Codeforces Round #270 A~D
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One way to create a task is to learn from math. You can generate some random math statement or modify some theorems to get something new and build a new task from that.
For example, there is a statement called the "Goldbach's conjecture". It says: "each even number no less than four can be expressed as the sum of two primes". Let's modify it. How about a statement like that: "each integer no less than 12 can be expressed as
the sum of two composite numbers." Not like the Goldbach's conjecture, I can prove this theorem.
You are given an integer n no less than 12, express it as a sum of two composite numbers.
The only line contains an integer n (12 ≤ n ≤ 106).
Output two composite integers x and y (1 < x, y < n) such
that x + y = n. If there are multiple solutions, you can output any of them.
12
4 8
15
6 9
23
8 15
1000000
500000 500000
In the first example, 12 = 4 + 8 and both 4, 8 are composite numbers. You can output "6 6" or "8 4" as well.
In the second example, 15 = 6 + 9. Note that you can't output "1 14" because 1 is not a composite number.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; bool isp[1001000]; void get_prime()
{
isp[1]=isp[0]=true;
for(int i=2;i<=1000010;i++)
{
if(isp[i]==false)
for(int j=i*2;j<=1000010;j+=i)
isp[j]=true;
}
} int main()
{
get_prime();
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int x,y;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(isp[i]==true&&isp[n-i]==true)
{
printf("%d %d\n",i,n-i);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One way to create a task is to learn from life. You can choose some experience in real life, formalize it and then you will get a new task.
Let's think about a scene in real life: there are lots of people waiting in front of the elevator, each person wants to go to a certain floor. We can formalize it in the following way. We have n people
standing on the first floor, the i-th person wants to go to the fi-th
floor. Unfortunately, there is only one elevator and its capacity equal to k (that is at most k people
can use it simultaneously). Initially the elevator is located on the first floor. The elevator needs |a - b| seconds to move from the a-th
floor to the b-th floor (we don't count the time the people need to get on and off the elevator).
What is the minimal number of seconds that is needed to transport all the people to the corresponding floors and then return the elevator to the first floor?
The first line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 2000) —
the number of people and the maximal capacity of the elevator.
The next line contains n integers: f1, f2, ..., fn (2 ≤ fi ≤ 2000),
where fi denotes
the target floor of the i-th person.
Output a single integer — the minimal time needed to achieve the goal.
3 2
2 3 4
8
4 2
50 100 50 100
296
10 3
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
8
In first sample, an optimal solution is:
- The elevator takes up person #1 and person #2.
- It goes to the 2nd floor.
- Both people go out of the elevator.
- The elevator goes back to the 1st floor.
- Then the elevator takes up person #3.
- And it goes to the 2nd floor.
- It picks up person #2.
- Then it goes to the 3rd floor.
- Person #2 goes out.
- Then it goes to the 4th floor, where person #3 goes out.
- The elevator goes back to the 1st floor.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; int n,k;
int f[2200];
int all[2200]; int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",f+i);
all[f[i]]++;
}
int now=0,high=1,ans=0;
for(int i=2000;i>=1;(all[i]==0)?i--:i+=0)
{
if(all[i])
{
if(now==0) high=i;
if(now+all[i]<=k)
{
now+=all[i];
all[i]=0;
}
else /// now + all[i]>k
{
int res=k-now;
all[i]-=res;
now=k;
}
}
if(now==k||i==1)
{
ans+=(high-1)*2;
now=0;high=1;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A way to make a new task is to make it nondeterministic or probabilistic. For example, the hard task of Topcoder SRM 595, Constellation, is the probabilistic version of a convex hull.
Let's try to make a new task. Firstly we will use the following task. There are n people, sort them by their name. It is just an ordinary sorting problem,
but we can make it more interesting by adding nondeterministic element. There are n people, each person will use either his/her first name or last name
as a handle. Can the lexicographical order of the handles be exactly equal to the given permutation p?
More formally, if we denote the handle of the i-th person as hi,
then the following condition must hold: 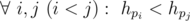 .
.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
the number of people.
The next n lines each contains two strings. The i-th
line contains strings fi and si (1 ≤ |fi|, |si| ≤ 50) —
the first name and last name of the i-th person. Each string consists only of lowercase English letters. All of the given 2n strings
will be distinct.
The next line contains n distinct integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n).
If it is possible, output "YES", otherwise output "NO".
