1.1 BASIC PROGRAMMING MODEL(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.1.1
private static void exercise111()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.1:");
StdOut.println((0+15)/2);
StdOut.println(2.0e-6 * 100000000.1);
StdOut.println(true && false || true && true);
StdOut.println();
}

1.1.2
private static void exercise112()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.2:");
StdOut.println((1 + 2.236)/2);
StdOut.println(1 + 2 + 3 + 4.0);
StdOut.println(4.1 >= 4);
StdOut.println(1 + 2 + "3");
StdOut.println();
}
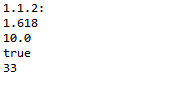
1.1.3
private static void exercise113(String[] args)
{
StdOut.println("1.1.3:");
boolean equalflag = true;
for(int i = 1; i < args.length; i++){ int prev = Integer.parseInt(args[i-1]);
int current = Integer.parseInt(args[i]); if(prev != current){
equalflag = false;
} }
if(equalflag)
StdOut.println("equal");
else
StdOut.println("not equal");
StdOut.println();
}

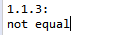




这里不进行异常处理
1.1.4
只有c是对的。
1.1.5
private static void exercise115()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.5:");
StdOut.println("please input two doubles");
double x = StdIn.readDouble();
double y = StdIn.readDouble(); if(x >= 0 && x <= 1 && y >= 0 && y <= 1) {
StdOut.println(true);
}
else {
StdOut.println(false);
}
StdOut.println(); }

1.1.6
private static void exercise116()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.6:");
int f = 0;
int g = 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= 15; i++) {
StdOut.println(f);
f = f + g;
g = f - g;
}
StdOut.println();
}
上述程序求得是f15,其中fn=fn-1 + fn-2 其中f0 = 0, f1 = 1

1.1.7
private static void exercise117()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.7:");
double t = 9.0;
while(Math.abs(t-9.0/t) > 0.01)
t = (9.0/t + t) / 2.0;
StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", t); int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < 1000; i++)
for(int j =0; j < i; j++)
sum++;
StdOut.println(sum); int s = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < 1000; i *= 2)
for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++)
s++;
StdOut.println(s);
StdOut.println(); }

上述程序中
a 不知道求得是什么
b 求得是1 + 2 + 3 + …… + 999 = ((1+999) * 999 )/ 2 = 499500
c 求得是1000 * (⌊log2999⌋ + 1) = 10000
1.1.8
private static void exercise118()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.8:");
//print char type
System.out.println('b');
//print int type
System.out.println('b' + 'c');
//print char type
System.out.println((char) ('a' + 4));
StdOut.println(); }

注释解释了原因
1.1.9
private static void exercise119()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.9:");
StdOut.println("please input a int N");
int n = StdIn.readInt();
StdOut.println(Integer.toBinaryString(n));
StdOut.println();
}

1.1.10
没有给数组分配内存
1.1.11-1.1.13略
1.1.14
private static void exercise1114()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.14:");
StdOut.println("please input a N(Integer) to compute lg2N"); int n = StdIn.readInt();
int lg2n = lg(n); StdOut.printf("the largest int not larger than lg2N is %d\n", lg2n);
StdOut.println();
} public static int lg(int N)
{
int lg2N = 0; //IllegalArgument Exception
if(!(N > 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument N in function lg should larger than 0"); for(N = N/2; N >= 1; N = N/2)
lg2N ++; return lg2N;
}


1.1.15
private static void exercise1115() {
int[] test = {
1,6,3,4,1,4,0,2,7,5,7,6,8,0,5,3,2,8
};
int[] result;
StdOut.println("1.1.15:");
StdOut.printf("total: %d\n", test.length);
result = histogram(test, 9);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(result));
StdOut.println();
}
public static int[] histogram(int[] a, int M)
{
int[] b = new int[M];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
{
//the value of array a should be [0,M)
//if no, ignore
if(a[i] < M && a[i] >= 0) {
b[a[i]] ++;
}
}
return b;
}

