剑指offer26:将二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
1 题目描述
2 思路和方法
在二叉搜索树中,每个结点都有两个分别指向其左、右子树的指针,左子树结点的值总是小于父结点的值,右子树结点的值总是大于父结点的值。
在双向链表中,每个结点也有两个指针,它们分别指向前一个结点和后一个结点。
所以这两种数据结构的结点是一致,二叉搜索树和双向链表,只是因为两个指针的指向不同而已举个例子,如下图中的二叉搜索树,转换后的双向链表为:
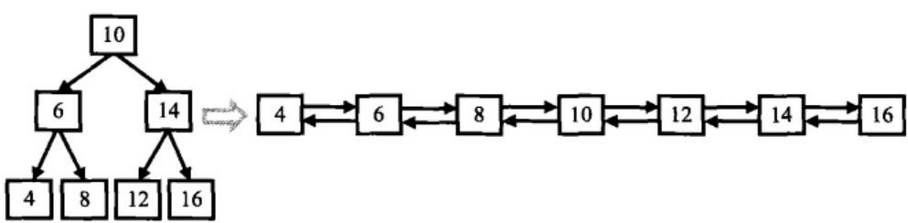
思路:
为了减少指针的变换次数,并让操作更加简单,在转换成排序双向链表时,原先指向左子结点的指针调整为链表中指向前一个结点的指针,原先指向右子结点的指针调整为链表中指向下一个结点的指针。
由于要求链表是有序的,可以借助二叉树中序遍历,因为中序遍历算法的特点就是从小到大访问结点。当遍历访问到根结点时,假设根结点的左侧已经处理好,只需将根结点与上次访问的最近结点(左子树中最大值结点)的指针连接好即可。进而更新当前链表的最后一个结点指针。
方法:
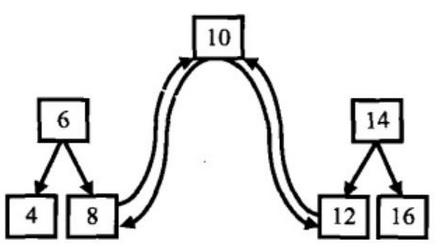
如上图的二叉排序树,就分成了根结点、以结点为根的左子对和以结点为根的右子树。从变换的链表中我们可以看到,应当把结点的left指针指向结点,把结点的right指针指向结点,而由于我们采用的是中序遍历,所以当我们遍历到结点时,结点的左子树已经转化为一个有序的双向链表,而结点是这个已经转化的双向链表的尾结点,所以我们应该用一个变量last_node来保存最后一个结点的指针,以便在与根结点连续时使用。然后把这个变量last_node的值更新为指向根结点。对于结点的右子树,采取相似的操作。
3 C++核心代码
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode *cur = pRootOfTree; //为临时节点用来遍历树的节点,初始值为根节点root
TreeNode *pre = pRootOfTree; // 用于保存中序遍历序列的上一节点
TreeNode *head = pRootOfTree; //用于记录双向链表的头结点
bool isFirst = true; //判断是否为左子树链表的第一个节点
while(cur||!st.empty())
{
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
cur = st.top(); //此时的cur为左子树最左边的节点
st.pop();
if(isFirst) //假如是左子树链表的第一个节点
{ //将cur赋值给root节点
head = pre = cur; //将中序遍历序列中的第一个节点记为根节点(root node)
isFirst = false;
}
else
{
pre->right = cur;
cur->left = pre;
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur->right;
}
return head;
}
};
4 C++完整代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; //二叉树结点定义
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int Value;
BinaryTreeNode* Left;
BinaryTreeNode* Right;
}; //创建二叉树结点
BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode();
pNode->Value = value;
pNode->Left = NULL;
pNode->Right = NULL;
return pNode;
} //连接树结点
void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight)
{
if (pParent != NULL)
{
pParent->Left = pLeft;
pParent->Right = pRight;
}
} //中序遍历
void InOrderPrintTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
//遍历左边
if (pRoot->Left != NULL)
{
InOrderPrintTree(pRoot->Left);
}
//根
cout << "value of this node is " << pRoot->Value << endl;
//遍历右边
if (pRoot->Right != NULL)
{
InOrderPrintTree(pRoot->Right);
} }
else
{
cout << "this node is null." << endl;
} } //转换排序二叉树为双向链表
void Convert(BinaryTreeNode* pNode, BinaryTreeNode** pLastNodeLnList)
{
if (pNode == NULL)
{
return;
} BinaryTreeNode* pCurrent = pNode; //左子树转换,遍历到左子树的叶子结点
if (pCurrent->Left != NULL)
{
Convert(pCurrent->Left, pLastNodeLnList);
}
pCurrent->Left = *pLastNodeLnList;
if ((*pLastNodeLnList) != NULL)
{
(*pLastNodeLnList)->Right = pCurrent;
}
*pLastNodeLnList = pCurrent; //右子树转换
if (pCurrent->Right != NULL)
{
Convert(pCurrent->Right, pLastNodeLnList);
} } //获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* Convert(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
//指向双向链表的尾结点
BinaryTreeNode* pLastNodeInList = NULL;
//转换排序二叉树为双向链表
Convert(pRoot, &pLastNodeInList); //求双向链表的头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = pLastNodeInList;
while (pHeadOfList != NULL&&pHeadOfList->Left != NULL)
{
pHeadOfList = pHeadOfList->Left;
}
return pHeadOfList;
} //打印双向链表
void PrintList(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = pRoot; while (pNode != NULL)
{
cout << pNode->Value << " ";
pNode = pNode->Right;
} cout << endl;
cout << "PrintList ends." << endl << endl; } // ====================测试代码====================
void Test1()
{
// 10
// / \
// 6 14
// /\ / \
// 4 8 12 16 cout << "The Test1:" << endl; //创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(); //连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16); //中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode10);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode10);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList); } void Test2()
{
// 5
// /
// 4
// /
// 3
// /
// 2
// /
// cout << "The Test2:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(); //连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, NULL); //中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode5);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode5);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList); } void Test3()
