Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) 本来以为这个时间是晚上的,下午就没做
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
At regular competition Vladik and Valera won a and b candies respectively. Vladik offered 1 his candy to Valera. After that Valera gave Vladik 2 his candies, so that no one thought that he was less generous. Vladik for same reason gave 3 candies to Valera in next turn.
More formally, the guys take turns giving each other one candy more than they received in the previous turn.
This continued until the moment when one of them couldn’t give the right amount of candy. Candies, which guys got from each other, they don’t consider as their own. You need to know, who is the first who can’t give the right amount of candy.
Single line of input data contains two space-separated integers a, b (1 ≤ a, b ≤ 109) — number of Vladik and Valera candies respectively.
Pring a single line "Vladik’’ in case, if Vladik first who can’t give right amount of candy, or "Valera’’ otherwise.
1 1
Valera
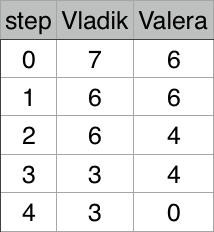
7 6
Vladik
Illustration for first test case:
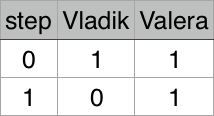
Illustration for second test case:
两个人的糖果数分别-1-3-5-7,-2-4-6-8,看谁更持久,等差数列求和啊,因为数据量不大,所以直接模拟也是可以过的
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ll a, b, n, m;
cin >> a >> b;
n = sqrt(a);
m = (-1.0+sqrt(+*b))/2.0;
if (n > m){
cout << "Valera";
}
else cout << "Vladik";
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vladik had started reading a complicated book about algorithms containing n pages. To improve understanding of what is written, his friends advised him to read pages in some order given by permutation P = [p1, p2, ..., pn], where pi denotes the number of page that should be read i-th in turn.
Sometimes Vladik’s mom sorted some subsegment of permutation P from position l to position r inclusive, because she loves the order. For every of such sorting Vladik knows number x — what index of page in permutation he should read. He is wondered if the page, which he will read after sorting, has changed. In other words, has px changed? After every sorting Vladik return permutation to initial state, so you can assume that each sorting is independent from each other.
First line contains two space-separated integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 104) — length of permutation and number of times Vladik's mom sorted some subsegment of the book.
Second line contains n space-separated integers p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — permutation P. Note that elements in permutation are distinct.
Each of the next m lines contains three space-separated integers li, ri, xi (1 ≤ li ≤ xi ≤ ri ≤ n) — left and right borders of sorted subsegment in i-th sorting and position that is interesting to Vladik.
For each mom’s sorting on it’s own line print "Yes", if page which is interesting to Vladik hasn't changed, or "No" otherwise.
5 5
5 4 3 2 1
1 5 3
1 3 1
2 4 3
4 4 4
2 5 3
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
6 5
1 4 3 2 5 6
2 4 3
1 6 2
4 5 4
1 3 3
2 6 3
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Explanation of first test case:
- [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] — permutation after sorting, 3-rd element hasn’t changed, so answer is "Yes".
- [3, 4, 5, 2, 1] — permutation after sorting, 1-st element has changed, so answer is "No".
- [5, 2, 3, 4, 1] — permutation after sorting, 3-rd element hasn’t changed, so answer is "Yes".
- [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] — permutation after sorting, 4-th element hasn’t changed, so answer is "Yes".
- [5, 1, 2, 3, 4] — permutation after sorting, 3-rd element has changed, so answer is "No".
群里有大佬用了线数段的做法,可是div2怎么会那么难啊,统计下<=a[x]的不久好了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=+;
int n,m;
int p[maxn];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
int l,r,x;
for(int i=;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d %d %d",&l,&r,&x);
int hh=p[x];
int cnt=;
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++){
if(j==x)
continue;
if(p[j]<hh)
cnt++;
}
if(cnt+l-==x)
printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vladik often travels by trains. He remembered some of his trips especially well and I would like to tell you about one of these trips:
Vladik is at initial train station, and now n people (including Vladik) want to get on the train. They are already lined up in some order, and for each of them the city code ai is known (the code of the city in which they are going to).
Train chief selects some number of disjoint segments of the original sequence of people (covering entire sequence by segments is not necessary). People who are in the same segment will be in the same train carriage. The segments are selected in such way that if at least one person travels to the city x, then all people who are going to city x should be in the same railway carriage. This means that they can’t belong to different segments. Note, that all people who travel to the city x, either go to it and in the same railway carriage, or do not go anywhere at all.
Comfort of a train trip with people on segment from position l to position r is equal to XOR of all distinct codes of cities for people on the segment from position l to position r. XOR operation also known as exclusive OR.