1.1.16
private static void exercise1116()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.16:");
StdOut.println(exR1(6));
StdOut.println();
} public static String exR1(int n)
{
if(n <= 0)
{
return "";
}
return exR1(n-3) + n + exR1(n-2) + n;
}

解析:
exR1(6) = exR1(3) + 6 + exR1(4) + 6
exR1(3) = exR1(0) + 3 + exR1(1) + 3
exR1(0) = ""
exR1(1) = exR1(-2) + 1 + exR1(-1) + 1
exR1(-2) = ""
exR1(-1) = ""
exR1(1) = "11"
exR1(3) = "3113"
exR1(4) = exR1(1) + 4 + exR1(2) + 4
exR1(1) = "11" 省略再次递归过程
exR1(2) = exR1(-1) + 2 + exR1(0) + 2
exR1(-1) = ""
exR1(0) = ""
exR1(2) = "22"
exR1(4) = "114224"
exR1(6) = "311361142246"
1.1.17
public static String exR2(int n) {
if(n <= 0)
return "";
String s = exR2(n-3) + n + exR2(n-2) +n;
return s;
}
应该改为上述程序。否则会一直递归下去,没有停止。
1.1.18
private static void exercise1118() {
StdOut.println("1.1.18:");
StdOut.println(mystery(2, 25));
StdOut.println(mystery(3, 11));
StdOut.println(mystery1(2, 25));
StdOut.println(mystery1(3, 11));
StdOut.println("");
}
public static int mystery(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) return 0;
if(b % 2 == 0) return mystery(a+a, b/2);
return mystery(a+a, b/2) + a;
}
public static int mystery1(int a, int b) {
if(b == 0) return 1;
if(b % 2 == 0) return mystery1(a*a, b/2);
return mystery1(a*a, b/2) * a;
}

mystery函数是计算a*b
mystery1函数是计算a^b
1.1.19
private static void exercise1119()
{
StdOut.println("1.1.19:");
for(int N = 0; N < 100; N++)
{
Date date=new Date();
DateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String time=format.format(date);
StdOut.println(time);
StdOut.println(N + " " + fibonacci(N));
} for(int N = 0; N < 100; N++)
{
Date date=new Date();
DateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String time=format.format(date);
StdOut.println(time);
StdOut.println(N + " " + fibonacciarray(N));
}
StdOut.println();
} public static long fibonacci(int N)
{
//when N larger than 92, it will overflow //IllegalArgument Exception
if(N < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument N in function fibonacci should be nonnegative integer"); if(N == 0) return 0;
if(N == 1) return 1;
return fibonacci(N-1) + fibonacci(N-2);
} public static long fibonacciarray(int N)
{
//IllegalArgument Exception
if(N < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument N in function fibonacciarray should be nonnegative integer"); if(N == 0)
return 0;
if(N == 1)
return 1; //when N larger than 92, it will overflow
long[] result = new long[N+1]; result[0] = 0;result[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= N; i++)
{
result[i] = result[i-1] + result[i-2];
} return result[N];
}
测试结果是58,用时49分17秒。
fibonacci函数的递归方式有问题,重复计算了很多。
fibonacciarray函数是用内存来换取时间的做法。
当N大于92时,就会溢出。
1.1.20
private static void exercise1120()
{ StdOut.println("1.1.20:"); for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
StdOut.println(i + " " + lnFactorialN(i));
}
StdOut.println(-1 + " " + lnFactorialN(-1)); StdOut.println(); } public static double lnFactorialN(int N)
{
//IllegalArgument Exception
if(N < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument N in function lnFactorialN should be nonnegative integer"); if(N == 0)
return 0; return Math.log(N) + lnFactorialN(N-1);
}

1.1.21
private static void exercise1121()
{ StdOut.println("1.1.21:");
StdOut.println("please input your name and two integers followed by a newline"); String name = null;
int first, second; if(StdIn.hasNextLine())
{
name = StdIn.readString();
first = StdIn.readInt();
second = StdIn.readInt();
StdOut.printf("%-10s|%-10d|%-10d|%-10.3f", name, first, second, (first*1.0)/second);
} StdOut.println(); }