3
gennady korotkevich
petr mitrichev
gaoyuan chen
1 2 3
NO
3
gennady korotkevich
petr mitrichev
gaoyuan chen
3 1 2
YES
2
galileo galilei
nicolaus copernicus
2 1
YES
10
rean schwarzer
fei claussell
alisa reinford
eliot craig
laura arseid
jusis albarea
machias regnitz
sara valestin
emma millstein
gaius worzel
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
NO
10
rean schwarzer
fei claussell
alisa reinford
eliot craig
laura arseid
jusis albarea
machias regnitz
sara valestin
emma millstein
gaius worzel
2 4 9 6 5 7 1 3 8 10
YES
In example 1 and 2, we have 3 people: tourist, Petr and me (cgy4ever). You can see that whatever handle is chosen, I must be the first, then tourist and Petr must be the last.
In example 3, if Copernicus uses "copernicus" as his handle, everything will be alright.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; int n,p[100100];
struct NME
{
char str1[60],str2[60];
}name[100100]; int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s%s",name[i].str1,name[i].str2);
//cout<<name[i].str1<<" ... "<<name[i].str2<<endl;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",p+i);
int pos=-1,se=-1;
bool flag=true; if(strcmp(name[p[1]].str1,name[p[1]].str2)<0) pos=p[1],se=1;
else pos=p[1],se=2;
for(int i=2;i<=n&&flag;i++)
{
int id=p[i];
if(se==1)
{
bool ok1=false,ok2=false;
if(strcmp(name[pos].str1,name[id].str1)<0)
{
ok1=true;
}
if(strcmp(name[pos].str1,name[id].str2)<0)
{
ok2=true;
}
if(ok1&&ok2)
{
if(strcmp(name[id].str1,name[id].str2)<=0)
{
pos=id; se=1;
}
else if(strcmp(name[id].str2,name[id].str1)<0)
{
pos=id; se=2;
}
}
else if(ok1==true&&ok2==false)
{
pos=id; se=1;
}
else if(ok1==false&&ok2==true)
{
pos=id; se=2;
}
else
{
flag=false;
break;
}
}
else if(se==2)
{
bool ok1=false,ok2=false;
if(strcmp(name[pos].str2,name[id].str1)<0)
{
ok1=true;
}
if(strcmp(name[pos].str2,name[id].str2)<0)
{
ok2=true;
}
if(ok1&&ok2)
{
if(strcmp(name[id].str1,name[id].str2)<=0)
{
pos=id; se=1;
}
else if(strcmp(name[id].str2,name[id].str1)<0)
{
pos=id; se=2;
}
}
else if(ok1==true&&ok2==false)
{
pos=id; se=1;
}
else if(ok1==false&&ok2==true)
{
pos=id; se=2;
}
else
{
flag=false;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag==true) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
There is an easy way to obtain a new task from an old one called "Inverse the problem": we give an output of the original task, and ask to generate an input, such that solution to the original problem will produce the output we provided. The hard task of Topcoder
Open 2014 Round 2C, InverseRMQ, is a good example.
Now let's create a task this way. We will use the task: you are given a tree, please calculate the distance between any pair of its nodes. Yes, it is very easy, but the inverse version is a bit harder: you are given an n × n distance
matrix. Determine if it is the distance matrix of a weighted tree (all weights must be positive integers).
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2000)
— the number of nodes in that graph.
Then next n lines each contains n integers di, j (0 ≤ di, j ≤ 109)
— the distance between node i and node j.
If there exists such a tree, output "YES", otherwise output "NO".
3
0 2 7
2 0 9
7 9 0
YES
3
1 2 7
2 0 9
7 9 0
NO
3
0 2 2
7 0 9
7 9 0
NO
3
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
NO
2
0 0
0 0
NO
In the first example, the required tree exists. It has one edge between nodes 1 and 2 with weight 2, another edge between nodes 1 and 3 with weight 7.
In the second example, it is impossible because d1, 1 should
be 0, but it is 1.
