android 基本布局(RelativeLayout、TableLayout等)使用方法及各种属性
博客逐步迁移至 极客兔兔的小站
本文介绍 Android 界面开发中最基本的四种布局LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout、TableLayout 的使用方法及这四种布局中常用的属性。
- LinearLayout
线性布局,布局中空间呈线性排列- RelativeLayout
相对布局,通过相对定位的方式,控制控件位置- FrameLayout
帧布局,最简单的布局,所有控件放置左上角- TableLayout
表格布局,以行列方式控制控件位置
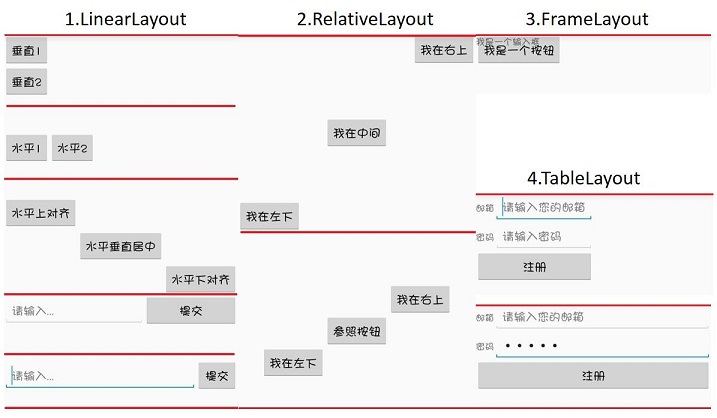
1.LinearLayout
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="垂直1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="垂直2" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="水平1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="水平2" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:text="水平上对齐" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="水平垂直居中" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:text="水平下对齐" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:hint="请输入..."/>
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="提交" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<EditText
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:hint="请输入..."/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="提交" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
- orientation:horizontal(水平)/vertical(垂直),表示线性排列的方向。
- layout_width/layout_height:元素的宽度与高度
- layout_gravity:top/bottom/center/left/right/etc,表示当前元素相对父元素的对齐方式,多种对齐方式用“|”隔开,右上对齐:
top|right。- layout_weight:占据空间的比例,例如元素A和B,A设置为1,B设置为3, 元素A、B分别占空间的1/4、3/4,此时元素宽度不由layout_width决定,设置为
0dp是比较规范的写法。- layout_weight 若元素A设置为1,元素B不设置,将layout_width设置为具体的值或wrap_content,那么元素B的宽度由layout_width决定,元素A将占满屏幕剩下的空间。
2.RelativeLayout
<LinearLayout ...>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="我在左下"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="我在中间"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="我在右上"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="参照按钮"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/button_2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button_2"
android:text="我在右上"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/button_2"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/button_2"
android:text="我在左下"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
以下属性值为true/false
- layout_centerHorizontal/layout_centerVertical: 水平居中、垂直居中
- layout_centerInparent: 相对父元素垂直&水平居中
- layout_alignParentBottom: 元素下边界和父元素下边界对齐
- layout_alignParentLeft: 左边界对齐
- layout_alignParentRight: 右边界对齐
- layout_alignParentTop: 上边界对齐
以下属性值为控件id
- layout_above/layout_below: 在某元素的上方/下方
- layout_toLeftOf/layout_toRightOf: 在某元素的左方/右方
- layout_alignTop/layout_alignBottom: 元素上(下)边界与某元素上(下)边界对齐
- layout_alignLeft/layout_alignRight: 左(右)边界对齐
3.FrameLayout
所有元素都放置在布局的左上角
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是一个按钮"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是一个输入框"/>
</FrameLayout>
4.TableLayout
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="邮箱"/>
<EditText
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
android:hint="请输入您的邮箱" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密码"/>
<EditText
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="请输入密码" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_span="2"
android:text="注册" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="1">
...
</TableLayout>
- TableRow: 代表表格布局的一行,行内一个元素代表一列。
- layout_span: 合并单元格,设置为2,代表该元素占据2列空间。
- stretchColumns: TableRow中无法指定空间宽度,那么需要用到该属性,设置为1,表示拉伸第2列(0为第1列)与屏幕一样宽,效果如TableLayout的第二张图。
5.自定义布局
Android中,布局下可以放置控件,也可以放置子布局。如果子布局内容较为独立且经常使用,例如标题栏,或者布局比较复杂,这时候可以考虑使用自定义布局的形式导入。方法很简单。
- 新建一个布局文件,例如
example.xml - 在父布局中引入:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<include layout="@layout/example"/>
</LinearLayout>
android 基本布局(RelativeLayout、TableLayout等)使用方法及各种属性的更多相关文章
- Android相对布局(RelativeLayout)
Android相对布局(RelativeLayout) 备注:这里的视图和元素是等同的概念. RelativeLayout是一个允许子视图相对于其他兄弟视图或是父视图显示的视图组(通过ID指定).每个 ...
