java框架之Struts2(3)-OGNL&ValueStack
OGNL
概述
OGNL 是 Object-Graph Navigation Language 的缩写,它是一种第三方的、功能强大的表达式语言,通过它简单一致的表达式语法,可以存取对象的任意属性,调用对象的方法,遍历整个对象的结构图,实现字段类型转化等功能。它使用相同的表达式去存取对象的属性。
入门
java工程下使用
package com.zze.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
com.zze.bean.User
@Test
public void test1() throws OgnlException {
// 获得 context
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
// 获得根对象
Object root = context.getRoot();
Object value = Ognl.getValue("'hello Struts2'.length()", context, root);
System.out.println(value);
/*
13
*/
}
例:调用对象方法
@Test
public void test2() throws OgnlException {
// 获得 context
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
// 获得根对象
Object root = context.getRoot();
// 执行表达式:@类名@方法名
Object value = Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@random()", context, root);
System.out.println(value);
/*
0.6367826736345159
*/
}
例:调用静态方法
@Test
public void test3() throws OgnlException {
// 获得 context
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(12);
context.setRoot(user);
// 表达式直接写放入 root 中对象的属性名称即可取到对应属性名的值
Object name = Ognl.getValue("name", context, context.getRoot());
Object age = Ognl.getValue("age", context, context.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(age.getClass());
/*
张三
12
class java.lang.Integer
*/
}
例:访问 Root 中的数据
@Test
public void test4() throws OgnlException {
// 获得 context
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(12);
context.put("user", user);
// 表达式直接写放入 context 中 #key 即可取到对应值
Object name = Ognl.getValue("#user.name", context, context.getRoot());
Object age = Ognl.getValue("#user.age", context, context.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
/*
张三
12
*/
}
例:访问 context 中的数据
Struts中使用
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--访问对象方法--%>
<s:property value="'hello Struts2'.length()"/>
<hr>
<%--
访问静态方法
需要设置常量:struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess = true
--%>
<s:property value="@java.lang.Math@random()"/>
</body>
</html>
例:访问对象方法 & 静态方法
特殊符号
#
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
request.setAttribute("str", "托马斯的小货车");
%>
<s:property value="#request.str"/>
</body>
</html>
'#' 号可以用来获取值栈中 context 区域的数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--构建 List--%>
<s:iterator var="letter" value="{'a','b','c'}">
<s:property value="letter"/>|<s:property value="#letter"/>
</s:iterator>
<hr>
<%--构建 Map--%>
<s:iterator var="entry" value="#{1:'aa',2:'bb',3:'cc'}">
<s:property value="key"/>|<s:property value="#entry.key"/>
<s:property value="value"/>|<s:property value="#entry.value"/>
<br>
</s:iterator>
</body>
</html>
'#' 号可以用来构建一个 Map
%
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
request.setAttribute("name", "托马斯");
%>
<s:property value="#request.name"/>
<br>
<%--
按如下嵌套标签会报错:
<s:textfield name="name" value="<s:property value="#request.name"/>" />
可以利用 %{} 强制解析表达式
--%>
<s:textfield name="name" value="%{#request.name}" />
