.net core 2.0的认证和授权
在asp.net core中,微软提供了基于认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)的方式,来实现权限管理的,本篇博文,介绍基于固定角色的权限管理和自定义角色权限管理,本文内容,更适合传统行业的BS应用,而非互联网应用。 在asp.net core中,我们认证(Authentication)通常是在Login的Post Action中进行用户名或密码来验证用户是否正确,如果通过验证,即该用户就会获得一个或几个特定的角色,通过ClaimTypes.Role来存储角色,从而当一个请求到达时,用这个角色和Controller或Action上加的特性 [Authorize(Roles = "admin,system")]来授权是否有权访问该Action。本文中的自定义角色,会把验证放在中间件中进行处理。 一、固定角色: 即把角色与具体的Controller或Action直接关联起来,整个系统中的角色是固定的,每种角色可以访问那些Controller或Action也是固定的,这做法比较适合小型项目,角色分工非常明确的项目。 项目代码: https://github.com/axzxs2001/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/tree/master/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86/RolePrivilegeManagement 始于startup.cs 需要在ConfigureServices中注入Cookie的相关信息,options是CookieAuthenticationOptions,关于这个类型提供如下属性,可参考:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/authentication/cookie?tabs=aspnetcore2x 它提供了登录的一些信息,或登录生成Cookie的一些信息,用以后 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
//添加认证Cookie信息
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(options =>
{
options.LoginPath = new PathString("/login");
options.AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/denied");
});
} public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseBrowserLink();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
//验证中间件
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
} HomeController.cs 对于Login Get的Action,把returnUrl用户想要访问的地址(有可能用户记录下想要访问的url了,但系统会转到登录页,登录成功后直接跳转到想要访问的returnUrl页) 对于Login Post的Action,验证用户密和密码,成功能,定义一个ClaimsIdentity,把用户名和角色,和用户姓名的声明都添回进来(这个角色,就是用来验证可访问action的角色 )作来该用户标识,接下来调用HttpContext.SignInAsync进行登录,注意此方法的第一个参数,必需与StartUp.cs中services.AddAuthentication的参数相同,AddAuthentication是设置登录,SigninAsync是按设置参数进行登录 对于Logout Get的Action,是退出登录 HomeController上的[Authorize(Roles=”admin,system”)]角色和权限的关系时,所有Action只有admin和system两个角色能访问到,About上的[Authorize(Roles=”admin”)]声明这个action只能admin角色访问,Contact上的[Authorize(Roles=”system”)]声明这个action只能system角色访问,如果action上声明的是[AllowAnomymous],说明不受授权管理,可以直接访问。 using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using RolePrivilegeManagement.Models;
using System.Security.Claims;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization; namespace RolePrivilegeManagement.Controllers
{
[Authorize(Roles = "admin,system")]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize(Roles = "admin")]
public IActionResult About()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Your application description page.";
return View();
}
[Authorize(Roles = "system")]
public IActionResult Contact()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Your contact page.";
return View();
}
public IActionResult Error()
{
return View(new ErrorViewModel { RequestId = Activity.Current?.Id ?? HttpContext.TraceIdentifier });
