Java基础—ArrayList源码浅析
注:以下源码均为JDK8的源码
一、 核心属性
基本属性如下:
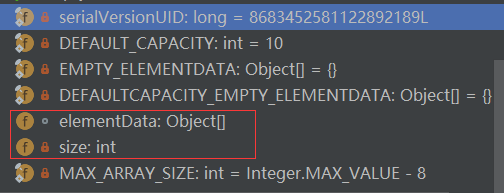
核心的属性其实是红框中的两个:
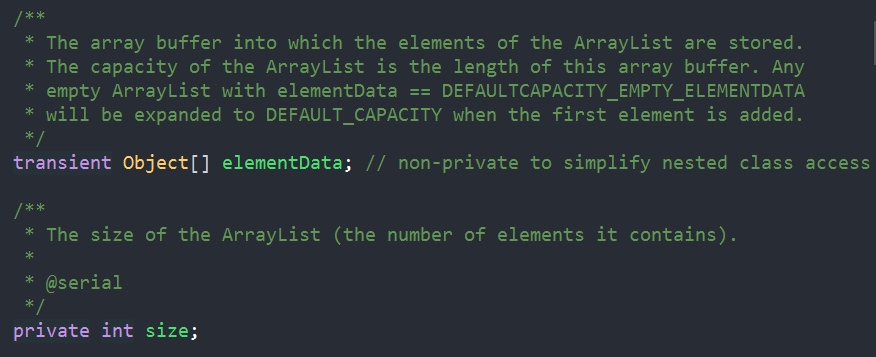
//从注释也容易看出,一个是集合元素,一个是集合长度(注意是逻辑长度,即元素的个数,而非数组长度)
其中:transient指明序列化时请忽略。
二、构造器
一共有3个构造器:

1.构造指定容量的ArrayList

2.默认构造器
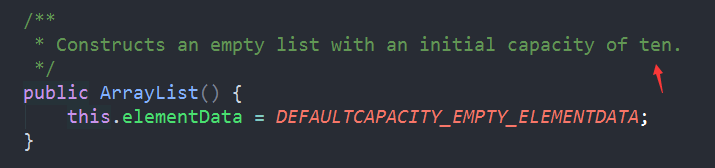
//可以看到,默认初始容量为10(基本属性中的DEFAULT_CAPACITY)
而 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是一个空数组,所有默认构造器初始化的都指向它,目的是为了防止我们创建过多的无用的List
如果创建ArrayList时用的是无参构造器,则第一次插入时会进行一次扩容并且扩到默认数组大小10
3.使用collection参数的构造器

//接收一个集合进行构造,按照迭代器返回的顺序排列
更多容器初始化的介绍,参考是清浅池塘知乎专栏:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27873515
三、添加元素
一共有5个(包含2个重载方法)
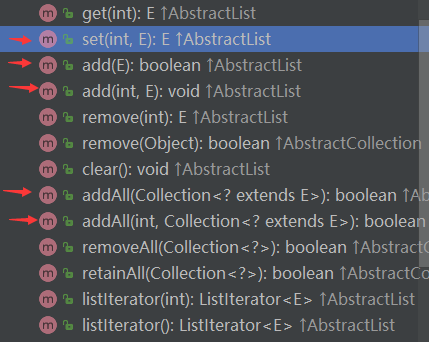
//由于是基于数组进行实现的,我们只要抓住它的特点,就能读懂总体的思路
1.set(int,E),使用新元素,替代指定位置旧元素