- Android UI布局之TableLayout
从字面上了解TableLayout是一种表格式的布局.这样的布局会把包括的元素以行和列的形式进行排列.表格的列数为每一行的最大列数.当然表格里边的单元格是能够为空的. 实例:LayoutDemo 执行 ...
- Android之布局RelativeLayout
线性布局的weight属性在等比例分配时比较方便,但是对复杂的界面,嵌套多层LinearLayout布局会导致渲染变慢,占用更多系统资源:而使用RelativeLayout的话,可能仅仅需要一层就可以 ...
- android的布局-----RelativeLayout(相对布局)
学习导图 注:父容器定位的属性值只能是Boolean ,兄弟组件定位的属性值只能是ID 典型案例(梅花) <?xml version="1.0" encoding=" ...
- Android 五大布局(LinearLayout、FrameLayout、AbsoulteLayout、RelativeLayout、TableLayout )
前言 欢迎大家我分享和推荐好用的代码段~~ 声明 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处: CSDN:http://www.csdn.net ...
- [转]浅谈Android五大布局(二)——RelativeLayout和TableLayout
在浅谈Android五大布局(一)中已经描述了LinearLayout(线性布局).FrameLayout(单帧布局)和AbsoulteLayout(绝对布局)三种布局结构,剩下的两种布局Relati ...
- 【深入篇】Android常用布局方式简介
LinearLayout 线性布局是程序中最常见的布局方式.一般分为水平线性布局和竖直线性布局,通过android.orientation属性可以设置线性布局的方向. 在布局中操作颜色时,要用的是十六 ...
- 动态布局--动态修改RelativeLayout宽高的方法
本文实例讲述了Android编程动态修改RelativeLayout宽高的方法.分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 我们经常会动态修改RelativeLayout的宽高,这样的代码,比较简单,就是修改R ...
- Android 表格布局<TableLayout>
表格布局即,tableLayout,表格布局通过行.列的形式来管理UI组件,TablelLayout并不需要明确地声明包含多少行.多少列,而是通过TableRow,以及其他组件来控制表格的行数和列数, ...
随机推荐
- 做10年Windows程序员与做10年Linux程序员的区别
如果一个程序员从来没有在linux,unix下开发过程序,一直在windows下面开发程序, 同样是工作10年, 大部分情况下与在linux,unix下面开发10年的程序员水平会差别很大.我写这篇文章 ...
- Nancy Scripts,CSS文件夹配置
public class Bootstrapper : DefaultNancyBootstrapper { protected override void ConfigureConventions( ...
- MFC 阶段学习总结
由于项目需求,需要用到C++开发软件,所以开始学习C++,重点是MFC,因为是窗体应用,感觉win32的比较麻烦,还是MFC方便点.至于为什么要用C++呢, 由于C++应用不需要客户额外安装环境和加密 ...
- jquery表单对象属性选择器
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- [函数] Firemonkey 取得 Windows 目前 User 的 Desktop 目录
下列方法仅提供 Windows 平台使用,所以需要使用编译开关,代码如下: uses {$IFDEF MSWINDOWS} Winapi.Windows, Winapi.SHFolder, {$END ...
- 2016暑假多校联合---Rikka with Sequence (线段树)
2016暑假多校联合---Rikka with Sequence (线段树) Problem Description As we know, Rikka is poor at math. Yuta i ...
- Java基础复习笔记系列 八 多线程编程
Java基础复习笔记系列之 多线程编程 参考地址: http://blog.csdn.net/xuweilinjijis/article/details/8878649 今天的故事,让我们从上面这个图 ...
- Maven+Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis+MySQL,搭建SSM框架环境
项目建设完成之后的结构: 数据库的表结构如下: 环境建设:搭建Maven环境.Tomcat环境.需要MySql 数据库支持,使用的编程工具Eclipse (这些是前期准备): 开始创建工程: 1.创建 ...
- jScrollPane 美化滚动条
在线实例 滚动条可见 滚动条隐藏 使用方法 <div class="container"> <h1>滚动条可见</h1> <div cla ...
- 使用 FocusPoint.js 实现图片的响应式裁剪
通常网站的布局都不是单一的.例如图像在电脑.平板和智能手机上可能显示的形状是不同的.特别是如果你使用的是全屏图像,在你必须使用相同的图像文件的情况下,你的主题可能会被截断或完全缺失,或者看起来很尴尬. ...