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet("login")]
public IActionResult Login(string returnUrl = null)
{
TempData["returnUrl"] = returnUrl;
return View();
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpPost("login")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(string userName, string password, string returnUrl = null)
{
var list = new List<dynamic> {
new { UserName = "gsw", Password = "", Role = "admin" },
new { UserName = "aaa", Password = "", Role = "system" }
};
var user = list.SingleOrDefault(s => s.UserName == userName && s.Password == password);
if (user!=null)
{
//用户标识
var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Sid, userName));
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Name));
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, user.Role));
await HttpContext.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, new ClaimsPrincipal(identity));
if (returnUrl == null)
{
returnUrl = TempData["returnUrl"]?.ToString();
}
if (returnUrl != null)
{
return Redirect(returnUrl);
}
else
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home");
}
}
else
{
const string badUserNameOrPasswordMessage = "用户名或密码错误!";
return BadRequest(badUserNameOrPasswordMessage);
}
}
[HttpGet("logout")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Logout()
{
await HttpContext.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet("denied")]
public IActionResult Denied()
{
return View();
}
}
} 前端_Layout.cshtml布局页,在登录成功后的任何页面都可以用@User.Identity.Name就可以获取用户姓名,同时用@User.Claims.SingleOrDefault(s=>s.Type== System.Security.Claims.ClaimTypes.Sid).Value可以获取用户名或角色。 <nav class="navbar navbar-inverse navbar-fixed-top">
<div class="container">
<div class="navbar-header">
<button type="button" class="navbar-toggle" data-toggle="collapse" data-target=".navbar-collapse">
<span class="sr-only">Toggle navigation</span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
<a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index" class="navbar-brand">RolePrivilegeManagement</a>
</div>
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Home</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="About">About</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Contact">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
<ul class="" style="float:right; margin:0;">
<li style="overflow:hidden;">
<div style="float:left;line-height:50px;margin-right:10px;">
<span style="color:#ffffff">当前用户:@User.Identity.Name</span>
</div>
<div style="float:left;line-height:50px;">
<a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Logout">注销</a>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
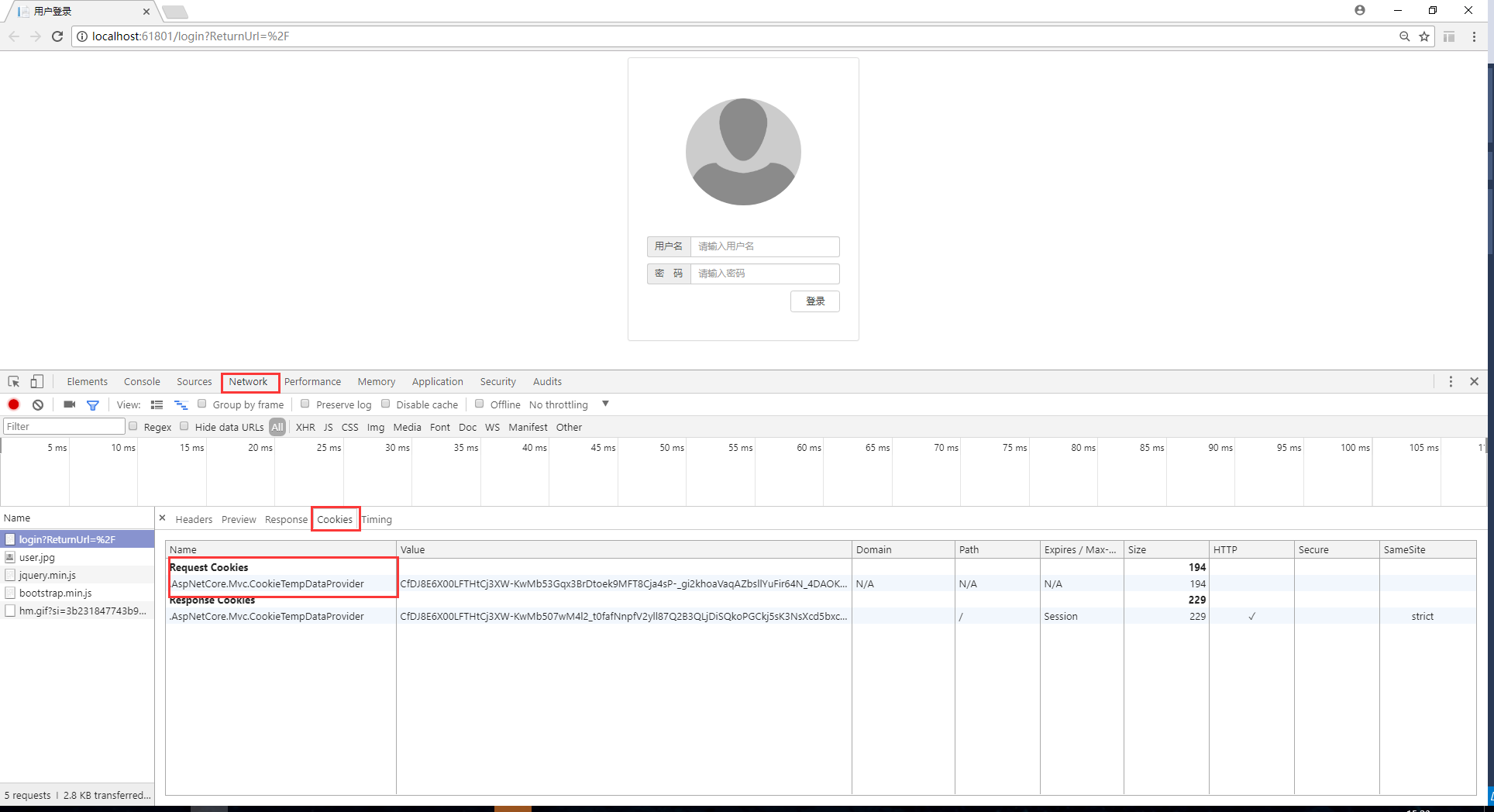
