[尊老爱幼] Queen
You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 1 to n
. A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex named root.
Ancestors of the vertex i
are all vertices on the path from the root to the vertex i, except the vertex i itself. The parent of the vertex i is the nearest to the vertex i ancestor of i. Each vertex is a child of its parent. In the given tree the parent of the vertex i is the vertex pi. For the root, the value pi is −1
.
An example of a tree with n=8
, the root is vertex 5. The parent of the vertex 2 is vertex 3, the parent of the vertex 1 is vertex 5. The ancestors of the vertex 6 are vertices 4 and 5, the ancestors of the vertex 7 are vertices 8, 3 and 5
You noticed that some vertices do not respect others. In particular, if ci=1
, then the vertex i does not respect any of its ancestors, and if ci=0
, it respects all of them.
You decided to delete vertices from the tree one by one. On each step you select such a non-root vertex that it does not respect its parent and none of its children respects it. If there are several such vertices, you select the one with the smallest number. When you delete this vertex v
, all children of v become connected with the parent of v
.
An example of deletion of the vertex 7
Once there are no vertices matching the criteria for deletion, you stop the process. Print the order in which you will delete the vertices. Note that this order is unique.
Input
The first line contains a single integer n
(1≤n≤105
) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The next n
lines describe the tree: the i-th line contains two integers pi and ci (1≤pi≤n, 0≤ci≤1), where pi is the parent of the vertex i, and ci=0, if the vertex i respects its parents, and ci=1, if the vertex i does not respect any of its parents. The root of the tree has −1 instead of the parent index, also, ci=0 for the root. It is guaranteed that the values pi define a rooted tree with n
vertices.
Output
In case there is at least one vertex to delete, print the only line containing the indices of the vertices you will delete in the order you delete them. Otherwise print a single integer −1
.
Examples
5
3 1
1 1
-1 0
2 1
3 0
1 2 4
5
-1 0
1 1
1 1
2 0
3 0
-1
8
2 1
-1 0
1 0
1 1
1 1
4 0
5 1
7 0
5
Note
The deletion process in the first example is as follows (see the picture below, the vertices with ci=1
are in yellow):
- first you will delete the vertex 1
, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the vertex 2) do not respect it, and 1
- is the smallest index among such vertices;
- the vertex 2
will be connected with the vertex 3
- after deletion;
- then you will delete the vertex 2
, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the only vertex 4
- ) do not respect it;
- the vertex 4
will be connected with the vertex 3
- ;
- then you will delete the vertex 4
- , because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (there are none) do not respect it (vacuous truth);
- you will just delete the vertex 4
- ;
- there are no more vertices to delete.
In the second example you don't need to delete any vertex:
- vertices 2
and 3
- have children that respect them;
- vertices 4
and 5
- respect ancestors.
In the third example the tree will change this way: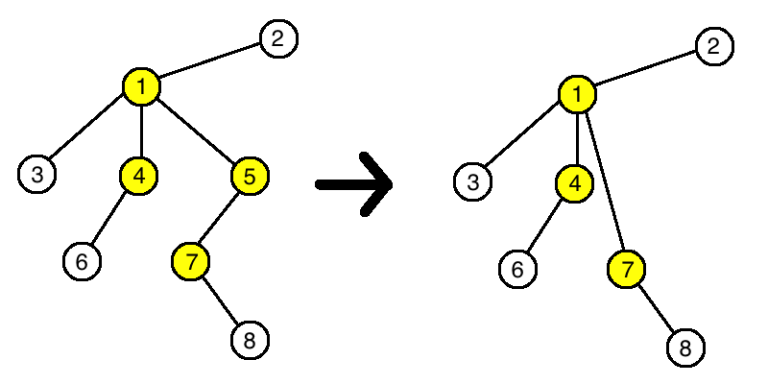
题意:输入一个n,接下来n行,每行2个数pi表示第i个结点的父结点,ci为1表示这个结点不尊重他的祖先,为0表示它尊重祖先
对于一个非根结点,如果它不尊重祖先且其孩子不尊重它,则它被删掉且它的孩子连到它的父结点上,输出被删去的结点编号
思路:一开始想如果一个结点被删除就等价于它被它的孩子结点代替,所以如果删除一个结点后就打上删除标记,访问一个被删去的结点时就去访问它的儿子碰到儿子时被删除的结点就递归地访问直到没有一个结点是要被删除的
这样dfs模拟,但这样在test10超时了.其实如果一个结点不尊重祖先,但它的孩子尊重它,则他是不能删的,所以对于一个不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点从它的父结点开始连续的不尊重祖先的结点都是需要删掉的,
所以我们先把不尊重祖先的结点标记,再标记出不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点,最后输出不尊重祖先且不被孩子尊重的结点
注意这里是先标记了不尊重祖先的结点,才看那些是不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点,如果在标记不尊重祖先的结点的同时看那些结点被孩子标记,可能会出现现在这个结点的孩子没被标记为不尊重祖先的结点,但后面的输入是被标记了,这样就错误的把当前这个结点标记为不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int amn=1e5+;
int n,ans[amn],p[amn],c[amn],root;
int main(){
int need[amn];
memset(need,,sizeof need);
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&p[i],&c[i]);
if(p[i]==-)root=i;
if(c[i])need[i]=;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
if(!c[i])need[p[i]]=;
}
int tp=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
if(!need[i]||i==root)continue;
if(c[i]&&need[i])
ans[++tp]=i;
}
if(tp){
for(int i=;i<=tp;i++)printf("%d%c",ans[i],i<tp?' ':'\n');
}
else printf("-1\n");
}
/**
题意:输入一个n,接下来n行,每行2个数pi表示第i个结点的父结点,ci为1表示这个结点不尊重他的祖先,为0表示它尊重祖先
对于一个非根结点,如果它不尊重祖先且其孩子不尊重它,则它被删掉且它的孩子连到它的父结点上,输出被删去的结点编号
思路:一开始想如果一个结点被删除就等价于它被它的孩子结点代替,所以如果删除一个结点后就打上删除标记,访问一个被删去的结点时就去访问它的儿子碰到儿子时被删除的结点就递归地访问直到没有一个结点是要被删除的
这样dfs模拟,但这样在test10超时了.其实如果一个结点不尊重祖先,但它的孩子尊重它,则他是不能删的,所以对于一个不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点从它的父结点开始连续的不尊重祖先的结点都是需要删掉的,
所以我们先把不尊重祖先的结点标记,再标记出不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点,最后输出不尊重祖先且不被孩子尊重的结点
注意这里是先标记了不尊重祖先的结点,才看那些是不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点,如果在标记不尊重祖先的结点的同时看那些结点被孩子标记,可能会出现现在这个结点的孩子没被标记为不尊重祖先的结点,但后面的输入是被标记了,这样就错误的把当前这个结点标记为不尊重祖先但被孩子尊重的结点
**/
[尊老爱幼] Queen的更多相关文章
- ACM: Long Live the Queen - 树上的DP
Long Live the Queen Time Limit:250MS Memory Limit:4096KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u D ...
