>
<!ATTLIST resultMap
id CDATA #REQUIRED
type CDATA #REQUIRED
extends CDATA #IMPLIED
autoMapping (true|false) #IMPLIED
>
我怀疑是兼容以前的版本。
2.5 获取继承结果集和自动映射
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
这个两个属性都是在配置 XML 的时候可有可无的。
2.6 解析 的子节点
先看 DTD 约束
<!ELEMENT resultMap (constructor?,id*,result*,association*,collection*, discriminator?)>
可以有以下几个子节点:
| 子节点 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| constructor | 出现 0 次或 1 次 |
| id | 出现 0 次或 多 次 |
| result | 出现 0 次或 多 次 |
| association | 出现 0 次或 多 次 |
| collection | 出现 0 次或 多 次 |
| discriminator | 出现 0次或 1 次 |
子节点解析过程很简单
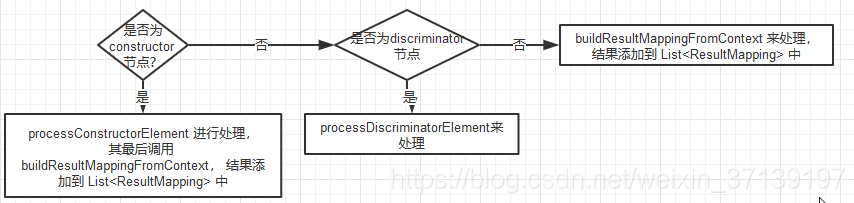
根据类型进行解析, 最后获得 resultMappings (List),有可能会获得 discriminator(Discriminator)。
// 创建一个 resultMappings 的链表
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// 将从其他地方传入的additionalResultMappings添加到该链表中
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// 获取子节点
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
// 遍历解析子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析构造函数元素,其下的没每一个子节点都会生产一个 ResultMapping 对象
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析 discriminator 节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
// 解析其余的节点
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
除了 discriminator 节点, 其余节点最后都会回到 buildResultMappingFromContext 方法上, 该方法是创建 ResultMapping 对象。
/**
* 获取一行, 如result等, 取得他们所有的属性, 通过这些属性建立 ResultMapping 对象
* @param context 对于节点本身
* @param resultType resultMap 的结果类型
* @param flags flag 属性, 对应 ResultFlag 枚举中的属性。 一般情况下为空
* @return 返回 ResultMapping
* @throws Exception
*/
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
// 获取节点的属性, 如果节点是构造函数(只有name属性, 没有property),
// 则获取的是 name, 否则获取 property
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
// 获取嵌套的结果集
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap",
processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList()));
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
// 以上获取各个属性节点
// 解析 javaType, typeHandler, jdbcType
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 创建resultMapping对象
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}
如果是 discriminator, 则处理该元素并创建鉴别器。
/**
* 处理鉴别器
* @param context 节点
* @param resultType 结果类型
* @param resultMappings 列结果集合
* @return 鉴别器
* @throws Exception
*/
private Discriminator processDiscriminatorElement(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
// 先获取各个属性
// 取得 javaType 对应的类型
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
// 取得 typeHandler 对应的类型
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
// 取得 jdbcType 对应的类型
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 创建 discriminatorMap, 并遍历子节点, 以 value->resultMap 的方式放入discriminatorMap中
Map<String, String> discriminatorMap = new HashMap<>();
for (XNode caseChild : context.getChildren()) {
String value = caseChild.getStringAttribute("value");
String resultMap = caseChild.getStringAttribute("resultMap", processNestedResultMappings(caseChild, resultMappings));
discriminatorMap.put(value, resultMap);
}
// 创建鉴别器
return builderAssistant.buildDiscriminator(resultType, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, typeHandlerClass, discriminatorMap);
}
鉴别器内部, 也是含有 ResultMapping 的
public class Discriminator {
private ResultMapping resultMapping;
private Map<String, String> discriminatorMap;
......