</body>
</html>
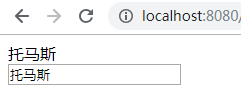
'%' 号可以用来强制解析字符串为表达式
$
<validators>
<field name=”intb”>
<field-validator type=”int”>
<param name=”min”>10</param>
<param name=”max”>100</param>
< message>BAction-test校验:数字必须为${min}为${max}之间!</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
</validators>
'$' 号可以用来在配置文件中引用值栈中的值
ValueStack
概述
ValueStack 是 Struts 的一个接口,字面意义为值栈,OgnlValueStack 是 ValueStack 的实现类,客户端发起一个请求 Struts2 架构会创建一个 Action 实例同时创建一个 OgnlValueStack 值栈实例,OgnlValueStack 贯穿整个Action 的生命周期,Struts2 中使用 OGNL 将请求 Action 的参数封装为对象存储到值栈中,并通过 OGNL 表达式读取值栈中对象的属性值。
ValueStack 其实类似一个数据中转站,Struts2 中的数据都保存在值栈中。
值栈的内部结构
ValueStack 中有两个主要的区域:
- root:其实就是一个 ArrayList。
- context:其实就是一个 Map。
context 中放置了 web 开发中常用对象的引用,例如:
request:原生 Servlet 请求对象。
session:会话对象。
application:ServletContext对象
parameters:请求参数对象。
attr:依次在 request、session、application 寻找匹配值。
所说的操作值栈,通常指的是操作 ValueStack 中的 root 区域。
在 request、session、application 中存取值就相当于操作 ValueStack 的 context 区域。
值栈与ActionContext的关系
首先请求时会经过核心过滤器,查看核心过滤器的 doFilter 方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter#doFilter
创建 ActionContext 就在第 11 行,查看 createActionContext 方法:
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ActionContext ctx;
Integer counter = 1;
Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER);
if (oldCounter != null) {
counter = oldCounter + 1;
}
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (oldContext != null) {
// detected existing context, so we are probably in a forward
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap<String, Object>(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null));
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter);
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.PrepareOperations#createActionContext
直接从 14 行开始看,在 14 行创建了值栈对象 stack ,接着在 16 行将 stack.getContext() 传给了 ActionContext 来创建 ActionContext 实例,而 stack.getContext() 中拥有对值栈的引用,也就是说这部分执行完后在 ActionContext 中是直接可以取到值栈的。
结论:ActionContext 之所以能访问 Servlet 的 API ,是因为在其内部有值栈的引用,而值栈的 context 部分又拥有对 Servlet 常用对象(request、session、servletContext)的引用。
ValueStack的获得
通过上一节,已经知道是可以通过 ActionContext 获取到值栈的引用的。接着看核心过滤器的 doFilter 方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter#doFilter
看到 21 行,这行用来开始执行 Action,查看 executeAction 方法:
public void executeAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, mapping);
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.ExecuteOperations#executeAction
接着看到 serviceAction 方法:
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping)
throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping);
// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
if (nullStack) {
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
ActionProxy proxy = getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
proxy.execute();
}
// If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
if (!nullStack) {
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