//比较容易读懂的一个方法:检查下标->取得旧元素->替代->返回新元素
2.add(E)/add(int,E),包含两个重载方法:在末尾添加元素与在指定位置添加元素
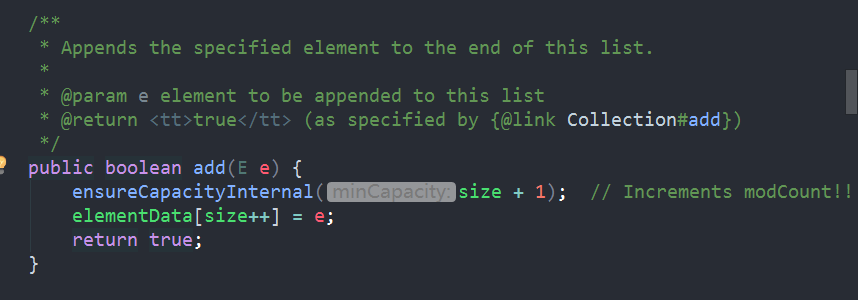
//先检查容量是否需要扩容(扩容算法不在这里展开),再在结尾添加元素(size+1)
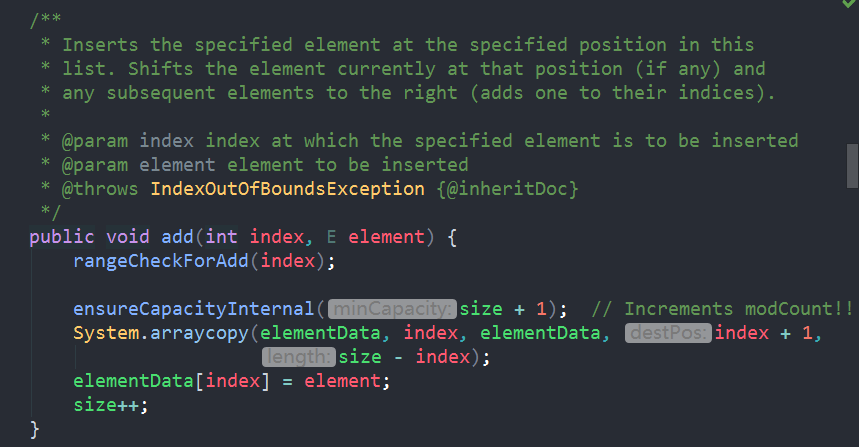
//同样的,涉及下标的都先检查下标,之后检查是否需要扩容,之后,由于是数组,先右移Index+1的元素,再添加
3.addAll(),两个addAll方法,与上面类似,一个为在末尾添加,一个在指定位置添加,顺序均为迭代器返回的顺序,这里就不展开:
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation
* is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is
* undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this
* list is nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
} /**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
四、获取元素
一个我们常见的get方法:
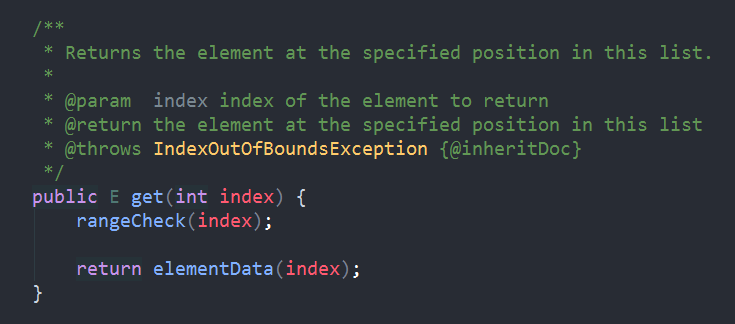
//比较简单的下标检查,获取元素
五、删除元素
3个基本的删除方法:

1.remove(int)/remove(Object),两个重载方法,分别是按照下标和按照元素删除:

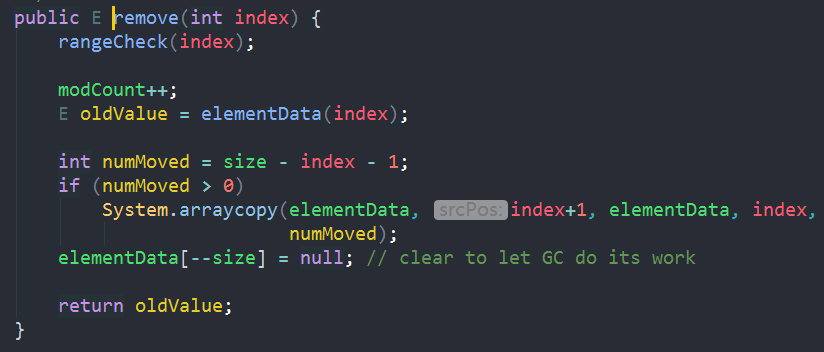
//范围检查->修改次数modCount加1->得到将要删除的元素,被删除元素后的元素向前进一位,末尾元素置空。
关于modCount:
ArrayList也采用了快速失败的机制,通过记录modCount参数来实现。在面对并发的修改时,迭代器很快就会完全失败,而不是冒着在将来某个不确定时间发生任意不确定行为的风险。
在使用迭代器遍历的时候,如果使用ArrayList中的remove(int index) remove(Object o) remove(int fromIndex ,int toIndex) add等方法的时候都会修改modCount,在迭代的时候需要保持单线程的唯一操作,如果期间进行了插入或者删除,就会被迭代器检查获知,从而出现运行时异常


