LeetCode-Queue
简单题
1. 数据流中的移动平均值 $(leetcode-346)
暂无
2. 最近的请求次数(leetcode-933)
写一个 RecentCounter 类来计算最近的请求。 它只有一个方法:ping(int t),其中 t 代表以毫秒为单位的某个时间。 返回从 3000 毫秒前到现在的 ping 数。
任何处于 [t - 3000, t] 时间范围之内的 ping 都将会被计算在内,包括当前(指 t 时刻)的 ping。
保证每次对 ping 的调用都使用比之前更大的 t 值。
示例:
输入:inputs = ["RecentCounter","ping","ping","ping","ping"], inputs = [[],[1],[100],[3001],[3002]]
输出:[null,1,2,3,3]
提示:
每个测试用例最多调用 10000 次 ping。
每个测试用例会使用严格递增的 t 值来调用 ping。
每次调用 ping 都有 1 <= t <= 10^9。
Related Topics 队列
1)队列
只会考虑最近 3000 毫秒到现在的 ping 数,因此可以使用队列存储这些 ping 的记录。当收到一个时间 t 的 ping 时,将它加入队列,并且将所有在时间 t - 3000 之前的 ping 移出队列。
队列
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue; class RecentCounter {private Queue<Integer> q;
public RecentCounter() {
q = new LinkedList<>();
} public int ping(int t) {
q.offer(t);
while(q.peek()<t-3000){
q.poll();
}
return q.size();
}
}
2)数组存储(不推荐!)
使用数组存储数据,每次遍历判断是否在区间内。浪费存储空间,3000ms以前的数据已经不需要了。
数组存储
import java.util.ArrayList; class RecentCounter {private ArrayList<Integer> time;
public RecentCounter() {
time = new ArrayList<Integer>();
} public int ping(int t) {
time.add(t);
int count = 0;
for(int i:time){
if((i>=t-3000)&&(i<=t)){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
中等
3. 贪吃蛇 $(leetcode-353)
暂无
4. 杀死进程 $(leetcode-582)
暂无
5. 任务调度器(leetcode-621)
暂无
给定一个用字符数组表示的 CPU 需要执行的任务列表。其中包含使用大写的 A - Z 字母表示的26 种不同种类的任务。任务可以以任意顺序执行,并且每个任务都可以在 1 个单位时间内执行完。CPU 在任何一个单位时间内都可以执行一个任务,或者在待命状态。
然而,两个相同种类的任务之间必须有长度为 n 的冷却时间,因此至少有连续 n 个单位时间内 CPU 在执行不同的任务,或者在待命状态。
你需要计算完成所有任务所需要的最短时间。
示例 :
输入:tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2
输出:8
解释:A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B.
在本示例中,两个相同类型任务之间必须间隔长度为 n = 2 的冷却时间,而执行一个任务只需要一个单位时间,所以中间出现了(待命)状态。
提示:
任务的总个数为 [1, 10000]。
n 的取值范围为 [0, 100]。
Related Topics 贪心算法 队列 数组
展示代码
代码
展示代码
代码
6. 设计循环队列(leetcode-622)
