[转帖]043、TiDB特性_缓存表和分区表
针对于优化器在索引存在时依然使⽤全表扫描的情况下,使⽤缓存表和分区表是提升查询性能的有效⼿段。
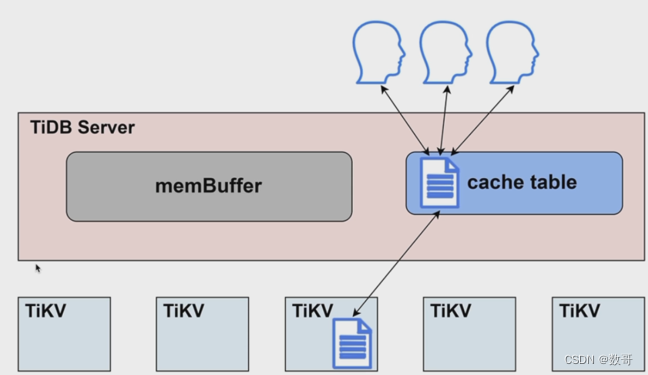
缓存表
- 缓存表是将表的内容完全缓存到 TiDB Server 的内存中
- 表的数据量不⼤,⼏乎不更改
- 读取很频繁
- 缓存控制: ALTER TABLE table_name CACHE|NOCACHE;
# 使用trace跟踪下
tidb> TRACE SELECT * FROM test.c1;
+-------------------------------------------+-----------------+---
---------+
| operation | startTS |
duration |
+-------------------------------------------+-----------------+---
---------+
| trace | 18:39:25.485266 |
501.582µs |
| ├─session.ExecuteStmt | 18:39:25.485270 |
432.208µs |
| │ ├─executor.Compile | 18:39:25.485281 |
132.616µs |
| │ └─session.runStmt | 18:39:25.485433 |
249.488µs |
| │ └─UnionScanExec.Open | 18:39:25.485572 |
72.776µs |
| │ ├─TableReaderExecutor.Open | 18:39:25.485575 |
13.24µs |
| │ ├─buildMemTableReader | 18:39:25.485605 |
3.283µs |
| │ └─memTableReader.getMemRows | 18:39:25.485615 | # memTableReader.getMemRows 表示从缓存取数
20.558µs |
| ├─*executor.ProjectionExec.Next | 18:39:25.485712 |
12.911µs |
| │ └─*executor.UnionScanExec.Next | 18:39:25.485714 |
3.823µs |
| └─*executor.ProjectionExec.Next | 18:39:25.485733 |
8.943µs |
| └─*executor.UnionScanExec.Next | 18:39:25.485735 |
1.33µs |
+-------------------------------------------+-----------------+---
---------+
12 rows in set (0.00 sec)
小表缓存-原理
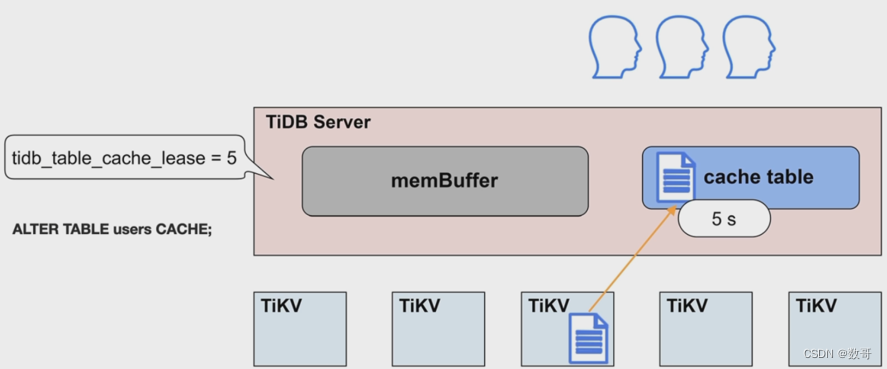
缓存租约
租约时间内,无法进行写操作
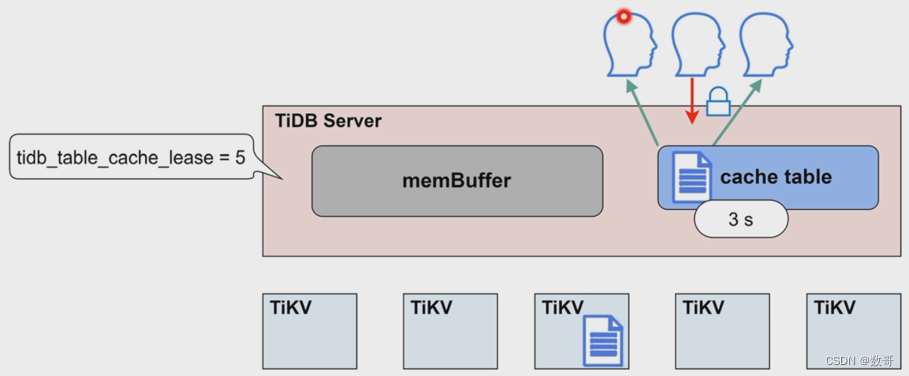
租约到期,数据过期
写操作不再被阻塞
读写直接到TiKV节点上执行
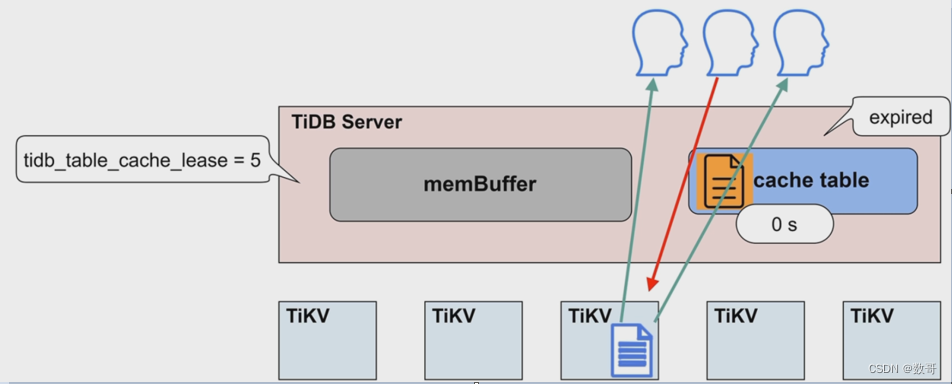
数据更新完毕,租约继续开启
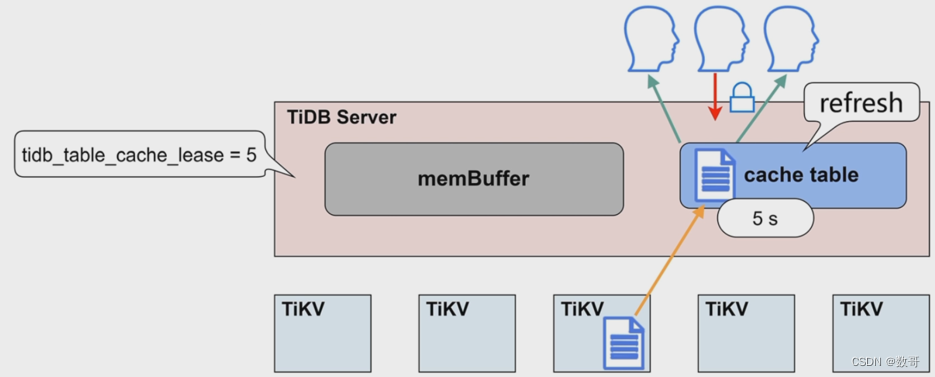
应用场景
- 每张缓存表的大小限制为64MB
- 适用于查询频繁、数据量不大、修改极少的场景
- 在租约(tidb_table_cache_lease) 时间内,写操作会被阻塞
- 当租约到期(tidb_table_cache_lease)时,读性能会下降
- 不支持对缓存表直接做DDL操作,需要先关闭
- 对于表加载较慢或者极少修改的表,可以适当延长tidb_table_cache_lease保持读性能稳定
分区表
分区类型与适用场景
- range: 分区剪裁,节省IO开销
- Hash: 用于大规模写入的情况下将数据打散,平均地分配到各个分区里
Range分区表
create table t1(x int) partition by name(x) (
partition p0 values less than(5),
partition p1 values less than (10));
)
分区类型与适⽤场景
- Range
分区裁剪, 节省 I/O 开销
/* Range Partition t1 */
drop table if exists test.t1;
create table test.t1 (x int) partition by range (x) (
partition p0 values less than (5),
partition p1 values less than (10));
insert into test.t1 values (0),(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9);
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
/* Check Partition Pruning */
explain select * from test.t1 where x between 1 and 4;
查看执行计划