}
2.7 创建 ResultMap 对象
在解析完 <resultMap> 的各个属性和子节点之后。 创建 ResultMapResolver 对象, 通过对象可以生成 ResultMap。
/**
* 创建并添加 ResultMap 到 Configuration 对象中
* @param id id, 配置了 id 可以提高效率
* @param type 类型
* @param extend 继承
* @param discriminator 鉴别器
* @param resultMappings 列集
* @param autoMapping 是否自动映射
* @return 返回创建的 ResultMap 对象
*/
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
if (extend != null) {
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
// 从 configuration 中获取继承的结果集
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
// 获取所集成结果集的所有 ResultMapping 集合
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 移除需要覆盖的 ResultMapping 集合
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// 如果该 resultMap 中定义了构造节点, 则移除其父节点的构造器
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
Iterator<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappingsIter = extendedResultMappings.iterator();
while (extendedResultMappingsIter.hasNext()) {
if (extendedResultMappingsIter.next().getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
extendedResultMappingsIter.remove();
}
}
}
// 添加需要被继承的 ResultMapping 集合
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 通过建造者模式创建 ResultMap 对象
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
// 添加到 Configuration 对象中
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}
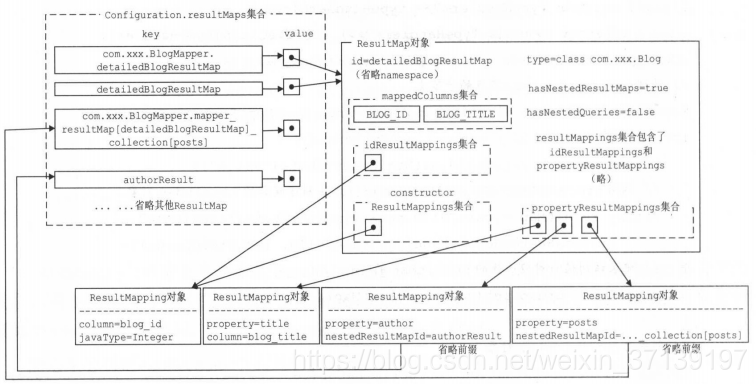
3 解析结果
有如下的数据库表
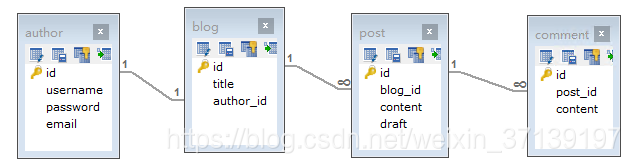
通过代码生成器生成 XML 和 Mapper。
添加结果集

对应的 sql

则最后解析出的结果
4 一起来学习 mybatis
你想不想来学习 mybatis? 学习其使用和源码呢?那么, 在博客园关注我吧!!
我自己打算把这个源码系列更新完毕, 同时会更新相应的注释。快去 star 吧!!
mybatis源码-原来resultMap解析完是这样的更多相关文章
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 配置文件解析过程
* 本文速览 由于本篇文章篇幅比较大,所以这里拿出一节对本文进行快速概括.本篇文章对 MyBatis 配置文件中常用配置的解析过程进行了较为详细的介绍和分析,包括但不限于settings,typeAl ...
- MyBatis源码 核心配置解析 properties元素
XMLConfigBuilder的parseConfiguration(XNode)方法,用于解析配置文件 XMLConfigBuilder的propertiesElement(XNode)方法,用于 ...
- Spring mybatis源码篇章-XMLLanguageDriver解析sql包装为SqlSource
前言:通过阅读源码对实现机制进行了解有利于陶冶情操,承接前文Spring mybatis源码篇章-MybatisDAO文件解析(二) 首先了解下sql mapper的动态sql语法 具体的动态sql的 ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 映射文件解析过程
1.简介 在上一篇文章中,我详细分析了 MyBatis 配置文件的解析过程.由于上一篇文章的篇幅比较大,加之映射文件解析过程也比较复杂的原因.所以我将映射文件解析过程的分析内容从上一篇文章中抽取出来, ...