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环
队列,能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
提示:
所有的值都在 0 至 1000 的范围内;
操作数将在 1 至 1000 的范围内;
请不要使用内置的队列库。
Related Topics 设计 队列
1)数组
思路一:
front直线对列首元素,rear指向队列尾元素的后一个位置。因此,当front==rear时表示队列为空,front == (rear+1)%maxsize时,队列满。
有一个闲置元素,因此对k个大小容量的队列,需要k+1个元素的数组。
实现1
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MyCircularQueue {
private int front;
private int rear;
private int maxSize;
private int[] l;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
front = 0;
rear = 0;
maxSize = k+1; //预留一个空位,数组长度若为4 实际数据长度为3
l = new int[maxSize];
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(!isFull()){
l[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if(!isEmpty()){
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if(!isEmpty()){
return l[front];
}else{
return -1;
}
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if(!isEmpty()){
return l[(rear-1+maxSize)%maxSize];
}else{
return -1; //找不到,题目要求返回-1
}
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
}
思路二:
queue:一个固定大小的数组,用于保存循环队列的元素。
headIndex:一个整数,保存队首 head 的索引。
count:循环队列当前的长度,即循环队列中的元素数量。使用 hadIndex 和 count 可以计算出队尾元素的索引,因此不需要队尾属性。
capacity:循环队列的容量,即队列中最多可以容纳的元素数量。该属性不是必需的,因为队列容量可以通过数组属性得到,但是由于该属性经常使用,所以我们选择保留它。这样可以不用在 Python 中每次调用 len(queue) 中获取容量。但是在 Java 中通过 queue.length 获取容量更加高效。为了保持一致性,在两种方案中都保留该属性。
实现2
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] queue;
private int headIndex;
private int count;
private int capacity;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.capacity = k;
this.queue = new int[k];
this.headIndex = 0;
this.count = 0;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (this.count == this.capacity)
return false;
this.queue[(this.headIndex + this.count) % this.capacity] = value;