- 皇后(queen)
皇后(queen)[题目描述] 众所不知,rly现在不会玩国际象棋.但是,作为一个OIer,rly当然做过八皇后问题.这里再啰嗦几句,皇后可以攻击到同行同列同对角线,在n*n的方格中摆n个皇后使其互不 ...
- 1976 Queen数列
1976 Queen数列 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 黄金 Gold 题解 查看运行结果 题目描述 Description 将1到N的整数数列(1 ...
- Uva 11538 - Chess Queen
http://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&p ...
- 组合数学 UVa 11538 Chess Queen
Problem A Chess Queen Input: Standard Input Output: Standard Output You probably know how the game o ...
- uva 10401 Injured Queen Problem(dp)
题目链接:10401 - Injured Queen Problem 题目大意:给出一个字符串,要求在n * n(n为字符串的长度)的棋盘上摆放n个受伤的皇后,受伤的皇后只能攻击到同一列和它周围8个格 ...
- C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) dfs
C. Queen time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input outpu ...
- 高可用OpenStack(Queen版)集群-1. 集群环境
参考文档: Install-guide:https://docs.openstack.org/install-guide/ OpenStack High Availability Guide:http ...
- 143. Long Live the Queen 树形dp 难度:0
143. Long Live the Queen time limit per test: 0.25 sec. memory limit per test: 4096 KB The Queen of ...
随机推荐
- Flutter混合开发:Android接入Flutter
Flutter Google推出已经已经一年多了,单个 Flutter 项目的开发流程已经很成熟了.对与个人开发者来说使用 Flutter 开发一个跨平台的App挺有意思.但是对于现有的项目改造来说还 ...
- 网络编程01 · 艺
Web Socket和Socket 套接字,实际就是传输层的接口.用于抽象传输层,隐藏细节.一对套接字可以进行通信. Web Socket,是基于TCP协议的.类似于,http. 为什么需要Web S ...
- VMWare vCenter 4.x 数据库由SQL Express 迁移至SQL Server 2008 R2
默认安装下的 VMware vCenter 4.x 会在本地安装 SQL Express 2005 版本,如果你有需要迁移至 Full SQL Server版本比如 SQL Server 2008 R ...
- 【Art】物理课题——虹吸
前言(无关闲话):在此之前,课题小组讨论了三.四次,得有10个小时了总共,但是具体还是在普及常识,那就在这里深入地讲一下. 进入正题—— 这就是虹吸的基本模型,再看一下百度的官方说法: “虹吸(sip ...
- 浅谈ConcurrentDictionary与Dictionary
在.NET4.0之前,如果我们需要在多线程环境下使用Dictionary类,除了自己实现线程同步来保证线程安全外,我们没有其他选择.很多开发人员肯定都实现过类似的线程安全方案,可能是通过创建全新的线程 ...
- 量化投资学习笔记34——《Python机器学习应用》课程笔记08
岭回归 解决某些训练样本线性相关,导致回归结果不稳定的情况. 它是一种用于共线性数据分析的有偏估计回归方法.是一种改良的最小二乘估计法. 在sklearn中使用sklearn.linear_model ...
- MVC07
1. 讲解ASP.net MVC的I/O操作 新建一个控制台程序,输入代码如下 using System; using System.IO; namespace IO { class Program ...
- direction和writing-mode的介绍
direction介绍 属性值和兼容都很好 CSSdirection属性简单好记,属性值少,兼容性好,关键时候省心省力,是时候给大家宣传宣传,不要埋没了人家的特殊技能. Chrome Safari F ...
- Eureka在有虚拟网卡的情况下获取正确的IP
发现问题 最近项目在Eureka注册时,发现一个问题:注册的IP地址不是 192.168.0.XXX 的网络IP,而是另外一个网段的地址,如图 通过 ipconfig 命令查看本机的IP地址发现,该I ...
- Echarts 自定义legend图片,修改点击之后的颜色图解
第一个问题:echarts 可以自定义图例的图标,百度上很多回答都是引用的相对路径,但是不知道为啥,我的vue项目就是引用不显示,在network里面找不到相应图片 后来我想了个法子,就是先获取到这个 ...