In the third example, it is impossible because d1, 2 should
equal d2, 1.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long int LL; const int maxn=2222; int n;
LL d[maxn][maxn]; int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
bool flag=true;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&d[i][j]);
if(i==j&&d[i][j]) flag=false;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n&&flag;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n&&flag;j++)
{
if(d[i][j]!=d[j][i]) flag=false;
if(i!=j&&d[i][j]==0) flag=false;
}
if(flag==false)
{
puts("NO");
return 0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n&&flag;i++)
{
LL MINI=(1LL<<62),pos=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(d[i][j]<MINI&&i!=j)
{
MINI=d[i][j]; pos=j;
}
}
for(int j=1;j<=n&&flag;j++)
{
if(j==i||j==pos) continue;
if(abs(d[pos][j]-d[i][j])!=d[i][pos])
{
flag=false;
}
}
}
if(flag==false)
{
puts("NO");
}
else
{
puts("YES");
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:来自: 代码代码猿猿AC路 http://blog.csdn.net/ck_boss
Codeforces Round #270 A~D的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #270 1003
Codeforces Round #270 1003 C. Design Tutorial: Make It Nondeterministic time limit per test 2 second ...
- Codeforces Round #270 1002
Codeforces Round #270 1002 B. Design Tutorial: Learn from Life time limit per test 1 second memory l ...
- Codeforces Round #270 1001
Codeforces Round #270 1001 A. Design Tutorial: Learn from Math time limit per test 1 second memory l ...
- Codeforces Round #270(利用prim算法)
D. Design Tutorial: Inverse the Problem time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 mega ...
- codeforces水题100道 第七题 Codeforces Round #270 A. Design Tutorial: Learn from Math (math)
题目链接:http://www.codeforces.com/problemset/problem/472/A题意:给你一个数n,将n表示为两个合数(即非素数)的和.C++代码: #include & ...
- 多种方法过Codeforces Round #270的A题(奇偶法、打表法和Miller_Rabin(这个方法才是重点))
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/472/problem/A 题目: 题意:哥德巴赫猜想是:一个大于2的素数一定可以表示为两个素数的和.此题则是将其修改为:一个大于 ...
- Codeforces Round #270 D Design Tutorial: Inverse the Problem --MST + DFS
题意:给出一个距离矩阵,问是不是一颗正确的带权树. 解法:先按找距离矩阵建一颗最小生成树,因为给出的距离都是最短的点间距离,然后再对每个点跑dfs得出应该的dis[][],再对比dis和原来的mp是否 ...
- Codeforces Round #270 D C B A
谈论最激烈的莫过于D题了! 看过的两种做法不得不ORZ,特别第二种,简直神一样!!!!! 1th:构造最小生成树. 我们提取所有的边出来按边排序,因为每次我们知道边的权值>0, 之后每次把边加入 ...
- Codeforces Round #270
A 题意:给出一个数n,求满足a+b=n,且a+b均为合数的a,b 方法一:可以直接枚举i,n-i,判断a,n-i是否为合数 #include<iostream> #include< ...
随机推荐
- (转)WINDOWS内核对象
WINDOWS内核对象 原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/misterliwei/article/details/976988 支持原创 一.前言 Windows中有很多像进程对象 ...
- 杭电ACM 汉字统计
汉字统计 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
- 最短路径算法—Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法分析与实现(C/C++)
Dijkstra算法 ———————————最后更新时间:2011.9.25———————————Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路径路由算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径. ...
- (C)高级排序法
1.快速排序法 //方法1 从大到小 #include <iostream.h> void run(int* pData,int left,int right) { int i,j; in ...
- PCB设计铜铂厚度、线宽和电流关系
以下总结了网上八种电流与线宽的关系公式,表和计算公式,虽然各不相同(大体相近),但大家可以在实际的PCB板设计中,综合考虑PCB板的大小,通过电流,选择一个合适的线宽. 一.PCB电流与线宽 PCB载 ...
- python 中函数参数传递形式
python中函数参数的传递是通过赋值来传递的.函数参数的使用又有俩个方面值得注意:1.函数参数是如何定义的 2.在调用函数的过程中参数是如何被解析 先看第一个问题,在python中函数参数的定义主要 ...
- perl 安装Net::ZooKeeper
<pre name="code" class="python"><pre name="code" class=" ...
- Java面试题之三
十一.谈谈final,finally,finalize的区别? 1.final:是修饰符,是一个关键字.修饰变量,如果是基本类型表示该变量的值不能修改:如果是引用类型表示该变量不能指向别的对象:修饰类 ...
- Boost.Asio基础(三)
Socket控制 以下的函数进行处理一些高级的socket选项: get_io_service():返回io_service实例 get_option(option):返回socket option对 ...
- 【Tomcat】本地域名访问设置
原路径:localhost:8080/tidyko 1.去掉8080端口 打开%TOMCAT_HOME%/conf/server.xml 修改里面的 <Connector connectionT ...