mysql> explain select * from test.t1 where x between 1 and 4;
+-------------------------+-----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+-------------------------+-----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
| TableReader_9 | 12288.00 | root | | data:Selection_8 |
| └─Selection_8 | 12288.00 | cop[tikv] | | ge(test.t1.x, 1), le(test.t1.x, 4) |
| └─TableFullScan_7 | 491520.00 | cop[tikv] | table:t1, partition:p0 | keep order:false |
+-------------------------+-----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.03 sec)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
/* Check regions */
show table test.t1 regions;
mysql> show table test.t1 regions;
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
| REGION_ID | START_KEY | END_KEY | LEADER_ID | LEADER_STORE_ID | PEERS | SCATTERING | WRITTEN_BYTES | READ_BYTES | APPROXIMATE_SIZE(MB) | APPROXIMATE_KEYS |
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
| 5019 | t_79_ | t_80_ | 5020 | 1001 | 5020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 877551 |
| 1002 | t_80_ | | 1003 | 1001 | 1003 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 421921 |
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
2 rows in set (0.02 sec)
- Hash
可以⽤于⼤规模写⼊的情况下将数据打散, 平均地分配到各个分区⾥
/* Hash Partition t1 */
drop table if exists test.t1;
CREATE TABLE test.t1 (x INT)
PARTITION BY HASH(x)
PARTITIONS 4;
insert into test.t1 values (0),(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9);
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
insert into test.t1 select * from test.t1;
查看分区的执行计划
- 默认是通过mod方式分配分区
/* Check Partition Distribution */
explain select from test.t1 where x=0;
explain select from test.t1 where x=1;
explain select from test.t1 where x=2;
explain select from test.t1 where x=3;
explain select from test.t1 where x=4;
explain select from test.t1 where x=5;
explain select from test.t1 where x=6;
explain select from test.t1 where x=7;
explain select from test.t1 where x=8;
explain select from test.t1 where x=9;
/* Negative /
explain select from test.t1 where x between 7 and 9;
mysql> explain select * from test.t1 where x between 7 and 9;
+------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
| id | estRows | task | access object | operator info |
+------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
| PartitionUnion_10 | 750.00 | root | | |
| ├─TableReader_13 | 250.00 | root | | data:Selection_12 |