1.1.22 1.1.23 1.1.28
//exercise 1.1.22
//exercise 1.1.23
//exercise 1.1.28
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class BinarySearch { public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
//a is empty
if(a == null)
return -1; StdOut.println("Search for " + key);
return rank(key, a, 0, a.length - 1, 0);
} public static int rank(int key, int[] a, int lo, int hi, int depth)
{
//a is empty
if(a == null)
return -1; //indented by the depth of the recursion
for(int i = 0; i < depth; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
//print information about lo and hi
StdOut.printf("lo is %d, hi is %d\n", lo, hi); if(lo > hi)
return -1; int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; if(key < a[mid])
return rank(key, a, lo, mid - 1, ++depth);
else if(key > a[mid])
return rank(key, a, mid + 1, hi, ++depth);
else
return mid;
} private static int[] removeDuplicate(int[] input)
{
int[] result;
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(input[0]);
for(int i = 1; i < input.length; i++)
{
if(input[i] != input[i-1])
list.add(input[i]);
} result = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0;i < list.size(); i++)
result[i] = list.get(i); return result;
} public static void main(String[] args) { //it is better to judge the length of args
if(args.length < 2)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: BinarySearch whitelistfile [option]");
StdOut.println("option: + to print numbers from StdIn that are not in the whitelistfile");
StdOut.println("option: - to print numbers from StdIn that are in the whitelistfile");
return;
} int[] whitelist = In.readInts(args[0]);
boolean printwhiteflag = false; if(args[1].equals("+"))
printwhiteflag = false;
else if(args[1].equals("-"))
printwhiteflag = true; Arrays.sort(whitelist);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(whitelist)); whitelist = removeDuplicate(whitelist);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(whitelist)); //when redirect standard input stream to a file
//the application cannot terminate
while(!StdIn.isEmpty())
{
//read key
int key = StdIn.readInt();
int index = rank(key, whitelist); //if not in whitelist, print
if(index == -1 && printwhiteflag ==false)
StdOut.println(key);
//if in whitelist, print
if(index != -1 && printwhiteflag == true)
StdOut.println(key);
} } }


[10, 10, 11, 12, 16, 18, 18, 23, 29, 33, 48, 48, 54, 57, 68, 77, 84, 98]
[10, 11, 12, 16, 18, 23, 29, 33, 48, 54, 57, 68, 77, 84, 98]
Search for 23
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 4, hi is 6
23
Search for 50
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 10
lo is 8, hi is 8
lo is 9, hi is 8
Search for 10
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 0, hi is 2
lo is 0, hi is 0
10
Search for 99
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 14, hi is 14
lo is 15, hi is 14
Search for 18
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 4, hi is 6
lo is 4, hi is 4
18
Search for 23
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 4, hi is 6
23
Search for 98
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 14, hi is 14
98
Search for 84
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
84
Search for 11
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 0, hi is 2
11
Search for 10
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 0, hi is 2
lo is 0, hi is 0
10
Search for 48
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 10
lo is 8, hi is 8
48
Search for 77
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 12
77
Search for 13
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 0, hi is 6
lo is 0, hi is 2
lo is 2, hi is 2
lo is 3, hi is 2
Search for 54
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 10
54
Search for 98
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 14, hi is 14
98
Search for 77
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 12
77
Search for 77
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 14
lo is 12, hi is 12
77
Search for 68
lo is 0, hi is 14
lo is 8, hi is 14
68
1.1.24 1.1.30
//exercise 1.1.24
//exercise 1.1.30
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Euclid { public static void main(String[] args) { //it is better to judge the length of args
if(args.length < 2)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: Euclid p q");
return;
} int p = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int q = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); int result = gcd(p,q); if(result == -1)
StdOut.println("p and q both must larger than 0");
else
StdOut.printf("the greatest common divisor of %d and %d is %d\n", p, q, result); boolean[][] test = isRelaPrime(10, 10); for(int i = 0; i < test.length; i++){ StdOut.printf("%-6d", i);
for(int j = 0; j < test[i].length; j++)
{
StdOut.printf("%-6s", test[i][j] + "");
}
StdOut.printf("\n"); } } public static boolean[][] isRelaPrime(int M, int N)
{
//error
if(M < 0 || N < 0)
return null; boolean[][] result = new boolean[M][N]; for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if(gcd(i, j) == 1)
result[i][j] = true;
else
result[i][j] = false;
} return result;
} public static int gcd(int p, int q)
{
//if p or q isn't nonnegative, error
if(p < 0 || q < 0)
return -1; // StdOut.println(p + " " + q); if(q == 0)
return p; int r = p % q;
return gcd(q, r);
} }