logConfigurationException(request, e);
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (handleException || devMode) {
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} else {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.Dispatcher#serviceAction
直接看 41 行,当值栈不为空时,将值栈的引用放入了 request 域。
结论:除了通过 ActionContext 获得值栈,我们还可以通过 request 获取到值栈。
所以在 Action 中我们可以通过如下代码获取值栈:
// 获取值栈方式 1 、通过 ActionContext ValueStack valueStack1 = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); // 获取值栈方式 2 、通过 request // STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY = "struts.valueStack"; ValueStack valueStack2 = (ValueStack)ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY); System.out.println(valueStack1 == valueStack2); // true
操作值栈
方法一:在Action中提供属性的get方法
默认情况下,Struts2 会将访问的 Action 对象压入值栈,所以在 Action 中提供的属性会随之存入值栈:
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Test1Action extends ActionSupport {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
this.name = "张三";
this.age = 19;
return super.execute();
}
}
Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:property value="name"/>
<s:property value="age"/>
</body>
</html>
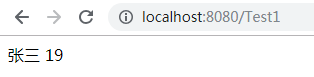
jsp
方法二:手动调用值栈方法
我们已经知道了如何在 Action 中获取值栈,当然也可以在 Action 中操作值栈:
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Test2Action extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack().set("name","张三");
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack().set("age",20);
return super.execute();
}
}
Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:property value="name"/>
<s:property value="age"/>
</body>
</html>
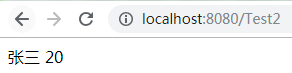
jsp
查看值栈数据
Struts2 为方便我们调试,给我们提供了一个标签,我们用这个标签可以直接查看到值栈中的数据:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:debug/>
</body>
</html>
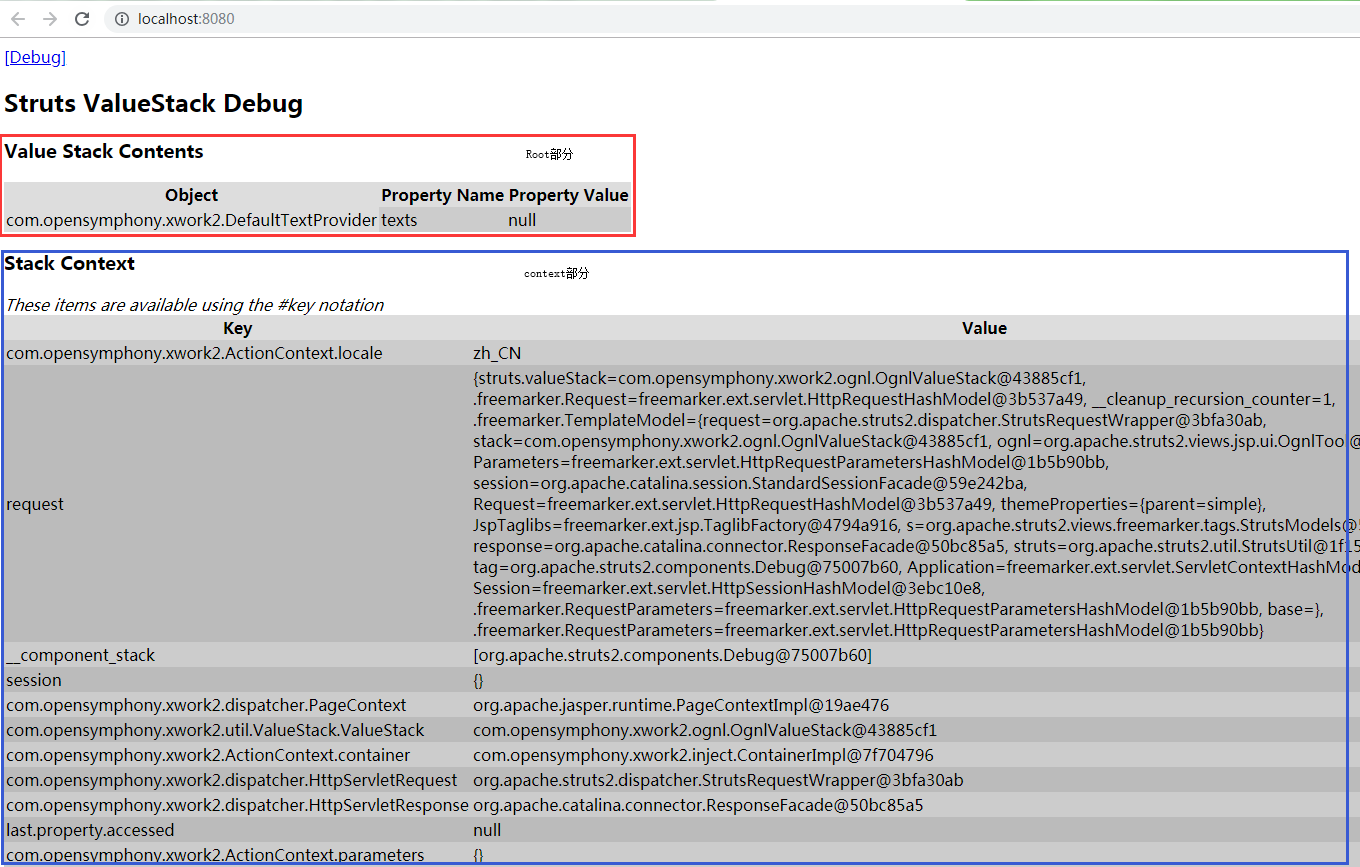
jsp
标签获取值栈数据
已经知道如何操作值栈,现在我们看一下如何在页面中获取到值栈中的数据。
Struts2 为简易我们在页面中获取值栈数据的操作,给我们提供了一些标签,看如下示例:
准备
package com.zze.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
com.zze.bean.User
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true"/>
<package name="test" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="*" class="com.zze.action.{1}Action">
<result>/index.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
struts.xml
例1:root中获取JavaBean对象
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.zze.bean.User;
public class Test1Action extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(29);
// 将 user 压入栈顶
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack().push(user);
return super.execute();
}
}
com.zze.action.Test1Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--可直接访问栈顶对象属性--%>
<s:property value="name"/>
<s:property value="age"/>
<s:debug/>
</body>
</html>
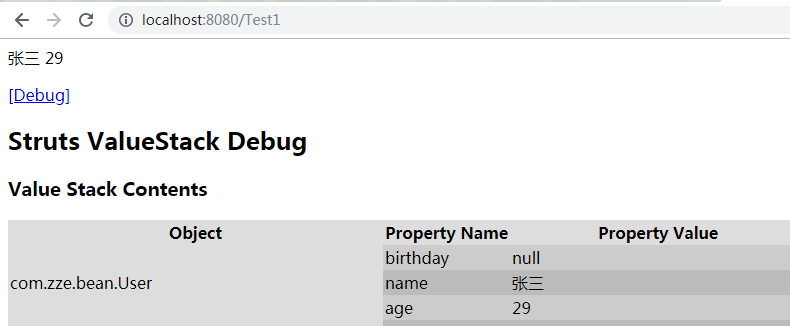
index.jsp
例2:root中获取JavaBean对象集合
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.zze.bean.User;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test2Action extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName("张三");