{
// 1
// \
// 2
// \
// 3
// \
// 4
// \
// cout << "The Test3:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode();
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(); //连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, pNode2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, NULL, pNode3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, NULL, pNode4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, NULL, pNode5); //中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList); } void Test4()
{
// 树中只有1个结点 cout << "The Test4:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(); //连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, NULL); //中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList); } void Test5()
{
// 树中没有结点 cout << "The Test5:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(NULL); //连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, NULL); //中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList); } void main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
system("pause");
}
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/u012477435/article/details/83351659
https://blog.csdn.net/yanxiaolx/article/details/52073221
https://blog.csdn.net/jyy305/article/details/76383723(Solution中函数不同时)
https://blog.csdn.net/ljianhui/article/details/22338405(完整代码另一个版本)
剑指offer26:将二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。的更多相关文章
- 【Java】 剑指offer(36) 二叉搜索树与双向链表
本文参考自<剑指offer>一书,代码采用Java语言. 更多:<剑指Offer>Java实现合集 题目 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不 ...
- Go语言实现:【剑指offer】二叉搜索树与双向链表
该题目来源于牛客网<剑指offer>专题. 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. Go语言实现: type T ...
- 【剑指Offer】二叉搜索树与双向链表 解题报告(Python)
[剑指Offer]二叉搜索树与双向链表 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): 剑指Offer 题目地址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interview ...
- 【剑指offer】二叉搜索树转双向链表
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/26623795 题目描写叙述: 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表. ...
- 剑指Offer 26. 二叉搜索树与双向链表 (二叉搜索树)
题目描述 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. 题目地址 https://www.nowcoder.com/practic ...
- 《剑指offer》-二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. 题目的描述不是很习惯.题目的意思是把二叉树从左到右遍历,相当于双向链表的遍历. 其实 ...
- 【剑指offer】二叉搜索树与双向链表
一.题目: 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. 二.思路: 对于一棵搜索二叉树来说,中序遍历得到的即是有序的结果,所以整 ...
- 【剑指offer】二叉搜索树转双向链表,C++实现
原创博文,转载请注明出处! # 题目 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. 二叉树节点的定义 struct TreeNod ...
- 剑指OFFER之二叉搜索树与双向链表(九度OJ1503)
题目描述: 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向. 输入: 输入可能包含多个测试样例.对于每个测试案例,输入的第一行为一个数 ...
随机推荐
- windows游戏编程 绘图基础
本系列文章由jadeshu编写,转载请注明出处.http://blog.csdn.net/jadeshu/article/details/22451353 作者:jadeshu 邮箱: jades ...
- sqlserver 存储过程的新建与执行
if Exists(select * from sysobjects where NAME = 'insert_custominfo' and type='P') drop procedure ins ...
- c++容器 算法 迭代
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { // 创建一个向量存储 int ...
- tomcat发布web项目
转:https://www.cnblogs.com/skyblue-li/p/7888951.html Tomcat是一种Web服务器,我们自己做好了一个Web项目,就可以通过Tomcat来发布.服务 ...
- jenkins的任务卡住
今天做jenkins任务的时候,发现一个启动后,一直卡住,在那转圈圈,其实这个时候,任务已经执行完了. 经过分析,因为这个任务是启动一个web服务,直接在机器上执行时,直接占用一个终端. 解决办法,放 ...
- pwn学习日记Day11 《程序员的自我修养》读书笔记
阅读基础 计算机系统软件体系结构采用一种层的结构--计算机科学领域的任何问题都可以通过增加一个间接的中间层来解决. 多线程的优势: 1.某个操作可能会陷入长时间等待,等待的线程会进入睡眠状态,无法继续 ...
- Linux设备驱动程序 之 get_free_page
get_free_page 如果模块需要分配大块的内存,使用面向页的分配会有很多优点: 分配页面可使用下面的函数: unsigned long get_zeroed_page(gfp_t gfp_ma ...
- 解决JAVA单步调试键盘输入被JDB占用的问题
解决JAVA单步调试键盘输入被JDB占用的问题 问题来源: 在完成本周任务时,编写的代码中含有Scanner类,编译及运行过程均正确,但使用JDB单步调试时,运行到输入行无法在JDB内部输入变量值. ...
- Linux学习笔记:fuser和lsof
fuser 和 lsof 可以用于系统安全检查.用fuser查看哪些用户和进程在某些地方作什么:fuser -cu /root 简略显示fuser -muv /mnt3 分列显示 lsof 拥有更多的 ...
- java.util.HashTable (JDK1.8)
1.Hashtable 特性(先总结下面会详细讲的): 1.Hashtable 存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射,其底层实现是一个Entry数组+链表. 2.Hashtable是线程安全( ...