</nav> 现在可以用chrome运行了,进行登录页后F12,查看Network—Cookies,可以看到有一个Cookie,这个是记录returnUrl的Cookie,是否记得HomeController.cs中的Login Get的Action中代码:TempData["returnUrl"] = returnUrl;这个TempData最后转成了一个Cookie返回到客户端了,如下图:
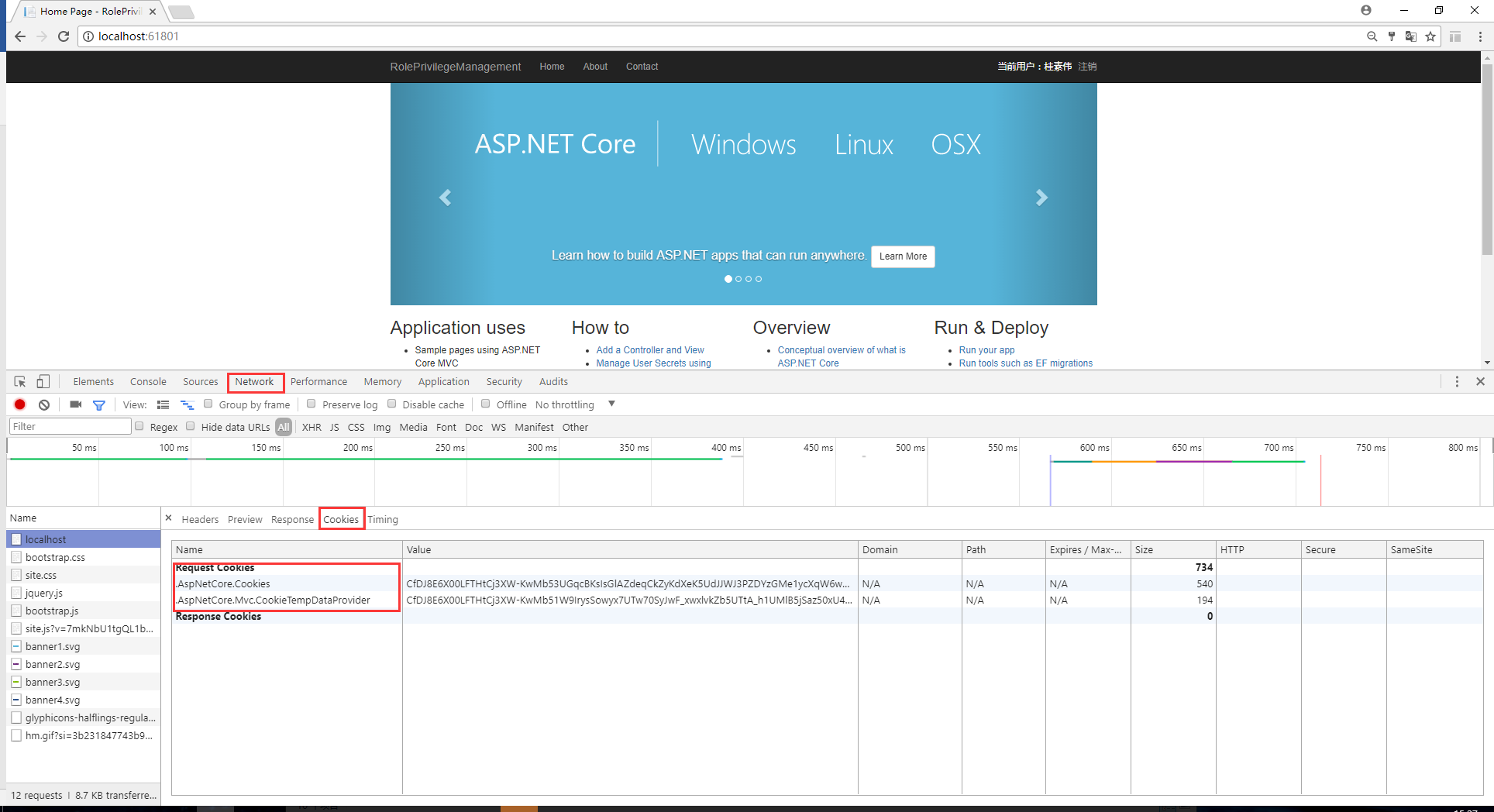
输入用户名,密码登录,再次查看Cookies,发现多了一个.AspNetCore.Cookies,即把用户验证信息加密码保存在了这个Cookie中,当跳转到别的页面时,这两个Cookie会继续在客户端和服务传送,用以验证用户角色。
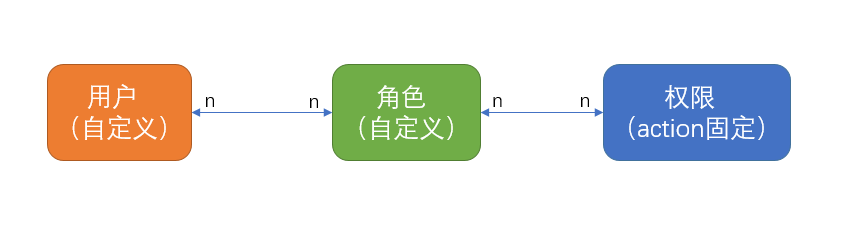
二、自定义角色 系统的角色可以自定义,用户是自写到义,权限是固定的,角色对应权限可以自定义,用户对应角色也是自定义的,如下图:
项目代码: https://github.com/axzxs2001/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/tree/master/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86/PrivilegeManagement 始于startup.cs 自定义角色与固定角色不同之处在于多了一个中间件(关于中间件学习参看:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/middleware),即在Configure方法中,一定要在app.UseAuthentication下面添加验证权限的中间件,因为UseAuthentication要从Cookie中加载通过验证的用户信息到Context.User中,所以一定放在加载完后才能去验用户信息(当然自己读取Cookie也可以)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using PrivilegeManagement.Middleware; namespace PrivilegeManagement
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(options =>
{
options.LoginPath = new PathString("/login");
options.AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/denied");
}
);
services.AddMvc();
} public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseBrowserLink();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
} app.UseStaticFiles();
//验证中间件
app.UseAuthentication();
////添加权限中间件, 一定要放在app.UseAuthentication后
app.UsePermission(new PermissionMiddlewareOption()
{
LoginAction = @"/login",
NoPermissionAction = @"/denied",
//这个集合从数据库中查出所有用户的全部权限
UserPerssions = new List<UserPermission>()
{
new UserPermission { Url="/", UserName="gsw"},
new UserPermission { Url="/home/contact", UserName="gsw"},
new UserPermission { Url="/home/about", UserName="aaa"},
new UserPermission { Url="/", UserName="aaa"}
}
});
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
} 下面看看中间件PermissionMiddleware.cs,在Invoke中用了context.User,如上面所述,首先要调用app.UseAuthentication加载用户信息后才能在这里使用,这个中间件逻辑较简单,如果没有验证的一律放过去,不作处理,如果验证过(登录成功了),就要查看本次请求的url和这个用户可以访问的权限是否匹配,如不匹配,就跳转到拒绝页面(这个是在Startup.cs中添加中间件时,用NoPermissionAction = @"/denied"设置的) using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace PrivilegeManagement.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 权限中间件
/// </summary>
public class PermissionMiddleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 管道代理对象
/// </summary>
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
/// <summary>
/// 权限中间件的配置选项
/// </summary>
private readonly PermissionMiddlewareOption _option; /// <summary>
/// 用户权限集合
/// </summary>
internal static List<UserPermission> _userPermissions; /// <summary>
/// 权限中间件构造
/// </summary>
/// <param name="next">管道代理对象</param>
/// <param name="permissionResitory">权限仓储对象</param>
/// <param name="option">权限中间件配置选项</param>
public PermissionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, PermissionMiddlewareOption option)
{
_option = option;
_next = next;
_userPermissions = option.UserPerssions;
}
/// <summary>
/// 调用管道
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context">请求上下文</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
//请求Url
var questUrl = context.Request.Path.Value.ToLower(); //是否经过验证
var isAuthenticated = context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated;
if (isAuthenticated)
{
if (_userPermissions.GroupBy(g=>g.Url).Where(w => w.Key.ToLower() == questUrl).Count() > )
{
//用户名
var userName = context.User.Claims.SingleOrDefault(s => s.Type == ClaimTypes.Sid).Value;
if (_userPermissions.Where(w => w.UserName == userName&&w.Url.ToLower()==questUrl).Count() > )
{
return this._next(context);
}
else
{
//无权限跳转到拒绝页面
context.Response.Redirect(_option.NoPermissionAction);
}
}
}
return this._next(context);
}
}
} 扩展中间件类PermissionMiddlewareExtensions.cs using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace PrivilegeManagement.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 扩展权限中间件
/// </summary>
public static class PermissionMiddlewareExtensions
{
/// <summary>
/// 引入权限中间件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="builder">扩展类型</param>
/// <param name="option">权限中间件配置选项</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static IApplicationBuilder UsePermission(
this IApplicationBuilder builder, PermissionMiddlewareOption option)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<PermissionMiddleware>(option);
}
}
} 中间件属性PermissionMiddlewareOption.cs using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace PrivilegeManagement.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 权限中间件选项
/// </summary>
public class PermissionMiddlewareOption
{
/// <summary>
/// 登录action
/// </summary>
public string LoginAction
{ get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 无权限导航action
/// </summary>
public string NoPermissionAction
{ get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 用户权限集合
/// </summary>
public List<UserPermission> UserPerssions
{ get; set; } = new List<UserPermission>();
}
} 中间件实体类UserPermission.cs using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace PrivilegeManagement.Middleware
{
/// <summary>
/// 用户权限
/// </summary>
public class UserPermission
{
/// <summary>
/// 用户名
/// </summary>
public string UserName
{ get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 请求Url
/// </summary>
public string Url
{ get; set; }
}
} 关于自定义角色,因为不需要授权时带上角色,所以可以定义一个基Controller类BaseController.cs,其他的Controller都继承BaseController,这样所有的action都可以通过中间件来验证,当然像登录,无权限提示页面还是在Action上加[AllowAnomymous] using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace PrivilegeManagement.Controllers
{
[Authorize]