当i或j为0时的处理不知是否正确。
1.1.27
package com.qiusongde;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Exercise1127 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StdOut.println(binomial(10, 5, 0.8) + "");
StdOut.println(binomialarray(10, 5, 0.8) + "");
}
public static double binomial(int N, int k, double p)
{
if(N == 0 && k == 0)
return 1.0;
if (N < 0 || k < 0)
return 0.0;
return (1.0 - p) * binomial(N-1, k, p) + p * binomial(N-1, k-1, p);
}
public static double binomialarray(int N, int k, double p)
{
if(N == 0 && k == 0)
return 1.0;
if(N < 0 || k < 0)
return 0.0;
//k > 0 or N > 0
//index cannot be negative, so add one per dimension
double binomial[][] = new double[N+2][k+2];
//plus one per dimension
for(int i = 0; i < N + 2; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < k + 2; j++)
{
if(i == 1 && j == 1)
binomial[i][j] = 1.0;
else if(i == 0 || j == 0)
binomial[i][j] = 0.0;
else
binomial[i][j] = (1.0 - p) * binomial[i-1][j]
+ p * binomial[i-1][j-1];
}
return binomial[N+1][k+1];
}
}

1.1.29
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Exercise1129 { public static void main(String[] args) { //it is better to judge the length of args
if(args.length < 1)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: BinarySearch whitelistfile");
return;
} int[] whitelist = In.readInts(args[0]); Arrays.sort(whitelist);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(whitelist)); //when redirect standard input stream to a file
//the application cannot terminate
while(!StdIn.isEmpty())
{
//read key
int key = StdIn.readInt();
int smallernumber = rank(key, whitelist);
int equalnumber = count(key, whitelist); StdOut.println("the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: " + smallernumber);
StdOut.println("the number of elements that equal the key is: " + equalnumber); }
} //return the number of elements that are smaller than the key
//the array has been sorted
public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = a.length - 1; while(lo <= hi)
{
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if(key < a[mid])
hi = mid - 1;
else if(key > a[mid])
lo = mid + 1;
else{
//a[mid] == key
while(--mid >= 0 && a[mid] == key);
//mid < 0 or a[mid] < key
return ++mid;
}
}
//if key isn't in array a
//hi is lower than lo
//key is between a[hi] and a[lo], so the number should be lo
return lo;
} //return the number of elements equal to the key
public static int count(int key, int[] a)
{
//the number, lower than key
int index = rank(key, a);
int result = 0; while(index < a.length && a[index++] == key)
result++; return result;
} }


