CompletableFuture 使用
Future的局限性,它没法直接对多个任务进行链式、组合等处理,而CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,增加了异步回调、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。 而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
使用CompletableFuture场景
执行比较耗时的操作时,尤其是那些依赖一个或多个远程服务的操作,使用异步任务可以改善程序的性能,加快程序的响应速度
使用CompletableFuture类,它提供了异常管理的机制,让你有机会抛出、管理异步任务执行种发生的异常
如果这些异步任务之间相互独立,或者他们之间的的某一些的结果是另一些的输入,你可以讲这些异步任务构造或合并成一个
@Test
public void FutureTest() throws Exception {
// 创建任务T2的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task());
// 创建任务T1的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task(ft2)); // 线程T1执行任务ft1
Thread T1 = new Thread(ft1);
T1.start();
// 线程T2执行任务ft2
Thread T2 = new Thread(ft2);
T2.start();
// 等待线程T1执行结果
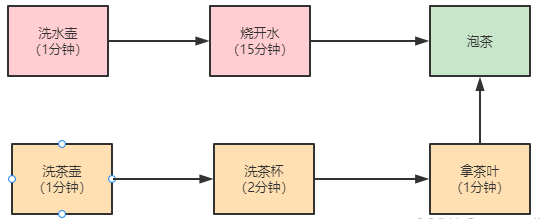
System.out.println(ft1.get()); } // T1Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶
class T1Task implements Callable<String> {
FutureTask<String> ft2; // T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTask
T1Task(FutureTask<String> ft2) {
this.ft2 = ft2;
} @Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水 完成...");
// 获取T2线程的茶叶
String tf = ft2.get();
System.out.println("T1:泡茶..." + tf);
return "上茶:" + tf;
}
} // T2Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶
class T2Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶 拿好 龙井...");
return "龙井";
}
}
CompletableFuture
@Test
public void CompletableFutureTest() {
//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水
CompletableFuture<Void> f1 = CompletableFuture
.runAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水 完成...");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯 完成..."); System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶 拿好 龙井...");
return "龙井";
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
return "";
}
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (p, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:泡茶..." + tf);
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
//join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。
// join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。
// get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
System.out.println(f3.join()); //
}
依赖关系
thenApply():把前面任务的执行结果,交给后面的Function
thenCompose():用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
and集合关系
thenCombine():合并任务,有返回值
thenAccepetBoth():两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAccepetBoth处理,无返回值
runAfterBoth():两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
or聚合关系
applyToEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就使用哪一个结果,有返回值
acceptEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就消费哪一个结果,无返回值
runAfterEither():任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
并行执行
allOf():当所有给定的 CompletableFuture 完成时,返回一个新的 CompletableFuture
anyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
结果处理
whenComplete:当任务完成时,将使用结果(或 null)和此阶段的异常(或 null如果没有)执行给定操作
exceptionally:返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当前面的CompletableFuture完成时,它也完成,当它异常完成时,给定函数的异常触发这个CompletableFuture的完成
通常的线程池接口类ExecutorService,其中execute方法的返回值是void,即无法获取异步任务的执行状态,3个重载的submit方法的返回值是Future,可以据此获取任务执行的状态和结果,示例如下:
@Test
public void FutureSubmitTest() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Double> cf = executorService.submit(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(false){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
});
System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成,如果已完成则直接返回结果
//如果执行任务异常,则get方法会把之前捕获的异常重新抛出
System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
supplyAsync / runAsync
supplyAsync表示创建带返回值的异步任务的,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable<T> task) 方法,runAsync表示创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法,这两方法的效果跟submit是一样的,测试用例如下:
/**
* 表示创建带返回值的异步任务的,相当于ExecutorService submit(Callable<T> task) 方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void supplyAsyncTest() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务,有返回值
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(false){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
});
System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
} /**
* 创建无返回值的异步任务,相当于ExecutorService submit(Runnable task)方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void runAsyncTest() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务,无返回值
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(false){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
});
System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
这两方法各有一个重载版本,可以指定执行异步任务的Executor实现,如果不指定,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),如果机器是单核的,则默认使用ThreadPerTaskExecutor,该类是一个内部类,每次执行execute都会创建一个新线程。测试用例如下:
@Test
public void supplyAsyncForkJoinPoolTest() throws Exception {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if (false) {
throw new RuntimeException("test");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
}, pool);
System.out.println("main thread start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} @Test
