spring——AOP原理及源码(五)
前情回顾:
在上一篇中,通过 wrapIfNecessary 方法,我们获取到了合适的增强器(日志方法)与业务
类进行包装,最终返回了我们业务类的代理对象。

本篇我们将从业务方法的执行开始,看看增强器(日志方法)是怎么在方法执行的前后和发
生异常时被调用的。以及在文章的最后总结整个AOP的执行流程。
1、调试的起点:
给测试方法打上断点,然后一直跳到下一个断点直到执行方法,如下

接着进入方法,会被intercept方法拦截
进入断点:
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
intercept
intercept 方法从上往下看:
16~18:获取目标类(注意不是代理对象)

19:通过目标类和目标方法获取拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
2、重点探究获取拦截器链的过程
进入 getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice

继续进入 this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(this, method, targetClass)
@Override
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
} return interceptorList;
}
getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
以上代码从上往下看:
5:创建拦截器链
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length)
12~32:
- 遍历所有增强器
- 经过一系列判断,将增强器放入interceptorList中 :
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors))
46:将拦截器链返回
接下来将拦截器链返回,并存入缓存中

最后将拦截器链返回

这就是拦截器链获取的过程
接下来来到 intercept 方法的真正执行部分:
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
通过new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy) 获取到方法拦截器链
一进来先调用父类方法:
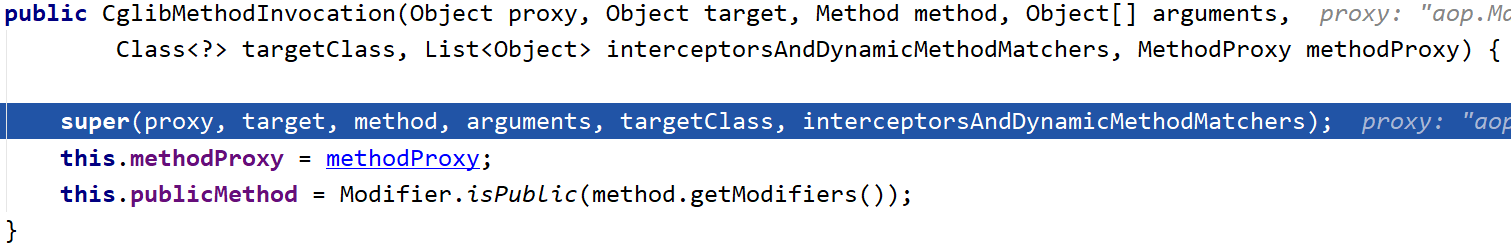
设置好代理对象、目标类、目标方法、拦截器链等一系列属性:
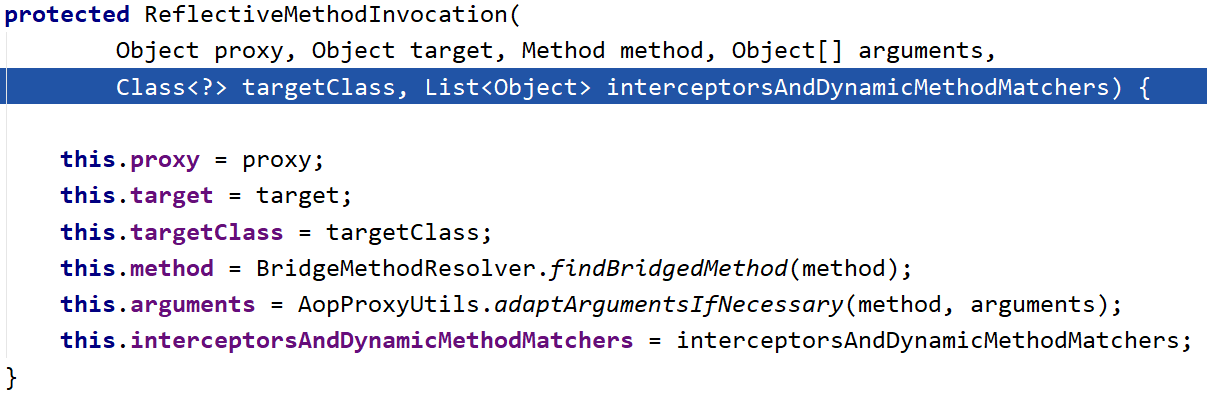
接着一路返回后调用 proceed 方法进行执行:
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
} Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
proceed
3~6:可以看到有一个从-1开始的索引,这是用来记录当前执行次数的(这里的size为5对应我们的五个增强器)

8~9:每次从拦截器链中获取一个增强器,索引加一
10:判断这个增强器是不是 InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher 类型,我们这里判断不满足,来到了else,返回调用 invoke 方法的结果