[10, 10, 11, 12, 16, 18, 18, 23, 29, 33, 48, 48, 54, 57, 68, 77, 84, 98]
23
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 7
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
50
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 12
the number of elements that equal the key is: 0
10
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 0
the number of elements that equal the key is: 2
99
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 18
the number of elements that equal the key is: 0
18
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 5
the number of elements that equal the key is: 2
23
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 7
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
98
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 17
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
84
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 16
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
11
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 2
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
10
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 0
the number of elements that equal the key is: 2
48
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 10
the number of elements that equal the key is: 2
77
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 15
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
13
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 4
the number of elements that equal the key is: 0
54
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 12
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
98
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 17
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
77
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 15
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
77
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 15
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
68
the number of elements that are smaller than the key is: 14
the number of elements that equal the key is: 1
1.1.31
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class Exercise1131 { private static class Point
{
double x, y; public Point(double x, double y)
{
//should add some Exception
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
} public double getX()
{
return x;
} public double getY()
{
return y;
}
} public static void main(String[] args) { if(args.length < 2)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: Exercise1131 N p");
StdOut.println("N is a nonnegative integer, p is a double value[0,1]");
return;
} //command argument
int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
double probability = Double.valueOf(args[1]); if(N < 0)
{
StdOut.println("N must be a nonnegative integer");
return;
} if(probability < 0 || probability > 1)
{
StdOut.println("p must be between 0 and 1");
return;
} //the drawing area is between 0 and 1 by default
//coordinates for circle and point
double centerX = 0.5;
double centerY = 0.5;
double R = 0.4;
Point[] points = new Point[N]; //generate points
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
double x = R * Math.cos(360.0 / N * i * Math.PI / 180.0);
double y = R * Math.sin(360.0 / N * i * Math.PI / 180.0);
points[i] = new Point(centerX + x, centerY +y);
} //draw circle
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.01);
StdDraw.circle(centerX, centerY, R); //draw points
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.05);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
StdDraw.point(points[i].getX(), points[i].getY());
} //draw lines
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.GRAY);
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.01);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
//probability, to draw a gray line connecting each pair of points
if(StdRandom.bernoulli(probability))
StdDraw.line(points[i].getX(), points[i].getY(),
points[j].getX(), points[j].getY());
}
} } }




1.1.32
//exercise 1.1.32
package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Histogram { public static void main(String[] args)
{
//usage
if(args.length < 3)
{
StdOut.println("Usage: Histogram N l r");
StdOut.println("Dividing [l,r) into N equal-sized intervals");
StdOut.println("N must larger than 0, r must larger than l");
return;
}
int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); if(!(N > 0))
{
StdOut.println("N must larger than 0");
return;
} double l = Double.parseDouble(args[1]);
double r = Double.parseDouble(args[2]); if(!(r > l))
{
StdOut.println("r must larger than l");
return;
} double interval = (r - l) / N;
int[] count = new int[N];
int sum = 0; while(!StdIn.isEmpty())
{
double temp = StdIn.readDouble();
//count[i] count the range [ l+i*interval, l+(i+1)interval )
int i = (int) ((temp - l) / interval);
//i should be between 0 and N-1, otherwise ignore it
if(i >= 0 && i <= N-1)
{
count[i]++;
sum ++;
}
} //draw the result
StdDraw.setXscale(l, r);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, sum);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double centerX = l + (i + 0.5) * interval;
double centerY = count[i] / 2.0;
double rw = (0.25 * interval);//leave some space
double rh = count[i] / 2.0;
StdDraw.filledRectangle(centerX, centerY, rw, rh);
}
} }