| │ └─Selection_12 | 250.00 | cop[tikv] | | ge(test.t1.x, 7), le(test.t1.x, 9) |
| │ └─TableFullScan_11 | 10000.00 | cop[tikv] | table:t1, partition:p0 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| ├─TableReader_16 | 250.00 | root | | data:Selection_15 |
| │ └─Selection_15 | 250.00 | cop[tikv] | | ge(test.t1.x, 7), le(test.t1.x, 9) |
| │ └─TableFullScan_14 | 10000.00 | cop[tikv] | table:t1, partition:p1 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
| └─TableReader_19 | 250.00 | root | | data:Selection_18 |
| └─Selection_18 | 250.00 | cop[tikv] | | ge(test.t1.x, 7), le(test.t1.x, 9) |
| └─TableFullScan_17 | 10000.00 | cop[tikv] | table:t1, partition:p3 | keep order:false, stats:pseudo |
+------------------------------+----------+-----------+------------------------+------------------------------------+
10 rows in set (12.69 sec)
查看region分布情况
/* Check regions */
# 查看对应的region情况,在4个region上
mysql> show table test.t1 regions;
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
| REGION_ID | START_KEY | END_KEY | LEADER_ID | LEADER_STORE_ID | PEERS | SCATTERING | WRITTEN_BYTES | READ_BYTES | APPROXIMATE_SIZE(MB) | APPROXIMATE_KEYS |
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
| 9003 | t_84_ | t_85_ | 9004 | 1001 | 9004 | 0 | 18449249 | 14117466 | 13 | 141205 |
| 9005 | t_85_ | t_86_ | 9006 | 1001 | 9006 | 0 | 18443067 | 14024508 | 10 | 58475 |
| 9007 | t_86_ | t_87_ | 9008 | 1001 | 9008 | 0 | 12295360 | 8703102 | 5 | 27228 |
| 1002 | t_87_ | | 1003 | 1001 | 1003 | 0 | 12295959 | 9218671 | 4 | 26666 |
+-----------+-----------+---------+-----------+-----------------+-------+------------+---------------+------------+----------------------+------------------+
4 rows in set (2 min 46.43 sec)
[转帖]043、TiDB特性_缓存表和分区表的更多相关文章
- (转载)详解网络传输中的三张表,MAC地址表、ARP缓存表以及路由表
郑重声明:原文转载于http://dengqi.blog.51cto.com/5685776/1223132 向好文章致敬!!! 一:MAC地址表详解 说到MAC地址表,就不得不说一下交换机的工作原理 ...
- Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强(转)
目录 Spring4.1新特性——综述 Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他 Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强 Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异 ...
- ARP缓存表的构成ARP协议全面实战协议详解、攻击与防御
ARP缓存表的构成ARP协议全面实战协议详解.攻击与防御 1.4.3 ARP缓存表的构成 在局域网的任何一台主机中,都有一个ARP缓存表.该缓存表中保存中多个ARP条目.每个ARP条目都是由一个IP ...
- Oracle11g新特性导致空表不能导出问题
ORACLE 11G在用EXP导出时,发现空表(没有数据或者没有用过的表)不能导出了. 查了一下资料,说是Oracle 11G中有个新特性,当表无数据时,不分配segment,以节省空 ...