user1.setAge(29);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setName("李四");
user2.setAge(30);
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack().set("userList",userList);
return super.execute();
}
}
com.zze.action.Test2Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:property value="userList[0].name"/>
<s:property value="userList[0].age"/>
<s:property value="userList[1].name"/>
<s:property value="userList[1].age"/>
<s:debug/>
</body>
</html>
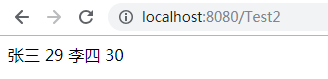
index.jsp
例3:context中获取域字段
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Test3Action extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext.getContext().put("name","张三");
ActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("name","李四");
ActionContext.getContext().getApplication().put("name","王五");
return super.execute();
}
}
com.zze.action.Test3Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:property value="#request.name"/>
<s:property value="#session.name"/>
<s:property value="#application.name"/>
<s:debug/>
</body>
</html>
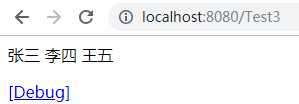
index.jsp
获取 root 区域中数据直接使用对象属性名即可,如果是 map 则使用 key;获取 context 中属性需在 key 前加上 ‘#’。
EL获取值栈数据
获取值栈数据的方式除了上面通过 Struts2 提供的标签的方式,还可以通过 EL 表达式获取,例如:
package com.zze.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.zze.bean.User;
public class Test4Action extends ActionSupport {
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setName("托马斯");
ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack().push(user);
return super.execute();
}
}
com.zze.action.Test4Action
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
${name}
<s:debug/>
</body>
</html>
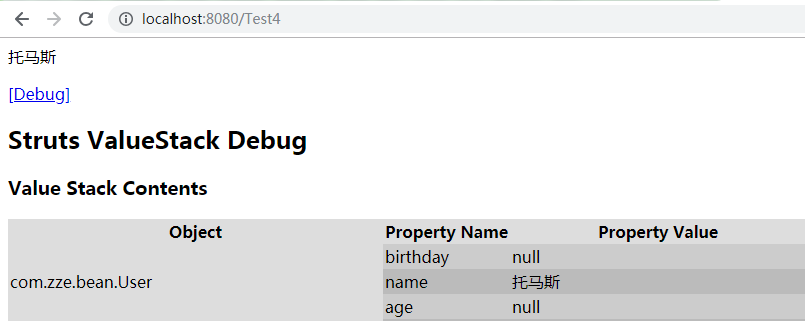
index.jsp
我们知道,EL 表达式本来就只能获取 11 个隐式对象中的数据,为什么在这里还能获取值栈中的数据呢?当然是 Struts2 做了手脚,依旧从核心过滤器开始查看源码:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter#doFilter
看到第 13 行,通过 prepare.wrapRequest(request) 将原生 request 进行了包装,查看 wrapRequest 方法:
public HttpServletRequest wrapRequest(HttpServletRequest oldRequest) throws ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = oldRequest;
try {
// Wrap request first, just in case it is multipart/form-data
// parameters might not be accessible through before encoding (ww-1278)
request = dispatcher.wrapRequest(request);
ServletActionContext.setRequest(request);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ServletException("Could not wrap servlet request with MultipartRequestWrapper!", e);
}
return request;
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.PrepareOperations#wrapRequest
继续进入 dispatcher.wrapRequest 方法:
public HttpServletRequest wrapRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
// don't wrap more than once
if (request instanceof StrutsRequestWrapper) {
return request;
}
String content_type = request.getContentType();
if (content_type != null && content_type.contains("multipart/form-data")) {