1.1.34
N Y N N N Y Y Y
1.1.35
//exercise 1.1.35
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class DiceSimulation { private static boolean match3Decimal(double a, double b)
{
//a and b are both between 0 and 1
// if(Math.abs(a - b) < 0.0001)
if( (int)(a*1000) == (int)(b*1000))
return true;
else
return false;
} private static boolean checkExactResult(double[] a, double[] b)
{
if(a.length != b.length)
return false; for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
{
if(match3Decimal(a[i], b[i]))
continue;
else
return false;
} return true;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int SIDES = 6;//[1,6]
double[] theoryp = new double[2*SIDES+1];//[0,1] will not be used //count
for(int i = 1; i <= SIDES; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= SIDES; j++)
theoryp[i+j] += 1.0;
//
for(int k = 2; k <= 2*SIDES; k++)
theoryp[k] /= 36.0; StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(theoryp)); int[] simulationcount = new int[2*SIDES+1];
double[] simulationfreq = new double[2*SIDES+1];
long N = 0; while(true)
{
N++;
int a = StdRandom.uniform(1, SIDES + 1);//[1,SIDES]
int b = StdRandom.uniform(1, SIDES + 1);//[1,SIDES]
simulationcount[a+b] ++;
// StdOut.println(N);
// StdOut.println(a + " " + b); //refresh
for(int l = 2; l <= 2*SIDES; l++)
simulationfreq[l] = (simulationcount[l] * 1.0) / N; //match the exact results to three decimal places
if(checkExactResult(theoryp, simulationfreq)){
break;
}
} StdOut.println(N);
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(simulationfreq)); } }
[0.0, 0.0, 0.027777777777777776, 0.05555555555555555, 0.08333333333333333, 0.1111111111111111, 0.1388888888888889, 0.16666666666666666, 0.1388888888888889, 0.1111111111111111, 0.08333333333333333, 0.05555555555555555, 0.027777777777777776]
1016258
[0.0, 0.0, 0.027505810532364814, 0.055725022582848054, 0.08382320237577466, 0.111000356208758, 0.13895979170643674, 0.1663947540880367, 0.1384618866468948, 0.1113191728871999, 0.08348667365964155, 0.05547410204888916, 0.027849227263155616]
1.1.36
//exercise 1136
//exercise 1137
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class ShuffleTest { public static void shuffle(double[] a)
{
int N = a.length; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Exchange a[i] with random element in a[i..N-1]
int r = i + StdRandom.uniform(N-i);
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp; }
} public static void badshuffle(double[] a)
{
int N = a.length; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Exchange a[i] with random element in a[0..N-1]
int r = StdRandom.uniform(N);
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
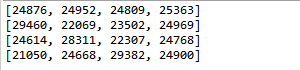
} public static void main(String[] args) { int M = 4;//the size of an array
int N = 100000;//times of shuffle
double[] init = new double[M];//array init
//array result, row i---value, column j----position
//result[i][j]---the number of times i wound up j
int[][] result = new int[M][M]; for(int i=0; i<N; i++){//ith shuffle //initial array init before each shuffle
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++)
init[j] = j; //shuffle array init
shuffle(init);
// badshuffle(init); //record result
for(int k = 0; k < M; k++){
int row = (int)init[k];//value
int col = k;//position
result[row][col] ++;
} } for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(result[i]));
}
} }

1.1.37
//exercise 1136
//exercise 1137
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class ShuffleTest { public static void shuffle(double[] a)
{
int N = a.length; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Exchange a[i] with random element in a[i..N-1]
int r = i + StdRandom.uniform(N-i);
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp; }
} public static void badshuffle(double[] a)
{
int N = a.length; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// Exchange a[i] with random element in a[0..N-1]
int r = StdRandom.uniform(N);
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
} public static void main(String[] args) { int M = 4;//the size of an array
int N = 100000;//times of shuffle
double[] init = new double[M];//array init
//array result, row i---value, column j----position
//result[i][j]---the number of times i wound up j
int[][] result = new int[M][M]; for(int i=0; i<N; i++){//ith shuffle //initial array init before each shuffle
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++)
init[j] = j; //shuffle array init
// shuffle(init);
badshuffle(init); //record result
for(int k = 0; k < M; k++){
int row = (int)init[k];//value
int col = k;//position
result[row][col] ++;
} } for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
StdOut.println(Arrays.toString(result[i]));
}
} }
1.1.39
//exercise 1.1.39
package com.qiusongde; import java.util.Arrays; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; public class RandomMatch { private static int[] geneSixDigitArray(int N)
{
int[] result = new int[N]; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
result[i] = StdRandom.uniform(1000000);
} return result;
} public static int rank(int key, int[] a)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = a.length - 1; while(lo <= hi)
{
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if(key < a[mid])
hi = mid - 1;
else if(key > a[mid])
lo = mid + 1;
else{
return mid;
}
} return -1;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int T = 40;
int[] valueNs = {1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000}; for(int i = 0; i < valueNs.length; i++)
{//for each value of N double averagecommon = 0; for(int j = 0; j < T; j++)
{//for every trial int commonnumber = 0;
//generate two arrays of N values
int[] testone = geneSixDigitArray(valueNs[i]);
int[] testtwo = geneSixDigitArray(valueNs[i]); //sorting before search
Arrays.sort(testtwo);
//seraching
for(int k = 0; k < testone.length; k++)
{
if(rank(testone[k], testtwo) != -1)
commonnumber ++;
} averagecommon += commonnumber;
} //average number over the T trials
averagecommon = averagecommon / (double)T;
StdOut.printf("%d\t%f\n", valueNs[i], averagecommon);
}
} }