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (this.count == 0)
return false;
this.headIndex = (this.headIndex + 1) % this.capacity;
this.count -= 1;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if (this.count == 0)
return -1;
return this.queue[this.headIndex];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if (this.count == 0)
return -1;
int tailIndex = (this.headIndex + this.count - 1) % this.capacity;
return this.queue[tailIndex];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (this.count == 0);
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return (this.count == this.capacity);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(1)。该数据结构中,所有方法都具有恒定的时间复杂度。
空间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是队列的预分配容量。循环队列的整个生命周期中,都持有该预分配的空间。
上述代码不能用于并发,是非线程安全的。参考
线程安全
class MyCircularQueue {
private Node head, tail;
private int count;
private int capacity;
// Additional variable to secure the access of our queue
private ReentrantLock queueLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.capacity = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
// ensure the exclusive access for the following block.
queueLock.lock();
try {
if (this.count == this.capacity)
return false;
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.count == 0) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.nextNode = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
this.count += 1;
} finally {
queueLock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
}
2)单链表
单链表实现
class Node {
public int value;
public Node nextNode;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.nextNode = null;
}
}
class MyCircularQueue {
private Node head, tail;
private int count;
private int capacity;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.capacity = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (this.count == this.capacity)
return false;
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.count == 0) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.nextNode = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (this.count == 0)
return false;
this.head = this.head.nextNode;
this.count -= 1;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if (this.count == 0)
return -1;
else
return this.head.value;
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if (this.count == 0)
return -1;
else
return this.tail.value;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (this.count == 0);
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return (this.count == this.capacity);
}
}
7. 设计循环双端队列(leetcode-641)
设计实现双端队列。
你的实现需要支持以下操作:
MyCircularDeque(k):构造函数,双端队列的大小为k。
insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回 true。
insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回 true。
deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回 true。
deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回 true。
getFront():从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
isEmpty():检查双端队列是否为空。
isFull():检查双端队列是否满了。
示例:
MyCircularDeque circularDeque = new MycircularDeque(3); // 设置容量大小为3
circularDeque.insertLast(1); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertLast(2); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(3); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 已经满了,返回 false
circularDeque.getRear(); // 返回 2
circularDeque.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.deleteLast(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 返回 true
circularDeque.getFront(); // 返回 4
提示:
所有值的范围为 [1, 1000]
操作次数的范围为 [1, 1000]
请不要使用内置的双端队列库。
Related Topics 设计 队列
数组实现
数组实现