public class BaseController:Controller
{
}
} HomeController.cs如下,与固定角色的HomeController.cs差异只在Controller和Action上的Authorize特性。 using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using PrivilegeManagement.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using System.Security.Claims;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication; namespace PrivilegeManagement.Controllers
{ public class HomeController : BaseController
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
} public IActionResult About()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Your application description page."; return View();
} public IActionResult Contact()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Your contact page."; return View();
} public IActionResult Error()
{
return View(new ErrorViewModel { RequestId = Activity.Current?.Id ?? HttpContext.TraceIdentifier });
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpGet("login")]
public IActionResult Login(string returnUrl = null)
{
TempData["returnUrl"] = returnUrl;
return View();
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpPost("login")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Login(string userName,string password, string returnUrl = null)
{
var list = new List<dynamic> {
new { UserName = "gsw", Password = "", Role = "admin",Name="桂素伟" },
new { UserName = "aaa", Password = "", Role = "system",Name="测试A" }
};
var user = list.SingleOrDefault(s => s.UserName == userName && s.Password == password);
if (user != null)
{
//用户标识
var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Sid, userName));
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Name));
identity.AddClaim(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, user.Role)); await HttpContext.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, new ClaimsPrincipal(identity));
if (returnUrl == null)
{
returnUrl = TempData["returnUrl"]?.ToString();
}
if (returnUrl != null)
{
return Redirect(returnUrl);
}
else
{
return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home");
}
}
else
{
const string badUserNameOrPasswordMessage = "用户名或密码错误!";
return BadRequest(badUserNameOrPasswordMessage);
}
}
[HttpGet("logout")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Logout()
{
await HttpContext.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home");
}
[HttpGet("denied")]
public IActionResult Denied()
{
return View();
}
}
} 全部代码:https://github.com/axzxs2001/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/tree/master/Asp.NetCoreExperiment/%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/axzxs2001/p/7482771.html
.net core 2.0的认证和授权的更多相关文章
- asp.net core 2.0的认证和授权
在asp.net core中,微软提供了基于认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)的方式,来实现权限管理的,本篇博文,介绍基于固定角色的权限管理和自定义角色权限管理, ...