1.1 BASIC PROGRAMMING MODEL(算法 Algorithms 第4版)的更多相关文章
- Algorithms 4th - 1.1 Basic Programming Model - CREATIVE PROBLEMS
欢迎交流 1.1.26 public class TestApp { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = StdIn.readInt(); ...
- Algorithms 4th - 1.1 Basic Programming Model - EXERCISES
欢迎交流 1.1.1 a. 7 b. 200.0000002 c. true 1.1.2 a. 1.618 b. 10.0 c. true d. 33 1.1.3 public class MainA ...
- 1.2 Data Abstraction(算法 Algorithms 第4版)
1.2.1 package com.qiusongde; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.St ...
- Udacity并行计算课程笔记-The GPU Programming Model
一.传统的提高计算速度的方法 faster clocks (设置更快的时钟) more work over per clock cycle(每个时钟周期做更多的工作) more processors( ...
- 【Udacity并行计算课程笔记】- lesson 1 The GPU Programming Model
一.传统的提高计算速度的方法 faster clocks (设置更快的时钟) more work over per clock cycle(每个时钟周期做更多的工作) more processors( ...
- PatentTips - Heterogeneous Parallel Primitives Programming Model
BACKGROUND 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates generally to a programming model ...
- .NET “底层”异步编程模式——异步编程模型(Asynchronous Programming Model,APM)
本文内容 异步编程类型 异步编程模型(APM) 参考资料 首先澄清,异步编程模式(Asynchronous Programming Patterns)与异步编程模型(Asynchronous Prog ...
- HttpWebRequest - Asynchronous Programming Model/Task.Factory.FromAsyc
Posted by Shiv Kumar on 23rd February, 2011 The Asynchronous Programming Model (or APM) has been aro ...
- Programming Model
上级:https://www.cnblogs.com/hackerxiaoyon/p/12747387.html Dataflow Programming Model 数据流的开发模型 Levels ...
随机推荐
- 【温故知新】——HTML基础重要知识点复习
前言:本文是自己在学习课程中的课程笔记,这里用来温故知新的,并非本人原创. 一.HTML快速入门(重点) 1.HTML概述 1.什么是HTML HTML : Hyper Text Markup Lan ...
- openssl之BIO系列之22---Cipher类型的BIO
Cipher类型BIO ---依据openssl doc\crypto\bio_f_cipher.pod翻译和自己的理解写成 (作者:DragonKing, Mail: wzhah@263.net , ...
- 【Excle数据透视表】如何快速选取所有标签并标注黄色底纹
如下图:需要把所有标签标注为黄色底纹该如何操作呢? 步骤 单击数据透视表任意单元格→数据透视表工具→分析→选择→整个数据透视表→选择→标签→开始→字体组合中"填充颜色" 第一次选择 ...
- js 解析json字符串
server端返回的数据例如以下: {"list":[{"id":1,"name":"汉族"},{"id&qu ...
- C# 调用API接口处理公共类 自带JSON实体互转类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Net ...
- C#:用SqlBulkCopy来实现批量插入数据
SqlBulkCopy是.net2.0的新特性,平时用的很少,但是其功能却是非常强大,对于批量插入数据性能非常优越 代码 /// /// bulk插入/// private void BulkInse ...
- ETL拉链算法汇总大全
拉链算法总结大全: 一.0610算法(追加) 1.删除仓库表的载入日期是本次载入日期的数据,以支持重跑 delete from xxx where start_dt >=$tx_date; 2. ...
- 用C语言解决迷宫问题
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define ROW 10 #define COL 10 /*迷宫中位置信息*/ typedef ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(七)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(六)>中研究了恐龙的跳跃过程,这一篇研究恐龙与障碍物之间的碰撞检测. 碰撞盒子 游戏中采用的是矩形(非旋转矩形)碰撞.这类碰撞优点是计算比较 ...
- oracle中v$sga_target_advice的用途
v$sga_target_advice:该视图可用于建议SGA大小设置是否合理. SELECT a.sga_size,--sga期望大小 a.sga_size_factor,-- ...