public void runAsyncExecutorTest() throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if (false) {
throw new RuntimeException("test");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, executorService);
System.out.println("main thread start,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
thenApply / thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中
@Test
public void thenApplyTest() throws Exception {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start job1,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit job1,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}, pool); //cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中
//thenApply这里实际创建了一个新的CompletableFuture实例
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf.thenApply((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " start job2,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " exit job2,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return "test:" + result;
});
System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->" + cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("run result->" + cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
thenAccept / thenRun
thenAccept 同 thenApply 接收上一个任务的返回值作为参数,但是无返回值;thenRun 的方法没有入参,也买有返回值
@Test
public void thenAcceptTest() throws Exception {
ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
},pool);
//cf关联的异步任务的返回值作为方法入参,传入到thenApply的方法中
CompletableFuture cf2=cf.thenApply((result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return "test:"+result;
}).thenAccept((result)-> {
//接收上一个任务的执行结果作为入参,但是没有返回值
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}).thenRun(()->{
//无入参,也没有返回值
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("thenRun do something");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
});
System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//cf2 等待最后一个thenRun执行完成
System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
exceptionally
exceptionally方法指定某个任务执行异常时执行的回调方法,会将抛出异常作为参数传递到回调方法中,如果该任务正常执行则会exceptionally方法返回的CompletionStage的result就是该任务正常执行的结果
@Test
public void exceptionally() throws Exception {
ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(true){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
},pool);
//cf执行异常时,将抛出的异常作为入参传递给回调方法
CompletableFuture<Double> cf2= cf.exceptionally((param)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("error stack trace->");
param.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return -1.1;
});
//cf正常执行时执行的逻辑,如果执行异常则不调用此逻辑
CompletableFuture cf3=cf.thenAccept((param)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("param->"+param);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
});
System.out.println("main thread start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成,此处无论是job2和job3都可以实现job2退出,主线程才退出,如果是cf,则主线程不会等待job2执行完成自动退出了
//cf2.get时,没有异常,但是依然有返回值,就是cf的返回值
System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
whenComplete
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常
@Test
public void whenComplete() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(false){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
});
//cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为null
CompletableFuture<Double> cf2=cf.whenComplete((a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(b!=null){
System.out.println("error stack trace->");
b.printStackTrace();
}else{
System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
});
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//如果cf是正常执行的,cf2.get的结果就是cf执行的结果
//如果cf是执行异常,则cf2.get会抛出异常
System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
handle
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值,且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法的执行结果或者回调方法执行期间抛出的异常,与原始CompletableFuture的result无关了
@Test
public void handle() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(true){
throw new RuntimeException("test");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job1 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
}
});
//cf执行完成后会将执行结果和执行过程中抛出的异常传入回调方法,如果是正常执行的则传入的异常为null
CompletableFuture<String> cf2=cf.handle((a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 start,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if(b!=null){
System.out.println("error stack trace->");
b.printStackTrace();
}else{
System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"job2 exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
if(b!=null){
return "run error";
}else{
return "run succ";
}
});
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("main thread start wait,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//get的结果是cf2的返回值,跟cf没关系了
System.out.println("run result->"+cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只有这两个都正常执行完了才会执行某个任务,区别在于,thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参传递到指定方法中,且该方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。
@Test
public void thenCombine() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
});
CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 3.2;
});
//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值
CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.thenCombine(cf2,(a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("job3 param a->"+a+",b->"+b);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return a+b;
}); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值
CompletableFuture cf4=cf.thenAcceptBoth(cf2,(a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("job4 param a->"+a+",b->"+b);
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}); //cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterBoth(cf3,()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("cf5 do something");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来,只要其中一个执行完了就会执行某个任务(job3 的参数为先执行结果),其区别在于
applyToEither会将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,并有返回值;
acceptEither同样将已经执行完成的任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是没有返回值;
runAfterEither没有方法入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果
@Test
public void applyToEither() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
});
CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 3.2;
});
//cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,且有返回值
CompletableFuture<Double> cf3=cf.applyToEither(cf2,(result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("job3 param result->"+result);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return result;
}); //cf和cf2的异步任务都执行完成后,会将其执行结果作为方法入参传递给cf3,无返回值
CompletableFuture cf4=cf.acceptEither(cf2,(result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("job4 param result->"+result);
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job4,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}); //cf4和cf3都执行完成后,执行cf5,无入参,无返回值
CompletableFuture cf5=cf4.runAfterEither(cf3,()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("cf5 do something");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job5,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}); System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread start cf5.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("cf5 run result->"+cf5.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
thenCompose
thenCompose方法会在某个任务执行完成后,将该任务的执行结果作为方法入参然后执行指定的方法,该方法会返回一个新的CompletableFuture实例,如果该CompletableFuture实例的result不为null,则返回一个基于该result的新的CompletableFuture实例;如果该CompletableFuture实例为null,则,然后执行这个新任务
@Test
public void thenCompose() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2= cf.thenCompose((param)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return "job3 test";
});
});
System.out.println("main thread start cf.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("cf run result->"+cf.get());
System.out.println("main thread start cf2.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("cf2 run result->"+cf2.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
allOf / anyOf
allOf返回的CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
@Test
public void test11() throws Exception {
// 创建异步执行任务:
CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job1,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 1.2;
});
CompletableFuture<Double> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job2,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 3.2;
});
CompletableFuture<Double> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" start job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// throw new RuntimeException("test");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" exit job3,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
return 2.2;
});
//allof等待所有任务执行完成才执行cf4,如果有一个任务异常终止,则cf4.get时会抛出异常,都是正常执行,cf4.get返回null
//anyOf是只有一个任务执行完成,无论是正常执行或者执行异常,都会执行cf4,cf4.get的结果就是已执行完成的任务的执行结果
CompletableFuture cf4=CompletableFuture.allOf(cf,cf2,cf3).whenComplete((a,b)->{
if(b!=null){
System.out.println("error stack trace->");
b.printStackTrace();
}else{
System.out.println("run succ,result->"+a);
}
}); System.out.println("main thread start cf4.get(),time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
//等待子任务执行完成
System.out.println("cf4 run result->"+cf4.get());
System.out.println("main thread exit,time->"+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
https://blog.csdn.net/sermonlizhi/article/details/123356877
https://blog.csdn.net/sermonlizhi/article/details/123356877
CompletableFuture 使用的更多相关文章
- Java CompletableFuture 详解
Future是Java 5添加的类,用来描述一个异步计算的结果.你可以使用isDone方法检查计算是否完成,或者使用get阻塞住调用线程,直到计算完成返回结果,你也可以使用cancel方法停止任务的执 ...
- 多线程并发执行任务,取结果归集。终极总结:Future、FutureTask、CompletionService、CompletableFuture
目录 1.Futrue 2.FutureTask 3.CompletionService 4.CompletableFuture 5.总结 ================正文分割线========= ...
- CompletableFuture CompletableFuture.supplyAsync 异常处理
CompletableFuture 异常处理completeExceptionally可以把异常抛到主线程 /** * User: laizhenwei * Date: 2018-01-30 Time ...
- 使用CompletableFuture实现异步编程
在开发中会碰到一种场景,如下 Object result1 = service1.func1();//执行80ms Object result2 =service2.func2();//执行50ms ...