接下来我们进入这个执行过程
invoke方法调用proceed方法
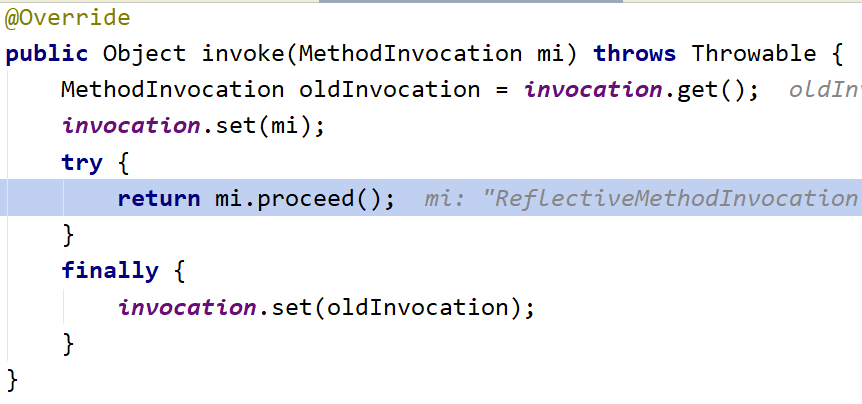
来到proceed方法继续判断索引大小

往下走又来到 invoke 方法,从下图可以看到当前是异常增强器的invoke()

进入invoke
先 return 调用 proceed 方法
可以看到下图中 catch 部分,说明如果有出现异常,会在catch部分调用增强器方法,并抛出异常
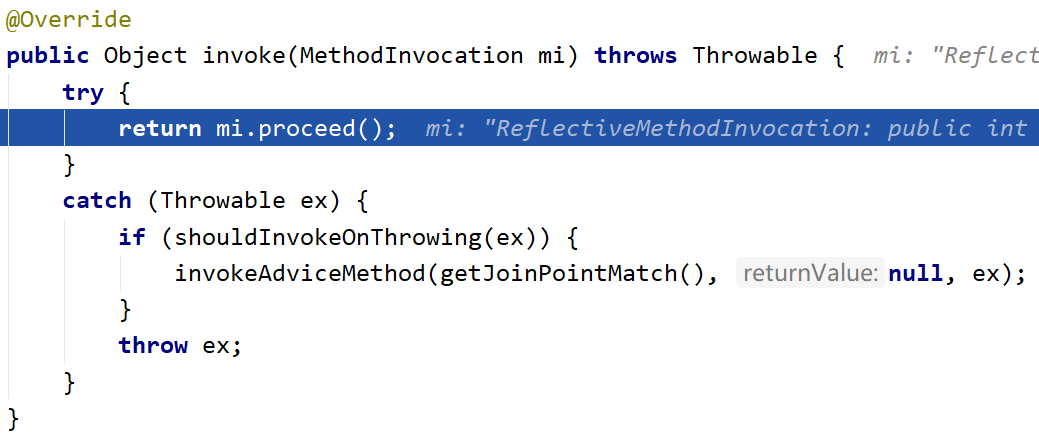
接下来又是调用AfterReturning的invoke过程

下图可以看到又调用了proceed

中间的过程也一样,这里就不演示了
最终我们的索引来到末尾
整个过程开始从内到外执行日志方法
开始调用日志方法打印:

抛出异常

最终拦截器链调用完毕,得到结果:

以上可以看到,整个执行流程是一个递归调用的过程,对之前排好序的拦截器链,通过索引判断界限,一层一层往里调用,最终递归回来一层层执行增强器(日志方法)