- Mybatis源码解析-BoundSql
mybatis作为持久层,其操作数据库离不开sql语句.而BoundSql则是其保存Sql语句的对象 前提 针对mybatis的配置文件的节点解析,比如where/if/trim的节点解析可见文章Sp ...
- MyBatis 源码分析系列文章导读
1.本文速览 本篇文章是我为接下来的 MyBatis 源码分析系列文章写的一个导读文章.本篇文章从 MyBatis 是什么(what),为什么要使用(why),以及如何使用(how)等三个角度进行了说 ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 插件机制
1.简介 一般情况下,开源框架都会提供插件或其他形式的拓展点,供开发者自行拓展.这样的好处是显而易见的,一是增加了框架的灵活性.二是开发者可以结合实际需求,对框架进行拓展,使其能够更好的工作.以 My ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 缓存原理
1.简介 在 Web 应用中,缓存是必不可少的组件.通常我们都会用 Redis 或 memcached 等缓存中间件,拦截大量奔向数据库的请求,减轻数据库压力.作为一个重要的组件,MyBatis 自然 ...
- MyBatis 源码分析 - 内置数据源
1.简介 本篇文章将向大家介绍 MyBatis 内置数据源的实现逻辑.搞懂这些数据源的实现,可使大家对数据源有更深入的认识.同时在配置这些数据源时,也会更清楚每种属性的意义和用途.因此,如果大家想知其 ...
随机推荐
- git 入门教程之协同开发
前面我们已经介绍过远程仓库的相关概念,不过那时并没有深入探讨,只是讲解了如何创建远程仓库以及推送最新工作成果到远程仓库,实际上远程仓库对于团队协同开发很重要,不仅仅是团队协同开发的基础,也是代码备份的 ...
- CSS之精灵图(雪碧图)与字体图标
本文内容: 精灵图 字体图标 首发日期:2018-05-01 精灵图: 在以前,每个图片资源都是独立的一张张图片,浏览器访问网站中的不同网页时是重复获取这一张张图片的,这代表需要访问很多次资源. 为了 ...
- 洗礼灵魂,修炼python(69)--爬虫篇—番外篇之feedparser模块
feedparser模块 1.简介 feedparser是一个Python的Feed解析库,可以处理RSS ,CDF,Atom .使用它我们可从任何 RSS 或 Atom 订阅源得到标题.链接和文章的 ...
- SQL Server DATA文件夹下audittrace20180124152845_52.trc类文件异常增多
同事告知某现场SQL Server2008R2数据库的DATA文件夹下audittrace开头的trc文件不断增多,占用较大空间,因此需要关停,尝试解决步骤如下: 1.查看是否有后台开启的trace ...
- February 17th, 2018 Week 7th Saturday
The happiest part of a man's life is what he passes lying awake in bed in the morning. 人生一大乐事莫过去早上醒来 ...
- 【工具大道】使用SSH远程登录Mac 电脑
本文地址 一.打开ssh Mac Terminal是自带SSH的,可以用whereis来看看: $ whereis ssh 但是在现有进程中找不到ssh对应的进程: $ ps aux | grep s ...
- ubuntu 安装 GCC 和 G++ C++ 开发环境
1.先安装 :sudo apt-get install build-essential 2.查看 gcc 版本 然后安装 统一版本的 g++ gcc --version gcc (Ubuntu/Lin ...
- 转 jQuery中的$.extend方法来扩展JSON对象
$.extend方法可以扩展JSON对象,用一个或多个其他对象来扩展一个对象,返回被扩展的对象. 例一 合并 settings 和 options,修改并返回 settings var setting ...
- 关于IDE的选择
以往忘了看到谁说的,说开发.NET就用VS,开发JS就用webStorm,开发java没钱用Eclipse,有钱用IDEA
- UVA12558-Efyptian Fractions(HARD version)(迭代加深搜索)
Problem UVA12558-Efyptian Fractions(HARD version) Accept:187 Submit:3183 Time Limit: 3000 mSec Pro ...