- 【转载】asp.net core 2.0的认证和授权
在asp.net core中,微软提供了基于认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)的方式,来实现权限管理的,本篇博文,介绍基于固定角色的权限管理和自定义角色权限管理, ...
- 如何使用Swagger为.NET Core 3.0应用添加JWT授权说明文档
简介 本教程采用WHY-WHAT-HOW黄金圈思维模式编写,黄金圈法则强调的是从WHY为什么学,到WHAT学到什么,再到HOW如何学.从模糊到清晰的学习模式.大家的时间都很宝贵,我们做事前先想清楚为什 ...
- Asp.net Core 系列之--5.认证、授权与自定义权限的实现
ChuanGoing 2019-11-24 asp.net core系列已经来到了第五篇,通过之前的基础介绍,我们了解了事件订阅/发布的eventbus整个流程,初探dapper ORM实现,并且简单 ...
- asp.net core 3.0 身份认证 替换为自已的提供程序 AuthenticationStateProvider replace to SelfAuthenticationStateProvider
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // 添加身份验证服务 services.AddAuthorizationCo ...
- .net core 1.0 Web MVC 自定义认证过程
通过官方的介绍可知,若要本地开始部署搭建一个基于.net core 1.0的Web应用,需要下载dotnet SDK,或在Visual Studio IDE之上安装相关插件以布置开发环境.为了使开发环 ...
- 聊聊 asp.net core 认证和授权
使用asp.net core 开发应用系统过程中,基本上都会涉及到用户身份的认证,及授权访问控制,因此了解认证和授权流程也相当重要,下面通过分析asp.net core 框架中的认证和授权的源码来分析 ...
- .Net Core Cookie-Based认证与授权
.Net Core的其中一种认证与授权模式是基于Cookie的,首先我们先创建一个.Net Core MVC 项目: 然后增加对页面访问的权限控制,对要访问的页面Conytroller增加Author ...
- 【翻译】asp.net core2.1认证和授权解密
asp.net core2.1认证和授权解密 本篇文章翻译自:https://digitalmccullough.com/posts/aspnetcore-auth-system-demystifie ...
随机推荐
- find、locate、whereis、which和type
1. find $ find . -name '*' 2. locate 很快速的搜寻档案系统内是否有指定的档案,比find要快很多 其方法是先建立一个包括系统内所有档案名称及路径的资料库,之后当寻找 ...
- (原)Ubuntu安装TensorRT
转载请注明出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/11129472.html 参考网址: https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplear ...
- Shell 编程 until语句
本篇主要写一些shell脚本until语句的使用. 计算1-50的和 #!/bin/bash i=0 s=0 until [ $i -eq 51 ];do let s+=i;let i++ done ...
- intellij idea 2019 右键包新建文件是没有java Class选项
今天要测试一个技术点于是新建了一个springboot工程, 在新建文件的时候发现右键后java class文件选项不见了. 以前真的没有碰到这种问题, 感觉很是意外于是百度Google后找到了解决办 ...
- Flask 中字典数据返回(jsonify)
不多说,直接上代码,flask中的字典数据的处理: from flask import Flask, jsonify app = Flask(__name__, static_folder=" ...
- JDK8 Steam流操作
原文:https://github.com/niumoo/jdk-feature/blob/master/src/main/java/net/codingme/feature/jdk8/Jdk8Str ...
- 用 Splashtop Wired XDisplay HD 让 ipad做电脑扩展屏幕__亲测有效
参考: [1]https://blog.csdn.net/Tang_Chuanlin/article/details/86433152
- 【转】Pandas学习笔记(三)修改&添加值
Pandas学习笔记系列: Pandas学习笔记(一)基本介绍 Pandas学习笔记(二)选择数据 Pandas学习笔记(三)修改&添加值 Pandas学习笔记(四)处理丢失值 Pandas学 ...
- 从websocket协议出发,了解应用层协议,传输层协议,网络的7层协议
其他关联连接 :TCP的三次握手(建立连接)和四次挥手(关闭连接) 1.websocket是全双工,不同于传统半双工通信 传统的Web应用中,浏览器与服务器交互都是半双工通信(但并不完全是半双工通信, ...
- Debian9下安装Python3 pip
Debian9下安装Python3 pip 使用apt-get安装Python3-pip包 apt-get install python3-pip