//先检查要删除的元素在不在,存在则删除返回true,不存在返回false
2.removeRange(int,int),按照范围删除,实际是将elementData从toIndex位置开始的元素向前移动到fromIndex,然后将toIndex位置之后的元素全部置空顺便修改size。这里就不展开频率使用不高的范围删除方法了:
/**
* Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between
* {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
* Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index).
* This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements.
* (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* fromIndex >= size() ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved); // clear to let GC do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
size = newSize;
}
清空元素也比较容易看懂:
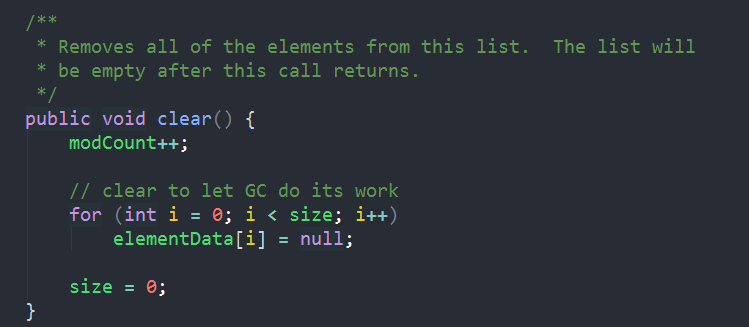
//元素置Null与size置0
在ArrayList中,底层数组存/取元素效率非常的高(get/set),时间复杂度是O(1),而查找,插入和删除元素效率不高,时间复杂度为O(n)。
并且由源码也知道,频繁地插入删除会导致底层数组地复制,这个应当由 LinkedList来弥补它地补足了。
Java基础—ArrayList源码浅析的更多相关文章
- Java基础 ArrayList源码分析 JDK1.8
一.概述 本篇文章记录通过阅读JDK1.8 ArrayList源码,结合自身理解分析其实现原理. ArrayList容器类的使用频率十分频繁,它具有以下特性: 其本质是一个数组,因此它是有序集合 通过 ...
- Java基础——集合源码解析 List List 接口
今天我们来学习集合的第一大体系 List. List 是一个接口,定义了一组元素是有序的.可重复的集合. List 继承自 Collection,较之 Collection,List 还添加了以下操作 ...
- Java集合——ArrayList源码详解
) ArrayList 实现了RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable三个标记接口,表示它自身支持快速随机访问,克隆,序列化. public clas ...
- java的Iterator源码浅析
在java的集合中,List接口继承Collection接口,AbstractList类实现了List接口,在AbstractList中的内部类Itr实现了Iterator接口 ArrayList实现 ...
- Java中ArrayList源码分析
一.简介 ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组.每个ArrayList实例都有自己的容量,该容量至少和所存储数据的个数一样大小,在每次添加数据时,它会使用ensureCapacity()保 ...
- Java集合ArrayList源码解读
最近在回顾数据结构,想到JDK这样好的代码资源不利用有点可惜,这是第一篇,花了心思.篇幅有点长,希望想看的朋友认真看下去,提出宝贵的意见. :) 内部原理 ArrayList 的3个字段 priva ...
- ArrayList源码浅析(jdk1.8)
ArrayList的实质就是动态数组.所以可以通过下标准确的找到目标元素,因此查找的效率高.但是添加或删除元素会涉及到大量元素的位置移动,所以效率低. 一.构造方法 ArrayList提供了3个构造方 ...
- Java集合-ArrayList源码解析-JDK1.8
◆ ArrayList简介 ◆ ArrayList 是一个数组队列,相当于 动态数组.与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长.它继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAcc ...
- 【thinking in java】ArrayList源码分析
简介 ArrayList底层是数组实现的,可以自增扩容的数组,此外它是非线程安全的,一般多用于单线程环境下(Vector是线程安全的,所以ArrayList 性能相对Vector 会好些) Array ...
随机推荐
- zt C++标准库set类型
C++标准库set类型 分类: C++编程语言 2012-11-06 10:53 909人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 目录(?)[-] 在set中添加元素 从set中获取元素 set容器只是单纯的键 ...
- git fetch 和 git pull 的区别
Git中从远程的分支获取最新的版本到本地有这样2个命令: 1. git fetch:相当于是从远程获取最新版本到本地,不会自动merge git fetch origin master git log ...
- JavaScript小游戏--2048(移动端)
HTML5中新添加了很多事件,但是由于他们的兼容问题不是很理想,应用实战性不是太强,所以在这里基本省略,咱们只分享应用广泛兼容不错的事件,日后随着兼容情况提升以后再陆续添加分享.今天为大家介绍的事件主 ...
- 开源项目之kisso
kisso开源项目:https://gitee.com/baomidou/kisso 一.简介 kisso = cookie sso 基于 Cookie 的 SSO 中间件,它是一把快速开发 ja ...
- mybatis分步查询与延迟加载
1.分步查询 先查询用户的部门 部门Mapper.xml <resultMap id="rMap" type="com.yunqing.mybatis.bean.D ...
- CentOS 安装postgresql
CentOS 安装postgresql 添加postgresql官网安装源 在/etc/yum.repos.d目录下新建pgdg-10-centos.repo 文件 [pgdg10] name=P ...
- unittest单元测试框架之unittest工作原理(一)
1.Unittest 核心组件 test case.test suite.test runner.test fixture 2.unittest 静态图 Testcase:一个 testcase 就是 ...
- 【转载】RETE算法研究
本文转自:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-drools/ RETE算法是大多数规则引擎采用的一种模式匹配算法,比如开源的Drool ...
- 04JavaScript语法
1.JavaScript 语法 JavaScript 是一个脚本语言. 它是一个轻量级,但功能强大的编程语言 2.JavaScript 字面量 在编程语言中,一般固定值称为字面量,如 3.14. 数字 ...
- Python模块、包、异常、文件(案例)
Python模块.包.异常.文件(案例) python.py #模块 # Python中的模块(Module),是一个Python文件,以.py文件结尾,包含了Python对象定义和Python语句, ...