class MyCircularDeque {private int[] queue;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int maxSize; /** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
front = 0;
rear = 0;
maxSize = k+1;
queue = new int[maxSize];
} /** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}else{
front = (front - 1 + maxSize) % maxSize;
queue[front] = value;
return true;
}
} /** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}else{
queue[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
return true;
}
} /** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}else{
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return true;
}
} /** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteLast() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}else{
rear = (rear - 1 + maxSize) % maxSize;
return true;
}
} /** Get the front item from the deque. */
public int getFront() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}else{
return queue[front];
}
} /** Get the last item from the deque. */
public int getRear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}else{
return queue[(rear - 1 + maxSize )%maxSize];
}
} /** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
} /** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return front == (rear + 1)%maxSize;
}
}
8. 第K个数(面试题 17.09)
有些数的素因子只有 3,5,7,请设计一个算法找出第 k 个数。注意,不是必须有这些素因子,而是必须不包含其他的素因子。
例如,前几个数按顺序应该是 1,3,5,7,9,15,21。
示例 1:
输入: k = 5
输出: 9
Related Topics 堆 队列 数学
1)动态规划
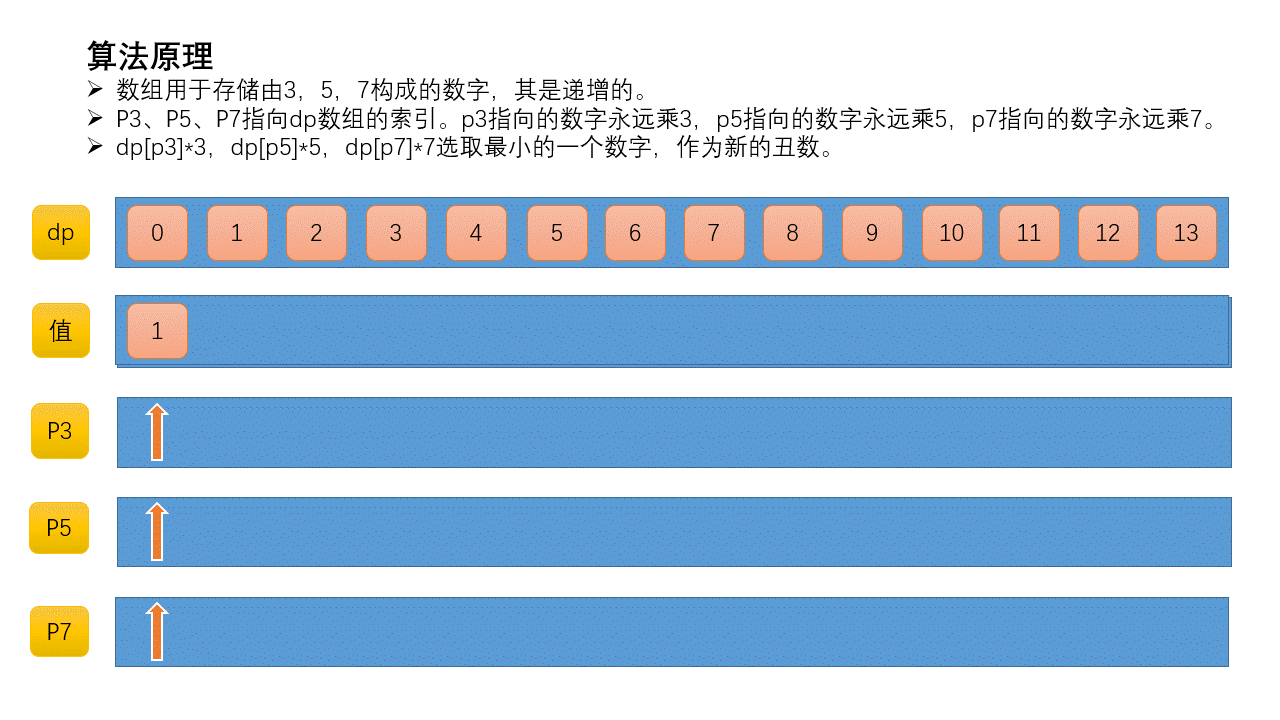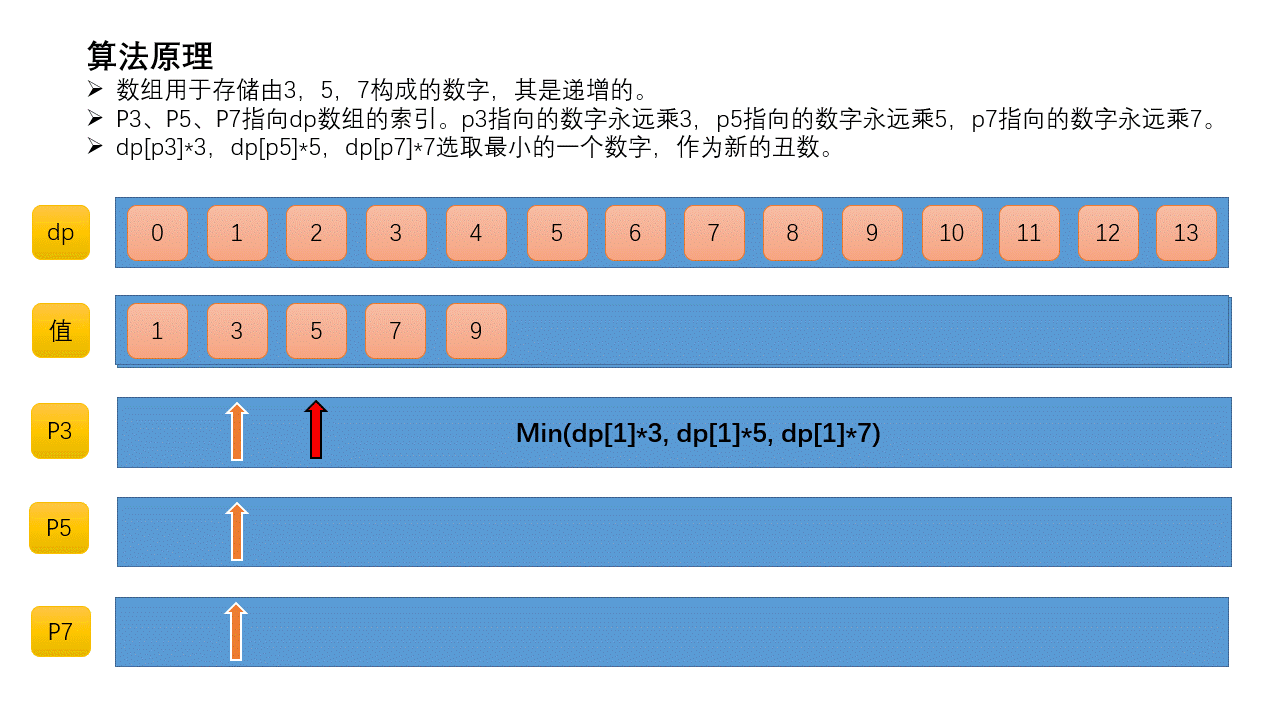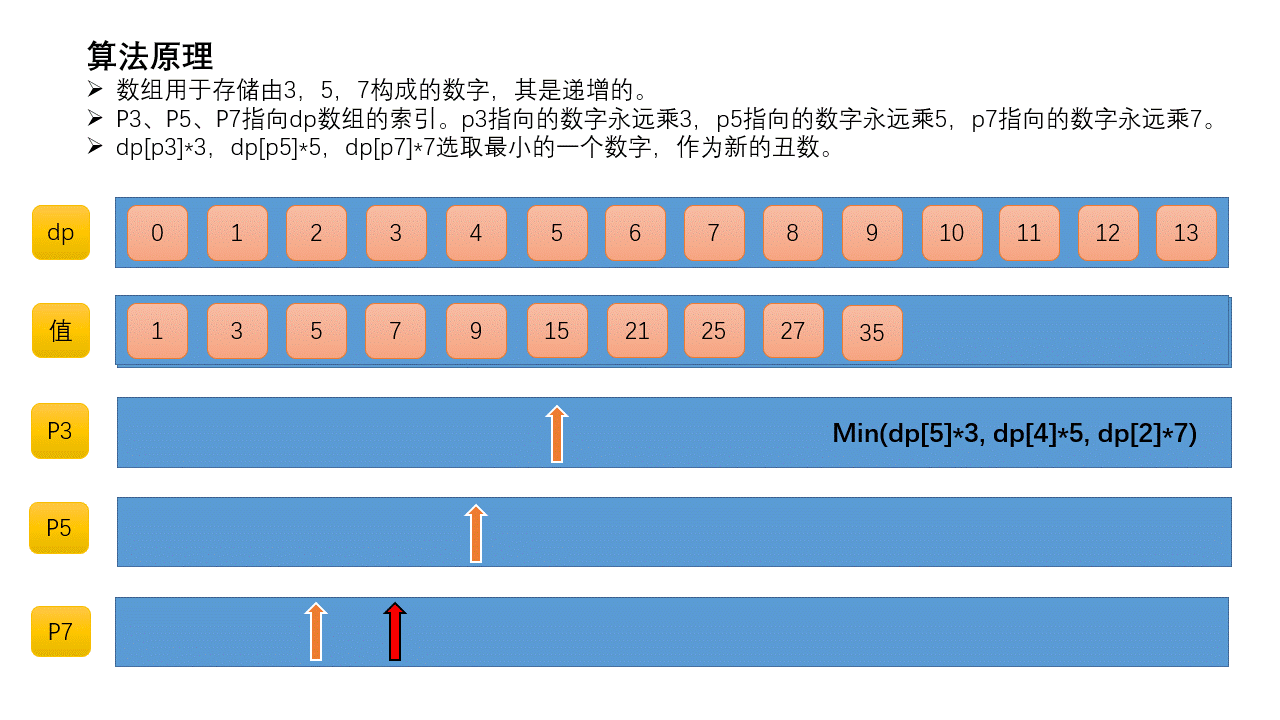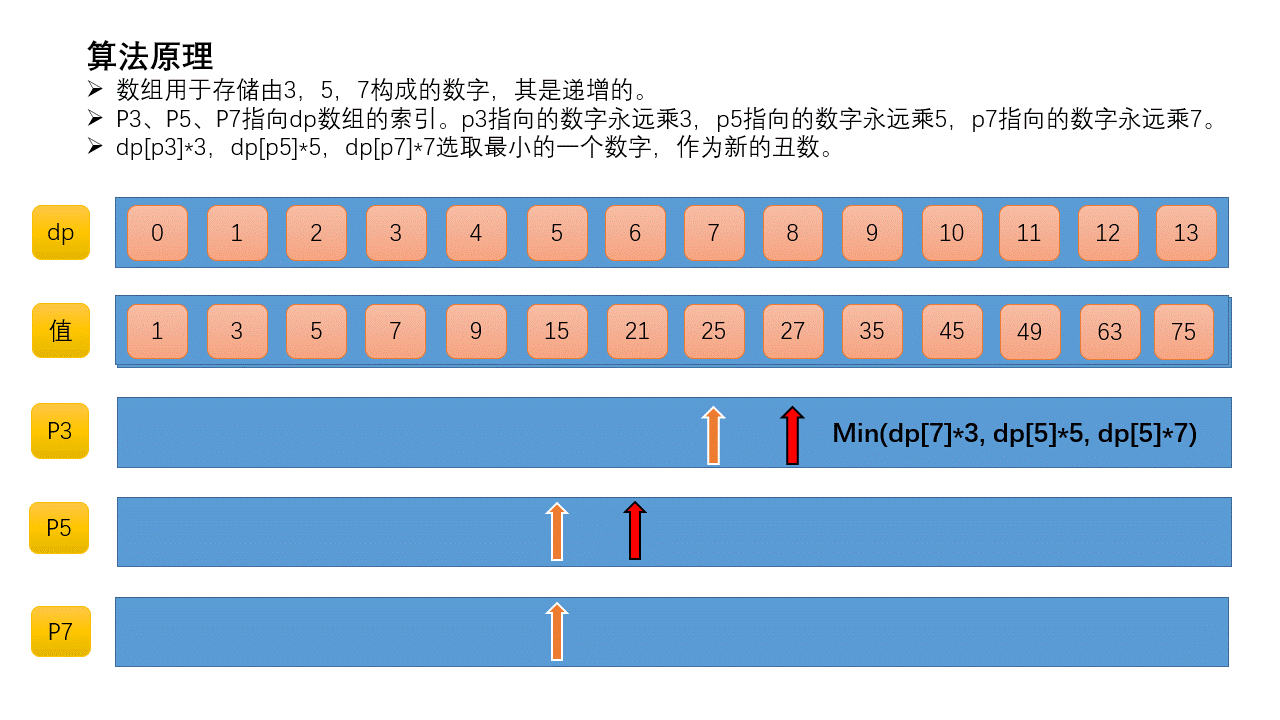
定义三个索引p3、p5、p7。p3指向的数字永远乘3,p5指向的数字永远乘5,p7指向的数字永远乘7。初始化所有指针都指向第一个丑数,即1。
从dp[p3]*3、dp[p5]*5、dp[p7]*7选取最小的一个数字,作为新的丑数。新的丑数就是3*dp[p3]=3*1=3,执行p3++。此时p5和p7指向第1个丑数,p3指向第2个丑数。然重复上一步。
这里基于的一个事实是,丑数数列是递增的,当p5指针在当前位置时,后面的数乘以5必然比前面的数乘以5大,所以下一个丑数必然是先考虑前面的数乘以5。p3、p7同理,所以才可以使用索引指针。
