Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2) A B C 水 找规律(大数对小数取模) dp
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One day Dima and Alex had an argument about the price and quality of laptops. Dima thinks that the more expensive a laptop is, the better it is. Alex disagrees. Alex thinks that there are two laptops, such that the price of the first laptop is less (strictly smaller) than the price of the second laptop but the quality of the first laptop is higher (strictly greater) than the quality of the second laptop.
Please, check the guess of Alex. You are given descriptions of n laptops. Determine whether two described above laptops exist.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of laptops.
Next n lines contain two integers each, ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n), where ai is the price of the i-th laptop, and bi is the number that represents the quality of the i-th laptop (the larger the number is, the higher is the quality).
All ai are distinct. All bi are distinct.
If Alex is correct, print "Happy Alex", otherwise print "Poor Alex" (without the quotes).
2
1 2
2 1
Happy Alex
题意:n个物品 a为价格 b为物品的质量 若满足价格越高质量越好 输出Poor Alex 反之输出Happy Alex
题解:水 注意结构体排序的一个细节....orz
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
struct node
{
int a,b;
}N[];
bool cmp(struct node aa,struct node bb)
{
return aa.a<bb.a;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int flag=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d %d",&N[i].a,&N[i].b);
if(N[i].a!=N[i].b)
flag=;
}
if(flag)
cout<<"Happy Alex"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Poor Alex"<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Fedya studies in a gymnasium. Fedya's maths hometask is to calculate the following expression:
(1n + 2n + 3n + 4n) mod 5
for given value of n. Fedya managed to complete the task. Can you? Note that given number n can be extremely large (e.g. it can exceed any integer type of your programming language).
The single line contains a single integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 10105). The number doesn't contain any leading zeroes.
Print the value of the expression without leading zeros.
4
4
124356983594583453458888889
0
Operation x mod y means taking remainder after division x by y.
Note to the first sample:
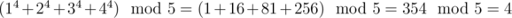
题意:计算(1n + 2n + 3n + 4n) mod 5 n为次幂 n为大数
枚举n的值可以发现规律 只要n%4==0则输出4 否则输出0 剩下的问题就是大数对小数取模了
题解:大数对小数取模 从高位到低位 具体看代码
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
char a[];
int main()
{
cin>>a;
n=strlen(a);
int exm=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
exm=exm*+a[i]-'';
exm%=;
}
if(exm==)
cout<<""<<endl;
else
cout<<""<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alex doesn't like boredom. That's why whenever he gets bored, he comes up with games. One long winter evening he came up with a game and decided to play it.
Given a sequence a consisting of n integers. The player can make several steps. In a single step he can choose an element of the sequence (let's denote it ak) and delete it, at that all elements equal to ak + 1 and ak - 1 also must be deleted from the sequence. That step brings ak points to the player.
Alex is a perfectionist, so he decided to get as many points as possible. Help him.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) that shows how many numbers are in Alex's sequence.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Print a single integer — the maximum number of points that Alex can earn.
2
1 2
2
3
1 2 3
4
9
1 2 1 3 2 2 2 2 3
10
Consider the third test example. At first step we need to choose any element equal to 2. After that step our sequence looks like this[2, 2, 2, 2]. Then we do 4 steps, on each step we choose any element equals to 2. In total we earn 10 points.
题意:给你n个值 每次取出一个值ak 则删除所有的ak +1 ,ak -1 一直到最后一个数
输出 取出的值的和的最大值
题解:这n个值的范围为1 ≤ ai ≤ 10^5 先标记 记录每个数i出现的次数dis[i]
转移方程 dp[i]=max(dp[i-2]+i*dis[i],dp[i-1]) 也就是相当于判断当前这个数是被删除?还是被取出?
i*dis[i]表示数i对结果的贡献 dp[i]代表以i为结尾的所要求的最大值
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
ll a[];
ll dis[];
ll ans[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
memset(ans,,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
dis[a[i]]++;
}
ans[]=dis[];
for(int i=;i<=1e5;i++)
ans[i]=max(ans[i-]+i*dis[i],ans[i-]);
printf("%I64d\n",ans[]);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2) A B C 水 找规律(大数对小数取模) dp的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #327 (Div. 2) C Median Smoothing(找规律)
分析: 三个01组合只有八种情况: 000 s001 s010 0011 s100 s101 1110 s111 s 可以看出只有010,101是不稳定的.其他都是稳定的,且连续地出现了1或0,标记为 ...
- Codeforces Round #272 (Div. 2) D.Dreamoon and Sets 找规律
D. Dreamoon and Sets Dreamoon likes to play with sets, integers and . is defined as the largest p ...
- DP Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A. Boredom
题目传送门 /* 题意:选择a[k]然后a[k]-1和a[k]+1的全部删除,得到点数a[k],问最大点数 DP:状态转移方程:dp[i] = max (dp[i-1], dp[i-2] + (ll) ...
- 递推DP Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) A. Boredom
题目传送门 /* DP:从1到最大值,dp[i][1/0] 选或不选,递推更新最大值 */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #in ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem(水.......没做出来)+C题
Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem A. Sweet Problem time limit per test 1 second memory ...
- Codeforces Round #334 (Div. 2) A. Uncowed Forces 水题
A. Uncowed Forces Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/604/pro ...
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A, B , C 水, map ,拓扑
A. Contest time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 2)AB
http://codeforces.com/contest/456/problem/A A. Laptops time limit per test 1 second memory limit per ...
随机推荐
- Andriod——区别DVM与JVM
区别DVM与JVM 1.首要差别 Dalvik: 基于寄存器,编译和运行都会更快些 JVM: 基于栈, 编译和运行都会慢些 2.字节码的区别 Dalvik: 执行.dex格式的字节码,是对.class ...
- 10 notorious computer virus
The history of computer virus is the same as computer history. With more and more powerful computers ...
- django.test.client 使用随记
import os,sys,django; sys.path.append("\\path\\to\\mysite")#ATTETION!,Err: "unable to ...
- wpf custom control
最近在做WPF,记录一下自定义控件的制作过程,源码请点击:源码. 1.目标 实现一个如图所示的可增减的数字框: 2.先画Template 可以在Generic.xaml中画,也可以用MergedDic ...
- JDBC 连接池
数据库连接池(connection pool) JDBC数据库连接池的必要性 在使用开发基于数据库的web程序时,传统的模式基本是按以下步骤: 在主程序(如servlet.beans)中建立数据库连接 ...
- 一步步学习JSON
什么是Json json是JavaScript Object Notation(javascript对象表示法)的缩写,是一种轻量的数据格式,是基于javascript的一个子集.与XML一样,jso ...
- JSON初步
1.什么是JSON (1)JSON(Java Script Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换语言, 以文本字符串为基础,且易于让人阅读 XML就是一个重量级的数据交换语言 (2) ...
- java基础之 创建对象的几种方式
有4种显式地创建对象的方式: 1.用new语句创建对象,这是最常用的创建对象的方式. 2.运用反射手段,调用java.lang.Class或者java.lang.reflect.Constructor ...
- error: unknown field 'ioctl' specified in initializer
error message: 原因: 从2.6.36开始,file_operations结构发生了重大变化 具体看 xx../include/linux/fs.h定义: 取消了原先的 int (*i ...
- matlab函数调用及数据传递
http://www.cnblogs.com/duanp/archive/2008/11/29/Matlab-GUIDE.html函数调用 在一个m文件中,可以定义多个函数,但是文件名一定要与第一个函 ...