MultiPartRequest mpr = getMultiPartRequest();
LocaleProvider provider = getContainer().getInstance(LocaleProvider.class);
request = new MultiPartRequestWrapper(mpr, request, getSaveDir(), provider, disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup);
} else {
request = new StrutsRequestWrapper(request, disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup);
}
return request;
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.Dispatcher#wrapRequest
看 8-14 行,如果不是文件上传类的请求,将会执行第 13 行,也就是说普通情况下请求 Action 该方法返回的 request 就是 StrutsRequestWrapper 的实例,查看该类:
package org.apache.struts2.dispatcher;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequestWrapper;
import static org.apache.commons.lang3.BooleanUtils.isTrue;
public class StrutsRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private static final String REQUEST_WRAPPER_GET_ATTRIBUTE = "__requestWrapper.getAttribute";
private final boolean disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup;
public StrutsRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest req) {
this(req, false);
}
public StrutsRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest req, boolean disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup) {
super(req);
this.disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup = disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup;
}
public Object getAttribute(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("You must specify a key value");
}
if (disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup || key.startsWith("javax.servlet")) {
return super.getAttribute(key);
}
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
Object attribute = super.getAttribute(key);
if (ctx != null && attribute == null) {
boolean alreadyIn = isTrue((Boolean) ctx.get(REQUEST_WRAPPER_GET_ATTRIBUTE));
if (!alreadyIn && !key.contains("#")) {
try {
// If not found, then try the ValueStack
ctx.put(REQUEST_WRAPPER_GET_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
ValueStack stack = ctx.getValueStack();
if (stack != null) {
attribute = stack.findValue(key);
}
} finally {
ctx.put(REQUEST_WRAPPER_GET_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.FALSE);
}
}
}
return attribute;
}
}
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.StrutsRequestWrapper
可以看到这个类其实就是将 getAttribute 方法进行了重写,当通过该方法获取一个值时,如果通过原生 request 未获取到,则继续从值栈中寻找这个 key 对应的值并返回。
而我们通过 EL 表达式获取值实际上也会调用 request.getAttribute 方法,此时 Struts2 对该方法进行了包装增强,这就是使用 EL 能获取到值栈数据的原因。
java框架之Struts2(3)-OGNL&ValueStack的更多相关文章
- Java - 框架之 Struts2
一. Package 标签 1. 标签属性:name : 包的名称,只有在一个项目中不重名即可.extends : 继承哪个包,默认为 struts-default.name ...
- Java框架之Struts2(一)
在学习Struts2之前,我们要知道Java为什么要有反射机制呢?反射机制可以说是填补Java不能动态访问某一个类的空白.利用反射机制,动态的创建一个对象.动态的访问类的某个属性,而且访问哪一个属性自 ...
- java框架之Struts2(4)-拦截器&标签库
拦截器 概述 Interceptor (拦截器):起到拦截客户端对 Action 请求的作用. Filter:过滤器,过滤客户端向服务器发送的请求. Interceptor:拦截器,拦截的是客户端对 ...