Total comfort of a train trip is equal to sum of comfort for each segment.
Help Vladik to know maximal possible total comfort.
First line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5000) — number of people.
Second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 5000), where ai denotes code of the city to which i-th person is going.
The output should contain a single integer — maximal possible total comfort.
6
4 4 2 5 2 3
14
9
5 1 3 1 5 2 4 2 5
9
In the first test case best partition into segments is: [4, 4] [2, 5, 2] [3], answer is calculated as follows: 4 + (2 xor5) + 3 = 4 + 7 + 3 = 14
In the second test case best partition into segments is: 5 1 [3] 1 5 [2, 4, 2] 5, answer calculated as follows: 3 + (2 xor 4) = 3 + 6 = 9.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define mem(s,v) memset(s,v,sizeof(s))
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
int a[],fi[],se[],dp[],vis[5010];
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
mem(a,);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(!fi[a[i]]) fi[a[i]]=i;
se[a[i]]=i;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-];
mem(vis,);
int st=i,res=;
for(int j=i;j;j--){
if(!vis[a[j]]){
if(se[a[j]]>i) break;
if(fi[a[j]]<st) st=fi[a[j]];
res^=a[j];vis[a[j]]=;
}
if(j<=st) dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[j-]+res);
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[n]);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) 本来以为这个时间是晚上的,下午就没做的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round#416 Div.2
A. Vladik and Courtesy 题面 At regular competition Vladik and Valera won a and b candies respectively. ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)(A,思维题,暴力,B,思维题,暴力)
A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:stand ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) C. Vladik and Memorable Trip
http://codeforces.com/contest/811/problem/C 题意: 给出一行序列,现在要选出一些区间来(不必全部选完),但是相同的数必须出现在同一个区间中,也就是说该数要么 ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/811/problem/D 题目: D. Vladik and Favorite Game time limit per test 2 ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) A+B
A. Vladik and Courtesy 2 seconds 256 megabytes At regular competition Vladik and Valera won a and ...
- Codeforces Round #416(Div. 2)-811A.。。。 811B.。。。 811C.dp。。。不会
CodeForces - 811A A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 meg ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) B. Vladik and Complicated Book
B. Vladik and Complicated Book time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)A B C 水 暴力 dp
A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- 【分类讨论】【spfa】【BFS】Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
那个人第一步肯定要么能向下走,要么能向右走.于是一定可以判断出上下是否对调,或者左右是否对调. 然后他往这个方向再走一走就能发现一定可以再往旁边走,此时就可以判断出另一个方向是否对调. 都判断出来以后 ...
随机推荐
- Bootstrap基础知识学习
Bootstrap中文网 http://www.bootcss.com/ Bootstrap菜鸟教程 http://www.runoob.com/bootstrap/bootstrap-tutoria ...
- Apache is running a threaded MPM, but your PHP module is not compiled to be threadsafe. you need to recompile php. pre-configuration failed
手动配置想要组合版本的wamp环境时,在服务器上直接下载的几个安装包怎么都组合安装不成功,纠结很久,终于找到原因.配置apache支持php后apache一直无法成功启动.后来发现php是nts的版本 ...
- vue对象和视图
1 Vue框架 1. vue 与 jQuery 区别 jQuery 仍然是操作DOM的思想, 主要jQuery 用来写页面特效 Vue是前端框架(MVVM) ,对项目进行分层. 处理数据 2 前端框架 ...
- Handler消息机制的一些原理(直接用code讲解)——Android开发
package com.example.handlertest; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Handler; import android ...
- Android属性系统简介
1.简介 在android 系统中,为统一管理系统的属性,设计了一个统一的属性系统.每个属性都有一个名称和值,他们都是字符串格式.属性被大量使用在Android系统中,用来记录系统设置或进程之间的信息 ...
- 【extjs6学习笔记】0.2 准备:类库结构
- IOS照相
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface AddPictureViewController : UIViewController<UIImagePicke ...
- ThreadLocal使用,应用场景,源码实现,内存泄漏
首先,ThreadLocal 不是用来解决共享对象的多线程访问问题的,一般情况下,通过ThreadLocal.set() 到线程中的对象是该线程自己使用的对象,其他线程是不需要访问的,也访问不到的.各 ...
- 电脑连接海信电视 HDMI
注意:我们家的电视是海信的,所以不能代表所有的电视哦~~~ 家里电视有线电视已经过期很长时间了,早就想把电脑连接到电视上用电视做显示器的心了,今天来兴趣了,就弄了一下!!! 用电脑连接电视需要先解决两 ...
- 添加 SSH 公钥
生成 SSH 密钥 ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "YOUR_EMAIL@YOUREMAIL.COM" 获取 SSH 公钥信息 cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pu ...