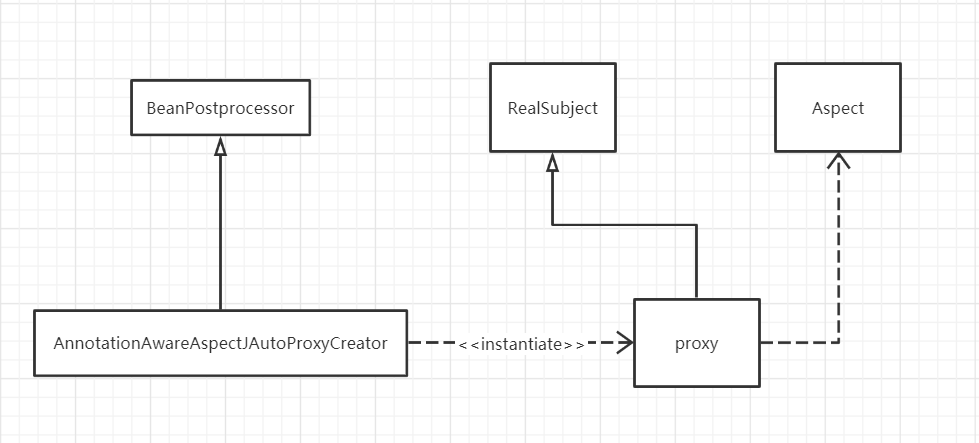
3、AOP总结:
通过@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解,给容器中注册 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,这个组件是一个后置处理器
会在每一个bean创建之前执行它的后置处理器方法来获取对应增强器,并获取到目标代理对象
在执行切面方法时,通过代理对象和增强器等信息,获取到拦截器链
拦截器链在包装处理后进入执行流程,嵌套调用后执行增强器方法
aop uml图
以下UML图是我对AOP的理解,如果有不对之处,欢迎大家指出
spring——AOP原理及源码(五)的更多相关文章
- spring——AOP原理及源码(一)
教程共分为五篇,从AOP实例的构建及其重要组件.基本运行流程.容器创建流程.关键方法调用.原理总结归纳等几个方面一步步走进AOP的世界. 本篇主要为读者演示构建AOP实例及AOP核心组件分析. 一.项 ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(四)
前情回顾: 上文我们一路分析了从容器创建开始直到我们的AOP注解导入的核心组件AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator执行postProcessBeforeInst ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(二)
回顾: 在上一篇中,我们提到@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解给容器中加入了一个关键组件internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition,实际类型为 An ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(三)
在上一篇中,我们创建并在BeanFactory中注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator组件.本篇我们将要探究,这个组件是在哪里以及何时发挥作用的. 调试的起 ...
- 【Spring】Spring IOC原理及源码解析之scope=request、session
一.容器 1. 容器 抛出一个议点:BeanFactory是IOC容器,而ApplicationContex则是Spring容器. 什么是容器?Collection和Container这两个单词都有存 ...
- Spring AOP介绍及源码分析
转自:http://www.uml.org.cn/j2ee/201301102.asp 软件开发经历了从汇编语言到高级语言和从过程化编程到面向对象编程:前者是为了提高开发效率,而后者则使用了归纳法,把 ...
- Spring中AOP原理,源码学习笔记
一.AOP(面向切面编程):通过预编译和运行期动态代理的方式在不改变代码的情况下给程序动态的添加一些功能.利用AOP可以对应用程序的各个部分进行隔离,在Spring中AOP主要用来分离业务逻辑和系统级 ...
- spring MVC 原理及源码解析
首先要知道springmvc的核心控制器dispatcherServlet(继承自httpServlet) 一般httpServlet的请求过程: 1.初始化(创建servlet实例时)时会执行ser ...
- 并发编程(十五)——定时器 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 实现原理与源码深度解析
在上一篇线程池的文章<并发编程(十一)—— Java 线程池 实现原理与源码深度解析(一)>中从ThreadPoolExecutor源码分析了其运行机制.限于篇幅,留下了Scheduled ...
随机推荐
- rest framework-解析器和渲染器-长期维护
############### 解析器 ############### # 解析器----数据解析器, # # 前端发送了json数据,在request的body里面, # 我们需要把json ...
- Java程序员常用Linux性能分析命令
性能分析 vmstat 虚拟内存统计 用法 Usage: vmstat [options] [delay [count]] Options: -a, --active active/inactive ...
- Excel-DNA项目只用1个文件实现Ribbon CustomUI和CustomTaskpane定制【C#版】
Excel-DNA项目中的自定义功能区和自定义任务窗格需要用到各种命名空间.添加所需文件,才能实现.后来我发现可以把所有代码都写在Class1.cs这个默认文件中. 大家可以在Visual Studi ...
- ddt-python测试数据驱动工具(转载)
背景 python 的unittest 没有自带数据驱动功能. 所以如果使用unittest,同时又想使用数据驱动,那么就可以使用DDT来完成. DDT是 “Data-Driven Tests”的缩写 ...
- [LC] 127. Word Ladder
Given two words (beginWord and endWord), and a dictionary's word list, find the length of shortest t ...
- python语法基础-函数-递归函数-长期维护
############### 递归 ############## # 递归的定义——在一个函数里再调用这个函数本身 # 递归的最大深度——998 # 二分查找算法 # 你观察这个列表,这是 ...
- CentOS-Samba服务安装与配置
title date tags layout CentOS6.5 Samba服务安装与配置 2018-09-03 Centos6.5服务器搭建 post 例题: 在服务器中安装Samba服务,创建共享 ...
- JavaScript学习总结(四)function函数部分
转自:http://segmentfault.com/a/1190000000660786 概念 函数是由事件驱动的或者当它被调用时执行的可重复使用的代码块. js 支持两种函数:一类是语言内部的函数 ...
- Ajax如何提交数据到springMVC后台
现在好多web项目实现前段和后端分离,实现前端和后端技术人员,使他们加快开发,减少沟通上的问题,后台只需要提供访问接口,而前天只需要调用提供的接口即可.减少前后端的沟通上的成本 本项目是开发中发现aj ...
- mybatis generator 使用教程(生成带注释的实体类)
引言: 最近的一个项目,由于数据库表巨多,导致需要创建N多个java实体.dao.mapper.xml映射文件,如果均使用纯手工编写,无疑需要耗费大量时间和精力.于是上网学习了mybatis gene ...