- Java框架之Struts2(六)
一.OGNL表达式语言 Ognl Object Graphic Navigation Language(对象图导航语言),它是一种功能强大的表达式语言(Expression Language,简称为E ...
- java框架篇---struts之OGNL详解
OGNL(Object Graph Navigation Language),是一种表达式语言.使用这种表达式语言,你可以通过某种表达式语法,存取Java对象树中的任意属性.调用Java对象树的方法. ...
- java框架之Struts2(1)-简介及入门
简介 Struts2 是一个基于 MVC 设计模式的 Web 应用框架,它本质上相当于一个 servlet,在 MVC 设计模式中,Struts2 作为控制器 (Controller) 来建立模型与视 ...
- Java框架之Struts2(二)
一.Action 配置说明 //请求的直接转发 <package name="packageUser" namespace="" extends=&quo ...
- java框架之Struts2(2)-访问Servlet API及请求数据封装
准备 为后面测试示例编写代码及配置如下: package com.zze.bean; import java.util.Date; public class User { private String ...
- java框架篇---Struts2的处理流程
一.Struts2的处理流程: 客户端产生一个HttpServletRequest的请求,该请求被提交到一系列的标准过滤器(Filter)组建链中(如ActionContextCleanUp:它主要是 ...
随机推荐
- 【Log】SLF4J简单入门
SLF4J介绍 SLF4J,即简单日志门面(Simple Logging Facade for Java),不是具体的日志解决方案,它只服务于各种各样的日志系统.按照官方的说法,SLF4J是一个用于日 ...
- oracle获取过去两年的今天时间
获取过去两年的今天时间: SELECT last_day(ADD_MONTHS(ADD_MONTHS(sysdate,-12), ROWNUM - 1)) as monthlist FROM DUAL ...
- 微信小程序——购物车结算
项目需要做个购物车结算功能,先分析需求: 1.全选,反选的功能.当选中的个数 = 购物车的数量时,勾选全选按钮,反之则取消选中全选按钮: 2.改变选中状态时,计算总价和总数量: 3.单个产品的数量加减 ...
- Java代码实现文件添加数字签名、验证数字签名
Linux下实现加签.验签 1.使用OpenSSL 生成公钥和密钥: #用 OpenSSL, Linux 上自带,常用命令如下: #生成 RSA 私钥(传统格式的) openssl genrsa -o ...
- Android大图片之缩略图,以及对原图依照指定宽高裁剪成缩略图
<Android大图片之变换缩略图,以及对原始大图片依照指定宽.高裁剪成缩略图> 在Android的ImageView载入图像资源过程中,出于性能和内存开销的须要.有时候须要把一个原 ...
- ELK日志收集
目前日志的痛点 运维要经常登陆到服务器上拿日志给开发.测试 每次都是出问题后才去看日志,不能提前通过日志预判问题 如果是集群服务,日志将要从多台机器取 开发人员搞出来的日志不规范,没有标准.日志目录不 ...
- Spark学习之常用算子介绍
1. reduceByKey reduceByKey的作用对像是(key, value)形式的rdd,而reduce有减少.压缩之意,reduceByKey的作用就是对相同key的数据进行处理,最终每 ...
- linux signal
1) SIGHUP 本信号在用户终端连接(正常或非正常)结束时发出, 通常是在终端的控制进程结束时, 通知同一session内的各个作业, 这时它们与控制终端不再关联. 登录Linux时,系统会分配给 ...
- nginx 报错 connect() failed (111: Connection refused) while connecting to upstream
公司网站搬迁到新服务器后,发现站点访问不了,network里面提示502,查看相关的server配置,感觉没有什么问题,经过测试发现txt.html.等非php文件能够直接访问,也就是php访问不了, ...
- CentOS7安装Go环境
下载go(我的当前目录是/data/work)$wget https://studygolang.com/dl/golang/go1.10.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz$tar -xvf ...
