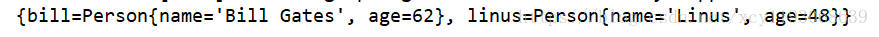Spring @Conditional注解 详细讲解及示例
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/xcy1193068639/article/details/81491071 </div>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/ck_htmledit_views-f57960eb32.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/ck_htmledit_views-f57960eb32.css">
<div class="htmledit_views" id="content_views">
<h2><a name="t0"></a>前言:</h2>
@Conditional是Spring4新提供的注解,它的作用是按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册bean。
@Conditional的定义:
-
//此注解可以标注在类和方法上
-
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
-
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
-
@Documented
-
public @interface Conditional {
-
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
-
}
从代码中可以看到,需要传入一个Class数组,并且需要继承Condition接口:
-
public interface Condition {
-
boolean matches(ConditionContext var1, AnnotatedTypeMetadata var2);
-
}
Condition是个接口,需要实现matches方法,返回true则注入bean,false则不注入。
示例:
首先,创建Person类:
-
public class Person {
-
-
private String name;
-
private Integer age;
-
-
public String getName() {
-
return name;
-
}
-
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
this.name = name;
-
}
-
-
public Integer getAge() {
-
return age;
-
}
-
-
public void setAge(Integer age) {
-
this.age = age;
-
}
-
-
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
-
this.name = name;
-
this.age = age;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public String toString() {
-
return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
-
}
-
}
创建BeanConfig类,用于配置两个Person实例并注入,一个是比尔盖茨,一个是林纳斯。
-
@Configuration
-
public class BeanConfig {
-
-
@Bean(name = "bill")
-
public Person person1(){
-
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
-
}
-
-
@Bean("linus")
-
public Person person2(){
-
return new Person("Linus",48);
-
}
-
}
接着写一个测试类进行验证这两个Bean是否注入成功。
-
public class ConditionalTest {
-
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
-
-
@Test
-
public void test1(){
-
Map<String, Person> map = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
-
System.out.println(map);
-
}
-
}
运行,输出结果是这样的,两个Person实例被注入进容器。
这是一个简单的例子,现在问题来了,如果我想根据当前操作系统来注入Person实例,windows下注入bill,linux下注入linus,怎么实现呢?
这就需要我们用到@Conditional注解了,前言中提到,需要实现Condition接口,并重写方法来自定义match规则。
首先,创建一个WindowsCondition类:
-
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
-
-
/**
-
* @param conditionContext:判断条件能使用的上下文环境
-
* @param annotatedTypeMetadata:注解所在位置的注释信息
-
* */
-
@Override
-
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
-
//获取ioc使用的beanFactory
-
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = conditionContext.getBeanFactory();
-
//获取类加载器
-
ClassLoader classLoader = conditionContext.getClassLoader();
-
//获取当前环境信息
-
Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();
-
//获取bean定义的注册类
-
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = conditionContext.getRegistry();
-
-
//获得当前系统名
-
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
-
//包含Windows则说明是windows系统,返回true
-
if (property.contains("Windows")){
-
return true;
-
}
-
return false;
-
}
-
}
matches方法的两个参数的意思在注释中讲述了,值得一提的是,conditionContext提供了多种方法,方便获取各种信息,也是SpringBoot中 @ConditonalOnXX注解多样扩展的基础。
接着,创建LinuxCondition类:
-
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
-
-
@Override
-
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
-
-
Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();
-
-
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
-
if (property.contains("Linux")){
-
return true;
-
}
-
return false;
-
}
-
}
接着就是使用这两个类了,因为此注解可以标注在方法上和类上,所以分开测试:
标注在方法上:
修改BeanConfig:
-
@Configuration
-
public class BeanConfig {
-
-
//只有一个类时,大括号可以省略
-
//如果WindowsCondition的实现方法返回true,则注入这个bean
-
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})
-
@Bean(name = "bill")
-
public Person person1(){
-
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
-
}
-
-
//如果LinuxCondition的实现方法返回true,则注入这个bean
-
@Conditional({LinuxCondition.class})
-
@Bean("linus")
-
public Person person2(){
-
return new Person("Linus",48);
-
}
-
}
修改测试方法,使其可以打印当前系统名:
-
@Test
-
public void test1(){
-
String osName = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
-
System.out.println("当前系统为:" + osName);
-
Map<String, Person> map = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
-
System.out.println(map);
-
}
运行结果如下:
我是运行在windows上的所以只注入了bill,嗯,没毛病。
接着实验linux下的情况,不能运行在linux下,但可以修改运行时参数:
修改后启动测试方法:
一个方法只能注入一个bean实例,所以@Conditional标注在方法上只能控制一个bean实例是否注入。
标注在类上:
一个类中可以注入很多实例,@Conditional标注在类上就决定了一批bean是否注入。
我们试一下,将BeanConfig改写,这时,如果WindowsCondition返回true,则两个Person实例将被注入(注意:上一个测试将os.name改为linux,这是我将把这个参数去掉):
-
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})
-
@Configuration
-
public class BeanConfig {
-
-
@Bean(name = "bill")
-
public Person person1(){
-
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
-
}
-
-
@Bean("linus")
-
public Person person2(){
-
return new Person("Linus",48);
-
}
-
}
结果两个实例都被注入:
如果将类上的WindowsCondition.class改为LinuxCondition.class,结果应该可以猜到:
结果就是空的,类中所有bean都没有注入。
多个条件类:
前言中说,@Conditional注解传入的是一个Class数组,存在多种条件类的情况。
这种情况貌似判断难度加深了,测试一波,新增新的条件类,实现的matches返回false(这种写死返回false的方法纯属测试用,没有实际意义O(∩_∩)O)
-
public class ObstinateCondition implements Condition {
-
-
@Override
-
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
-
return false;
-
}
-
}
BeanConfig修改一下:
-
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class,ObstinateCondition.class})
-
@Configuration
-
public class BeanConfig {
-
-
@Bean(name = "bill")
-
public Person person1(){
-
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
-
}
-
-
@Bean("linus")
-
public Person person2(){
-
return new Person("Linus",48);
-
}
-
}
结果:
现在如果将ObstinateCondition的matches方法返回值改成true,两个bean就被注入进容器:
结论得:
第一个条件类实现的方法返回true,第二个返回false,则结果false,不注入进容器。
第一个条件类实现的方法返回true,第二个返回true,则结果true,注入进容器中。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xcy1193068639/article/details/81491071
Spring @Conditional注解 详细讲解及示例的更多相关文章
- Spring Conditional注解使用小结
今天我们来总结下Conditional注解的使用. Conditional注解 增加配置类Config package condition; import org.springframework.co ...