- CompletableFuture基本用法
异步计算 所谓异步调用其实就是实现一个可无需等待被调用函数的返回值而让操作继续运行的方法.在 Java 语言中,简单的讲就是另启一个线程来完成调用中的部分计算,使调用继续运行或返回,而不需要等待计算结 ...
- 使用CompletableFuture优化你的代码执行效率
这篇文章详细讲解java8中CompletableFuture的特性,方法以及实例. 在java8以前,我们使用java的多线程编程,一般是通过Runnable中的run方法来完成,这种方式,有个很明 ...
- 多线程编程CompletableFuture与parallelStream
一.简介 平常在页面中我们会使用异步调用$.ajax()函数,如果是多个的话他会并行执行相互不影响,实际上Completable我理解也是和它类似,是java 8里面新出的异步实现类,Completa ...
- 从CompletableFuture到异步编程设计
从CompletableFuture到异步编程设计,笔者就分为2部分来分享CompletableFuture异步编程设计,前半部分总结下CompletableFuture使用实践,后半部分分享下Com ...
- Java CompletableFuture:allOf等待所有异步线程任务结束
private void method() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<String& ...
- 【JUC源码解析】CompletableFuture
简介 先说Future, 它用来描述一个异步计算的结果.isDone方法可以用来检查计算是否完成,get方法可以用来获取结果,直到完成前一直阻塞当前线程,cancel方法可以取消任务.而对于结果的获取 ...
随机推荐
- OpenGL 摄像机视角详解
1. 摄像机 摄像机就好像是我们的眼睛,我们从摄像机的方向观察世界空间中的模型.摄像机远离模型,模型自然就变小了(透视投影下),然而,在GL中事实上并没有摄像机的概念.但是我们可以通过移动世界空间远离 ...
- include 0。0
参考好文 php://filter的各种过滤器_php://filter过滤器种类-CSDN博客 打开页面是一段php代码 可以知道flag在flag.php文件里面,然后执行没有结果,就只能用文件读 ...
- 震惊,微信小程序可以设置网络字体!真香
准备工作,获取字体链接 还原设计稿的时候需要用到如下特殊字体(google 的 Montserrat): https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Montserrat 选择 ...
- MySQL-mysqldump 报错:[ERROR] unknown variable 'local_infile=1'.
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. ----- 作者:kirin mysqldump: [ERROR] unknown variable 'local_infile=1'. 解决方法: ...
- Navicat远程连接Centos8.4服务器MySQL8.0数据库
一.首先登陆服务器后台管理,使服务器开放3306策略 二.开启远程连接 1.登陆服务器的MySQL数据库 mysql -uroot -p 2.登录成功后,切换数据库 use mysql; 3.查看当前 ...
- 我用 AI 写的《JavaScript 工程师的 Python 指南》电子书发布啦!
关于本书 你好,我是 luckrnx09,一名靠 React 恰饭的前端工程师,很高兴向你介绍我的第一本开源电子书<JavaScript 工程师的 Python 指南>. 本书的内容完全免 ...
- 倒计时4天!解锁《2023 .NET Conf China》 云原生分会场精彩议程
.NET Conf China 2023 定于 12 月16 日于北京举办为期一天的技术交流,届时会有.NET 领域专家与大家一同庆祝 .NET 8 的发布和回顾过去一年来 .NET 在中国的发展成果 ...
- 微调baichuan2-7b遇到的显存坑
问题描述: 微调baichuan2-7b模型,验证一轮后继续训练第一个iteration显存大幅增加 项目链接: https://github.com/wp931120/baichuan_sft_lo ...
- bash shell笔记整理——basename和dirname命令
bashname命令作用 去掉给定name的目录部分,如果指定了 SUFFIX, 就 同时去掉SUFFIX(后缀).具体看示例吧. bashname语法 Usage: basename NAME [S ...
- Android对接微信登录记录
Android对接微信登录记录 - Stars-One的杂货小窝 Android项目要对接下微信登录,稍微记录下踩坑点 代码 1.添加依赖 implementation 'com.tencent.mm ...