动态规划
class Solution {public int getKthMagicNumber(int k) {
if(k<=0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("para is error");
}
int []dp = new int[k];
dp[0] = 1;
int p3=0,p5=0,p7=0; for(int i=1; i<k; i++){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[p3]*3, Math.min(dp[p5]*5, dp[p7]*7));
if(dp[i]==dp[p3]*3) p3++;
if(dp[i]==dp[p5]*5) p5++;
if(dp[i]==dp[p7]*7) p7++;
}
return dp[k-1];
}
}
2)优先队列(堆排序)
每一个magic number乘以3,5,7也是一个magic number。
通过优先队列,每次取出最小的一个,然后乘以3,5,7得到的值放入队列中。
注意处理重复的数据,比如3*5和5*3为重复数据。
展示代码
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue; class Solution {public int getKthMagicNumber(int k) {
HashSet<Long> set = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Long> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(); queue.offer(1L); while(true){
Long v = queue.poll(); if(!set.contains(v)){
set.add(v); //将最小值添加到集合中 queue.offer(v*3);
queue.offer(v*5);
queue.offer(v*7);
} if(set.size()==k) {
return v.intValue(); //将Long转为int类型
}
}
}
}
困难
9. 矩形区域不超过K的最大数值和(leetcode-363)
暂无
10. 和至少为K的最短子数组(leetcode-862)
暂无
11. 滑动窗口最大值(leetcode-239)
暂无
LeetCode-Queue的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Queue Reconstruction by Height 根据高度重建队列
Suppose you have a random list of people standing in a queue. Each person is described by a pair of ...
- LeetCode: Queue Reconstruction by Height
这题的关键点在于对数组的重排序方法,高度先由高到低排列不会影响第二个参数,因为list.add的方法在指定index后面插入,因此对于同高的人来说需要对第二个参数由低到高排,具体代码如下 public ...
- [LeetCode] Implement Queue using Stacks 用栈来实现队列
Implement the following operations of a queue using stacks. push(x) -- Push element x to the back of ...
- sort学习 - LeetCode #406 Queue Reconstruction by Height
用python实现多级排序,可以像C语言那样写个my_cmp,然后在sort的时候赋给参数cmp即可 但实际上,python处理cmp 是很慢的,因为每次比较都会调用my_cmp:而使用key和rev ...