- Spring @Conditional注解的使用
Spring Boot的强大之处在于使用了Spring 4框架的新特性:@Conditional注释,此注释使得只有在特定条件满足时才启用一些配置. 下面来介绍如何使用Condition 首先写一个类 ...
- Spring和SpringMvc详细讲解
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/doudouxiaoye/p/5693399.html 1. 为什么使用Spring ? 1). 方便解耦,简化开发 通过Spring提供的Io ...
- Spring常用注解(讲解的通俗易懂,很透彻)
使用注解来构造IoC容器 用注解来向Spring容器注册Bean.需要在applicationContext.xml中注册<context:component-scan base-package ...
- RabbitMQ与java、Spring结合实例详细讲解(转)
林炳文Evankaka原创作品.转载请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/evankaka 摘要:本文介绍了rabbitMq,提供了如何在Ubuntu下安装RabbitMQ 服务的方法. ...
- RabbitMQ与java、Spring结合实例详细讲解
林炳文Evankaka原创作品.转载请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/evankaka 摘要:本文介绍了rabbitMq,提供了如何在Ubuntu下安装RabbitMQ 服务的方法. ...
- Javascript正则表达式详细讲解和示例,通俗易懂
正则表达式可以: •测试字符串的某个模式.例如,可以对一个输入字符串进行测试,看在该字符串是否存在一个电话号码模式或一个信用卡号码模式.这称为数据有效性验证 •替换文本.可以在文档中使用一个正则表达式 ...
- 一文了解@Conditional注解说明和使用
@Conditional:Spring4.0 介绍了一个新的注解@Conditional,它的逻辑语义可以作为"If-then-else-"来对bean的注册起作用. @Con ...
- Spring @Conditional简单使用 以及 使用时注意事项一点
@Conditional注解在类的方法中 @Conditional注解失效的一种原因 @Conditional注解在类上 手写的低配版@ConditionalOnClass Spring @Cond ...
随机推荐
- 二分图判定+点染色/并查集 BestCoder Round #48 ($) 1002 wyh2000 and pupil
题目传送门 /* 二分图判定+点染色:因为有很多联通块,要对所有点二分图匹配,若不能,存在点是无法分配的,no 每一次二分图匹配时,将点多的集合加大最后第一个集合去 注意:n <= 1,no,两 ...
- ACM_错排(递推dp)
RPG的错排 Time Limit: 2000/1000ms (Java/Others) Problem Description: 今年暑假GOJ集训队第一次组成女生队,其中有一队叫RPG,但做为集训 ...
- spring简介及常用术语
1.引入 在开发应用时常会遇到如下问题: 1)代码耦合性高: 2)对象之间依赖关系处理繁琐: 3)事务控制繁琐: 2.Spring简介 1)Spring概述 什么是Spring: ①Spring是一个 ...
- php pdo oracle
<?php/** * Created by mestars. * User: mestars * Date: 6/13/16 * Time: 10:52 PM */header('Access- ...
- CSS + radius 五环
使用CSS的外链方式,写了一个五环 CSS的布局 附加radius的使用 思路: 一个大盒子里放两个子盒子: 两个子盒子上下排列,分别放3个和2个盒子用来制作圆环: 大盒子给相对定位,连个子盒子设为绝 ...
- Myeclipse2014安装&破解激活
市场上很多JavaWeb的IDE比如Idea(听说用好开发效率会很高),eclipse(插件丰富还免费),但是对于初学者还是为了提高学习的效率(Myeclipse创建web项目的时候可以自动生成一些配 ...
- [ POI 2012 ] Letters
\(\\\) \(Description\) 给出两个长度为 \(N\) 的字符串\(S_1,S_2\),且保证两个字符串中每一个字符出现次数相同. 现在一次操作可以交换相邻的两个字符,问将 \(S_ ...
- 好用的sublime插件以及快捷键
管理插件:使用Ctrl+`(Esc键下方)快捷键或者通过View->Show Console菜单打开命令行 import urllib.request,os,hashlib; h = '2915 ...
- 还是关于编码——decode & encode的探究
最近被py3.4中的编码折磨的不要不要的,decode & encode的使用.功能貌似在2.7—3.0有一个巨大的变化.网上查询的一些解答很多是基于2.7中的unicode功能,给出的解答是 ...
- vs2017 visual studio2017 密钥 激活码
企业版Enterprise: NJVYC-BMHX2-G77MM-4XJMR-6Q8QF 专业版Professional: KBJFW-NXHK6-W4WJM-CRMQB-G3CDH