java异常处理课后作
1、动手动脑

源码
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
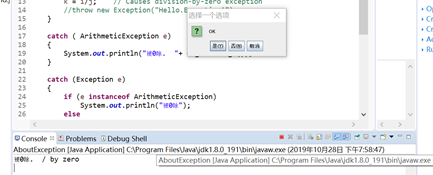
java把可能会发生错误的代码放进try语句块中,catch语句块中的代码用于处理错误,不管是否有异常发生,finally语句块中的语句始终保证被执行。如果没有提供合适的异常处理代码,JVM会结束掉整个应用程序。
2、动手动脑

源码
public class CatchWho {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
结果
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/内层try-catch
发生ArithmeticException
源码
public class CatchWho2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
结果
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/外层try-catch
3、动手动脑

源码
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
. System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
in Level 2
in Level 3
Level 3:class java.lang.ArithmeticException
In Level 3 finally
In Level 2 finally
In Level 1 finally
4、动手动脑

源码
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
}
catch(Exception e)
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
Exception is thrown in main
class MyException extends Exception
{
public MyException(String messege)
{
super(messege);
}
}
{
public int score(int a) throws MyException //当a<0或a>100时,抛出一个自定义异常
{
if(a<0 || a>100)
{
throw new MyException("成绩输入有误");//抛出异常
}
return a;//返回a
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyException
{
try
{
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
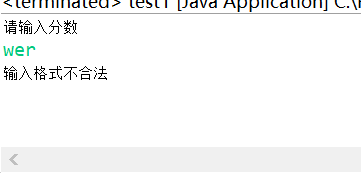
System.out.println("请输入分数");
int n = 0,i;
n=scan.nextInt();
numbertest k=new numbertest();
try
{
int t=k.score(n);
i=n/10;
switch(i)
{
case 10:
case 9:
System.out.println("优");break;
case 8:
System.out.println("良");break;
case 7:
System.out.println("中");break;
case 6:
System.out.println("及格");break;
default:
System.out.println("不及格");break;
}
}
catch(MyException e)
{
System.out.println(e);//输出
}
}
catch(Exception e)//由于变量定义为int型,所以输入字符时,则输出该异常信息
{
System.out.println("输入格式不合法");//输出
}
}
}

java异常处理课后作的更多相关文章
- java程序中的经常出现的的异常处理课后总结
一.JDK中常见的异常情况 1.常见异常总结图 2.java中异常分类 Throwable类有两个直接子类: (1)Exception:出现的问题是可以被捕获的 (2)Error:系统错误,通常由JV ...
- Java 异常处理笔记
Java程序运行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两类: §错误(Error):JVM系统内部错误.资源耗尽等严重情况 §违例(Exception): 其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,例如: ...
- 谈谈你对Java异常处理机制的理解
先谈谈我的理解:异常处理机制可以说是让我们编写的程序运行起来更加的健壮,无论是在程序调试.运行期间发生的异常情况的捕获,都提供的有效的补救动作,任何业务逻辑都会存在异常情况,这时只需要记录这些异常情况 ...
- 理解java异常处理机制
1. 引子 try…catch…finally恐怕是大家再熟悉不过的语句了,而且感觉用起来也是很简单,逻辑上似乎也是很容易理解.不过,我亲自体验的“教训”告诉我,这个东西可不是想象中的那么简单.听话. ...
- 2017.4.7 java异常处理总结
目录 1.java异常处理的几种错误做法 2.异常处理示例 3.常用异常 4.异常类的继承关系 5.异常处理机制 6.Throw和Throws的区别 7.e.toString(), e.getCaus ...
- Java异常处理总结Exception\Error
Java异常处理总结Exception\Error 2012-12-28 08:17:17| 分类: JAVA | 标签:java |举报|字号 订阅 Java异常处理总结 ...
- 札记:Java异常处理
异常概述 程序在运行中总会面临一些"意外"情况,良好的代码需要对它们进行预防和处理.大致来说,这些意外情况分三类: 交互输入 用户以非预期的方式使用程序,比如非法输入,不正当的操作 ...
- java异常处理(父子异常的处理)
我当初学java异常处理的时候,对于父子异常的处理,我记得几句话“子类方法只能抛出父类方法所抛出的异常或者是其子异常,子类构造器必须要抛出父类构造器的异常或者其父异常”.那个时候还不知道子类方法为什么 ...
- Java 异常处理
异常是程序中的一些错误,但并不是所有的错误都是异常,并且错误有时候是可以避免的. 比如说,你的代码少了一个分号,那么运行出来结果是提示是错误java.lang.Error:如果你用System.out ...
随机推荐
- 关于map 的几种方式
java为数据结构中的映射定义了一个接口java.util.Map;它有四个实现类,分别是==HashMap Hashtable LinkedHashMap 和TreeMap.== Map主要用于存储 ...
- JavaScript语法规则+JavaScript数据类型
JavaScript: ECMAScript + BOM +DOM javascript 标识符命名规则: 1.只能是字母.数字.下划线.$ 2.不能以数字开头 3.不能使用关键字和保留字 省略var ...
- 基于Docker的Consul集群实现服务发现
服务发现 其实简单说,服务发现就是解耦服务与IP地址之间的硬绑定关系,以典型的集群为例,对于集群来说,是有多个节点的,这些节点对应多个IP(或者同一个IP的不同端口号),集群中不同节点责任是不一样的. ...
- Spring Boot源码(五):BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring BeanFactory加载Bean后调用, BeanPostProcessor是Bean初始化前后调用. BeanFactoryPost ...
- centos 源码编译mysql5.7
1- 源码安装mysql5.7 [自动安装脚本:https://files-cdn.cnblogs.com/files/lemanlai/make_mysql.sh] groupadd mysql u ...
- 剑指offer-面试题42-连续子数组的最大和-动态规划
/*题目; 输入一个整形数组(可能有正数和负数),求数组中连续子数组(最少有一个元素)的最大和. 要求时间复杂度为O(n). 先输入数组的格式,再依次输入数组的值.*//*思路: f(i) = pDa ...
- HTTP Status 404 – 未找到 spring mvc
HTTP Status 404 – 未找到 Type Status Report 消息 /houseSale//houseSaleController/houseSaleList 描述 源服务器未能找 ...
- AE工程渲染的时间缓慢,两种方法减少对AE工程渲染的时间!
AE工程渲染的时间缓慢,两种方法减少对AE工程渲染的时间!3秒的片头,渲染时间竟然要花1个多小时,很多新手都产生过这样的疑问?是哪里不对吗?如何才能减少渲染视频的时间?且听我一一道来.主要原因是:工程 ...
- ubuntu set up 6 - NTFS Mount
1. NTFS Mounted as read-only https://askubuntu.com/questions/1138076/ubuntu-18-04-cant-write-on-ntfs ...
- 1.Docker Compose
一.Docker Compose 简介 概述 Compose 项目是 Docker 官方的开源项目,负责实现对 Docker 容器集群的快速编排.从功能上看,跟 OpenStack 中的 Heat 十 ...