- 【一天一道LeetCode】#232. Implement Queue using Stacks
一天一道LeetCode 本系列文章已全部上传至我的github,地址:ZeeCoder's Github 欢迎大家关注我的新浪微博,我的新浪微博 欢迎转载,转载请注明出处 (一)题目 Impleme ...
- [LeetCode] Design Circular Queue 设计环形队列
Design your implementation of the circular queue. The circular queue is a linear data structure in w ...
- LeetCode算法题-Implement Queue Using Stacks(Java实现)
这是悦乐书的第195次更新,第201篇原创 01 看题和准备 今天介绍的是LeetCode算法题中Easy级别的第57题(顺位题号是232).使用栈实现队列的以下操作. push(x) - 将元素x推 ...
- 【LeetCode OJ 232】Implement Queue using Stacks
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/ 题目:Implement the following operatio ...
- LeetCode 622:设计循环队列 Design Circular Queue
LeetCode 622:设计循环队列 Design Circular Queue 首先来看看队列这种数据结构: 队列:先入先出的数据结构 在 FIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素 ...
- [LeetCode] 899. Orderly Queue 有序队列
A string S of lowercase letters is given. Then, we may make any number of moves. In each move, we c ...
随机推荐
- Java实现 LeetCode 110 平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树. 本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为: 一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1. 示例 1: 给定二叉树 [3,9 ...
- Java实现背包问题
1 问题描述 给定n个重量为w1,w2,w3,-,wn,价值为v1,v2,-,vn的物品和一个承重为W的背包,求这些物品中最有价值的子集(PS:每一个物品要么选一次,要么不选),并且要能够装到背包. ...
- java实现第二届蓝桥杯四方定理
四方定理. 数论中有著名的四方定理:所有自然数至多只要用四个数的平方和就可以表示. 我们可以通过计算机验证其在有限范围的正确性. 对于大数,简单的循环嵌套是不适宜的.下面的代码给出了一种分解方案. 请 ...
- java实现第四届蓝桥杯空白格式化
空白格式化 本次大赛采用了全自动机器测评系统. 如果你的答案与标准答案相差了一个空格,很可能无法得分,所以要加倍谨慎! 但也不必过于惊慌.因为在有些情况下,测评系统会把你的答案进行"空白格式 ...
- mac下使用VMVARE安装win10虚拟机的一些坑
最近Mac上安装windows踩到了几个坑: 坑一:启动虚拟机后,提示找不到CD-ROM中找不到对应的ISO文件 硬盘格式请选择 在虚拟机->设置中选择启动磁盘为CD_ROM,然后重新启动. 坑 ...
- EasyARM-iMX257 linxu两年前的笔记
第三章续:简单总结第三章中出现的命令! 1) root@EasyARM-iMX257 ~# ddif=/dev/zero of=/dev/shm/disk bs=1024 count=10240 d ...
- 免费 IP 代理池示例
使用文档 import requests import re import random from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor impor ...
- Elasticsearch系列---生产数据备份恢复方案
前言 生产环境中运行的组件,只要有数据存储,定时备份.灾难恢复是必修课,mysql数据库的备份方案已经非常成熟,Elasticsearch也同样有成熟的数据备份.恢复方案,我们来了解一下. 概要 本篇 ...
- [Linux之旅一] .NET Core 2.2部署到Docker中
第一步,使用VS2017或者VS2019创建.NET Core 2.2或3.1的项目,如下图: 在创建项目的时候记得勾选Docker支持,这样会自动创建Dockerfile文件,这个文件用于构建Doc ...
- .NET Core加解密实战系列之——RSA非对称加密算法
目录 简介 功能依赖 生成RSA秘钥 PKCS1格式 PKCS8格式 私钥操作 PKCS1与PKCS8格式互转 PKCS1与PKCS8私钥中提取公钥 PEM操作 PEM格式密钥读取 PEM格式密钥写入 ...
