python-静态方法staticmethod、类方法classmethod、属性方法property
Python的方法主要有3个,即静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def foo(x): print "executing foo(%s)"%(x) class A(object): def foo(self,x): print "executing foo(%s,%s)"%(self,x) @classmethod def class_foo(cls,x): print "executing class_foo(%s,%s)"%(cls,x) @staticmethod def static_foo(x): print "executing static_foo(%s)"%x a=A() |
这个self和cls是对类或者实例的绑定,对于一般的函数来说我们可以这么调用foo(x),这个函数就是最常用的,它的工作跟任何东西(类,实例)无关.对于实例方法,我们知道在类里每次定义方法的时候都需要绑定这个实例,就是foo(self, x),为什么要这么做呢?因为实例方法的调用离不开实例,我们需要把实例自己传给函数,调用的时候是这样的a.foo(x)(其实是foo(a, x)).类方法一样,只不过它传递的是类而不是实例,A.class_foo(x).注意这里的self和cls可以替换别的参数,但是python的约定是这俩,还是不要改的好.
对于静态方法其实和普通的方法一样,不需要对谁进行绑定,唯一的区别是调用的时候需要使用a.static_foo(x)或者A.static_foo(x)来调用.
| \ | 实例方法 | 类方法 | 静态方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a = A() | a.foo(x) | a.class_foo(x) | a.static_foo(x) |
| A | 不可用 | A.class_foo(x) | A.static_foo(x) |
类的普通方法
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 静态类方法
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@staticmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 加上装饰器后运行会报错,原因是方法变为一个普通函数,脱离的与类的关系,不能引用构造函数中的变量了。
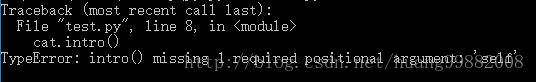
使用场景举例:python内置方法os中的方法,可以直接使用的工具包,跟类没关系。
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 报错信息
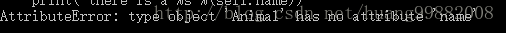
如果换成
class Animal(object):
name = 'cat'
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 可以正常运行。
结论:类方法只能调用类变量,不能调用实例变量
属性方法@property 把一个方法变为(伪装成)类属性。因为类属性的实质是一个类变量,用户可以调用变量就可以修改变量。某些特定场景要限制用户行为,就用到静态方法。
@property广泛应用在类的定义中,可以让调用者写出简短的代码,同时保证对参数进行必要的检查,这样,程序运行时就减少了出错的可能性。(摘自廖雪峰的博客)
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@property
def intro(self,food):
print('there is a %s eating %s'%(self.name,food))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 报错:
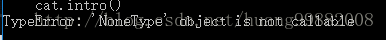
- 方法不能正常调用。如果要调用,如下:
cat.intro- 是这样的话,方法就没办法单独传入参数。如果要传入参数,如下:
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@property
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s eating %s'%(self.name,food))
@intro.setter
def intro(self,food):
pass
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro- cat.intro还有其他操作getter deleter等等。
一:staticmethod
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') @staticmethod
def get_instance():
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print('a id=', id(a))
print('b id=', id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
二:classmethod
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') @classmethod
def get_instance(cls):
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print('a id=', id(a))
print('b id=', id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
三:类属性方法
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') def get_instance():
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
四:__new__
常见的方法, 代码如下:
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __new__(cls, *args, **kw):
if not cls.instance:
# cls.instance = object.__new__(cls, *args)
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, *args, **kw)
return cls.instance a = Singleton()
b = Singleton()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
五:装饰器
代码如下:
def Singleton(cls):
instances = {} def getinstance():
if cls not in instances:
instances[cls] = cls()
return instances[cls]
return getinstance @Singleton
class MyClass:
pass a = MyClass()
b = MyClass()
c = MyClass() print(id(a))
print(id(b))
print(id(c))
六:元类
class Singleton(type):
def __init__(cls, name, bases, dct):
super(Singleton, cls).__init__(name, bases, dct)
cls.instance = None def __call__(cls, *args):
if cls.instance is None:
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args)
return cls.instance class MyClass(object):
__metaclass__ = Singleton a = MyClass()
b = MyClass()
c = MyClass()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
print(id(c))
print(a is b)
print(a is c)
或者:
class Singleton(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs["_instance"] = None
return super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls._instance is None:
cls._instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls._instance class Foo(object):
__metaclass__ = Singleton x = Foo()
y = Foo()
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
class Singleton(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs['instance'] = None
return super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls.instance is None:
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls.instance class Foo(metaclass=Singleton):
pass x = Foo()
y = Foo()
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
七:名字覆盖
class Singleton(object):
def foo(self):
print('foo') def __call__(self):
return self Singleton = Singleton() Singleton.foo() a = Singleton()
b = Singleton()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
python-静态方法staticmethod、类方法classmethod、属性方法property的更多相关文章
- Python 静态方法、类方法和属性方法
Python 静态方法.类方法和属性方法 静态方法(staticmethod) staticmethod不与类或者对象绑定,类和实例对象都可以调用,没有自动传值效果,Python内置函数staticm ...