- 关于我们_ | 腕表时代watchtimes.com.cn
关于我们_ | 腕表时代watchtimes.com.cn 关于我们 腕表时代是北京兰会时光科技有限公司旗下运营的手表网站.腕表时代于2013年5月17日正式上线.秉承专业.生动.实用 ...
- 网络传输中的三张表,MAC地址表、ARP缓存表以及路由表
一:MAC地址表详解 说到MAC地址表,就不得不说一下交换机的工作原理了,因为交换机是根据MAC地址表转发数据帧的.在交换机中有一张记录着局域网主机MAC地址与交换机接口的对应关系的表,交换机就是根据 ...
- SQL基本查询_单表查询(实验二)
SQL基本查询_单表查询(实验二) 查询目标表结构及数据 emp empno ename job hiedate sal comn deptno 1007 马明 内勤 1992-6-12 4000 2 ...
- SQL基本查询_多表查询(实验三)
SQL基本查询_多表查询(实验三) 题目要求(一) 针对emp.dept两表完成如下查询,并验证查询结果的正确性 使用显式内连接查询所有员工的信息,显示其编号.姓名.薪水.入职日期及部门名称: 使用隐 ...
- SQL Server 表的管理_关于表的操作增删查改的操作的详解(案例代码)
SQL Server 表的管理_关于表的操作增删查改的操作的详解(案例代码) 概述: 表由行和列组成,每个表都必须有个表名. SQL CREATE TABLE 语法 CREATE TABLE tabl ...
- 缓存表 内存表(将表keep到内存)
缓存表 内存表(将表keep到内存) 一.引言: 有时候一些基础表需要非常的频繁访问,尤其是在一些循环中,对该表中的访问速度将变的非常重要.为了提高系统的处理性能,可以考虑将一些表及索引读取并 ...
随机推荐
- electron入门之创建新窗口remote(一)
electron入门到入土,从渲染线程中创建新窗口.2022-03-21入门版本17.1.2 electron重要概念,只有一个主线程,其他都是渲染进程或者叫子线程,他们不能直接相互操作,可以通过ip ...
- 欧拉定理 & 扩展欧拉定理 笔记
欧拉函数 欧拉函数定义为:\(\varphi(n)\) 表示 \(1 \sim n\) 中所有与 \(n\) 互质的数的个数. 关于欧拉函数有下面的性质和用途: 欧拉函数是积性函数.可以通过这个性质求 ...
- flutter MaterialApp介绍
MaterialApp 是 Flutter 中常用的一个 widget,它是构建基于 Material Design 风格应用的根组件,主要负责各种全局状态的管理以及定义应用程序的主题样式等. voi ...
- CUDA C编程权威指南:1.3-CUDA基础知识点梳理
主要整理了N多年前(2013年)学习CUDA的时候开始总结的知识点,好长时间不写CUDA代码了,现在LLM推理需要重新学习CUDA编程,看来出来混迟早要还的. 1.CUDA数组 解析:CUDA数组 ...
- Spring Boot 整合 Log4j2 日志并压测性能
1/ Log4j2的性能测试 从图中不难看出,在线程数为 2~16 之间,混合使用同步和异步的logger来打印日志,性能是最好的. 2/ 目标 混合 sync/async 彩色日志 分类输出到不同文 ...
- 带你认识多模数据库GeminiDB架构与应用实践
本文分享自华为云社区<多模归一,一生万物--华为云多模数据库GeminiDB架构与应用实践>,作者: GaussDB 数据库 . 在这个信息爆炸的时代,数据的管理和应用变得越来越重要.互联 ...
- 技术驱动,数据赋能,华为云GaussDB给世界一个更优选择
摘要:5月16日,"数智深耕 让美好发生 2023华为云城市峰会广州站"成功举行. 5月16日,"数智深耕 让美好发生 2023华为云城市峰会广州站"成功举行. ...
- 连Python都不熟也能跑通AI人脸识别?“隐藏Boss”竟是它!
摘要:先把AI人脸识别跑起来,然后研究它是如何实现的,整个过程中确实收获不少.所谓先跟着做,再跟着学,实践与理论结合,自己感觉有理解了一些基础概念入个门,在此分享一下自己的捣鼓经验. 1.买台小&qu ...
- 云小课|MRS基础原理之Oozie任务调度
阅识风云是华为云信息大咖,擅长将复杂信息多元化呈现,其出品的一张图(云图说).深入浅出的博文(云小课)或短视频(云视厅)总有一款能让您快速上手华为云.更多精彩内容请单击此处. 摘要:Oozie是一个基 ...
- SPL:跑批有这么难么?
摘要:SPL实现了更优算法,性能远远超过存储过程,能显著提高单机计算效率,非常适合跑批计算. 本文分享自华为云社区<Java开源专业计算引擎:跑批真的这么难吗?>,作者: Java李杨勇. ...