- Python 静态方法,类方法,属性方法
方法的使用 静态方法 - 只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类或实例中的任何属性. class Dog(object): def __init__(self,name): self.nam ...
- Python静态方法、类方法、属性方法
静态方法 使用静态方法以后,相当于把下面的函数和类的关系截断了,它的作用相当于是类下面的一个独立函数,不会自动传入参数self. class people:..... @staticmethod de ...
- Python的3个方法:静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法
Python的方法主要有3个,即静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法,如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ...
- Python面向对象静态方法,类方法,属性方法
Python面向对象静态方法,类方法,属性方法 属性: 公有属性 (属于类,每个类一份) 普通属性 (属于对象,每个对象一份) 私有属性 (属于对象,跟普通属性相似,只是不能通过对象直接访问) 方法: ...
- python中静态方法、类方法、属性方法区别
在python中,静态方法.类方法.属性方法,刚接触对于它们之间的区别确实让人疑惑. 类方法(@classmethod) 是一个函数修饰符,表是该函数是一个类方法 类方法第一个参数是cls,而实例方法 ...
- Python的程序结构[1] -> 方法/Method[1] -> 静态方法、类方法和属性方法
静态方法.类方法和属性方法 在 Python 中有三种常用的方法装饰器,可以使普通的类实例方法变成带有特殊功能的方法,分别是静态方法.类方法和属性方法. 静态方法 / Static Method 在 ...
- 面向对象【day08】:静态方法、类方法、属性方法(九)
本节内容 概述 静态方法 类方法 属性方法 总结 一.概述 前面我们已经讲解了关于类的很多东西,今天讲讲类的另外的特性:静态方法(staticmethod).类方法(classmethod).属性方法 ...
- Python笔记_第四篇_高阶编程_实例化方法、静态方法、类方法和属性方法概念的解析。
1.先叙述静态方法: 我们知道Python调用类的方法的时候都要进行一个实例化的处理.在面向对象中,一把存在静态类,静态方法,动态类.动态方法等乱七八糟的这么一些叫法.其实这些东西看起来抽象,但是很好 ...
- python 面向对象静态方法、类方法、属性方法、类的特殊成员方法
静态方法:只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类或实例中的任何属性. 在类中方法定义前添加@staticmethod,该方法就与类中的其他(属性,方法)没有关系,不能通过实例化类调用方法使用 ...
随机推荐
- windows环境通过cmd命令到ftp上下载文件到linux服务器
转自:http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/6525d4b1300912ac7d2e941b.html
- 如何通过Keil将程序正确的下载进flash中
前面介绍了一些创建工程和调试的基本步骤,在这里准备介绍一下如何正确的将Keil程序在仿真调试中下载到flash.这里再次涉及到了debug的窗口. 工具/原料 Keil uVision 4/5 ...
- poj_1860 SPFA
题目大意 有N种货币,M个兑换点,每个兑换点只能相互兑换两种货币.设兑换点A可以兑换货币C1和C2,给出rate(C1--C2)表示1单位的C1货币可以兑换出的C2货币数目,rate(C2--C1)表 ...
- poj_3260 动态规划
题目大意 顾客拿着N种硬币(币值为value[i], 数量为c[i])去买价值为T的东西,商店老板也有同样N种币值的硬币,但是数量不限.顾客买东西可能需要用硬币找零来使得花出去的钱为T,求顾客给老板的 ...
- android基础---->AccessibilityService的简单使用(一)
AccessibilityService类可以帮助我们实现监听手机上别的应用,以下做一个简单的总结.我总是勇敢的离开一个人 却不懂如何巧妙的靠近一个人. AccessibilityService的使用 ...
- handlebears使用
Handlebars 文档笔记: http://www.ghostchina.com/handlebars-wen-dang-bi-ji/ Handlebars模板引擎中的each嵌套及源码浅读: h ...
- 【BZOJ3572】[Hnoi2014]世界树 虚树
[BZOJ3572][Hnoi2014]世界树 Description 世界树是一棵无比巨大的树,它伸出的枝干构成了整个世界.在这里,生存着各种各样的种族和生灵,他们共同信奉着绝对公正公平的女神艾莉森 ...
- 【BZOJ4262】Sum 单调栈+线段树
[BZOJ4262]Sum Description Input 第一行一个数 t,表示询问组数. 第一行一个数 t,表示询问组数. 接下来 t 行,每行四个数 l_1, r_1, l_2, r_2. ...
- axios post传参后台无法接收问题
起因是在angular项目中使用axios发送post请求,向后台传参后台一直无法接收,网上查了有说是请求头设置不对,需要把Content-Type:application/x-www-form-ur ...
- MySQL按照汉字的拼音排序、按照首字母分类
项目中有时候需要按照汉字的拼音排序,比如联系人列表.矿物分类等,有的还需要按拼音字母从A到Z分类显示. 如果存储汉字的字段编码使用的是GBK字符集,因为GBK内码编码时本身就采用了拼音排序的方法(常用 ...
