ThinkJava-新IO
package com.java.io; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class GetChannel {
private static final int BSIZE = 1024; @SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取通道,该通道允许写操作
FileChannel fc = new FileOutputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
// 将字节数组包装到缓冲区中
fc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Some text ".getBytes()));
// 关闭通道
fc.close(); // 随机读写文件流创建的管道
fc = new RandomAccessFile("data.txt", "rw").getChannel();
// fc.position()计算从文件的开始到当前位置之间的字节数
// 设置此通道的文件位置,fc.size()此通道的文件的当前大小,该条语句执行后,通道位置处于文件的末尾
fc.position(fc.size()); // Move to the end
fc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Some more".getBytes()));
fc.close(); // Read the file:
fc = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
// 将文件内容读到指定的缓冲区中
fc.read(buff);
//buffer.flip();一定得有,如果没有,就是从文件最后开始读取的,当然读出来的都是byte=0时候的字符。
//通过buffer.flip();这个语句,就能把buffer的当前位置更改为buffer缓冲区的第一个位置。
buff.flip();
while(buff.hasRemaining()){
System.out.print((char)buff.get());
}
}
}
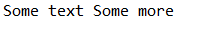
package com.java.io; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class ChannelCopy {
private static final int BSIZE = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if(args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("arguments: sourcefile destfile");
System.exit(1);
}
FileChannel in = new FileInputStream(args[0]).getChannel(),
out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]).getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
while(in.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip(); // Prepare for writing
out.write(buffer);
buffer.clear(); // Prepare for reading
}
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; public class TransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if(args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("arguments: sourcefile destfile");
System.exit(1);
}
FileChannel in = new FileInputStream(args[0]).getChannel(),
out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]).getChannel(); in.transferTo(0, in.size(), out);
// Or:
// out.transferFrom(in, 0, in.size());
}
}
package com.java.io; import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class BufferToText {
private static final int BSIZE = 1024; @SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileChannel fc = new FileOutputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
fc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Some text".getBytes()));
fc.close();
fc = new FileInputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
fc.read(buff);
buff.flip();
// Doesn't work:
System.out.println(buff.asCharBuffer()); // Decode using this system's default Charset:
buff.rewind();
String encoding = System.getProperty("file.encoding");
System.out.println("Decoded using " + encoding + ": " + Charset.forName(encoding).decode(buff)); // Or, we could encode with something that will print:
fc = new FileOutputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
fc.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Some text".getBytes("UTF-16BE")));
fc.close();
// Now try reading again:
fc = new FileInputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
buff.clear();
fc.read(buff);
buff.flip();
System.out.println(buff.asCharBuffer()); // Use a CharBuffer to write through:
fc = new FileOutputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(24); // More than needed
buff.asCharBuffer().put("Some text");
fc.write(buff);
fc.close(); // Read and display:
fc = new FileInputStream("data2.txt").getChannel();
buff.clear();
fc.read(buff);
buff.flip();
System.out.println(buff.asCharBuffer());
}
}
---------------
ThinkJava-新IO的更多相关文章
- java 21 - 15 新IO流 NIO
1:JDK4 新IO要了解的类 Buffer(缓冲),Channer(通道) 2:JDK7 要了解的新IO类 Path:与平台无关的路径. Paths:包含了返回Path的静态方法. public ...
- Java 新IO
NIO提供全新的底层I/O模型.与最初的java.io包中面向流(stream-oriented)概念不同,NIO采用了面向块的概念(block-oriented).在尽可能的情况下,I/O的操 ...
- JAVA(六)数据库/网络编程/新IO
成鹏致远 | lcw.cnblog.com |2014-02-05 数据库 1.JDBC概述 JDBC(Java Database Connectivity,Java数据库连接)提供了一种与平台无关的 ...
- Java -- 新IO -- 目录
20.1 Java 新IO简介 20.2 缓冲区与Buffer 例:演示缓冲区的操作流程 Class : IntBufferDemo01 20.2.2 深入缓冲区操作 20.2.3 创建子缓冲区 20 ...
- Pipelines - .NET中的新IO API指引(三) 边看边记
Pipelines - .NET中的新IO API指引 作者 marcgravell 原文 此系列前两篇网上已有的译文 Pipelines - .NET中的新IO API指引(一) Pipeline ...
- Java 8特性尝鲜:新新IO
Java 8特性尝鲜:新新IO 在这个专题前面的文章中,我们已经看到,使用Java8的lambda表达式对现有的JDK1.2 I/O库的提升,主要是可以使用lambda表达式来构造java.io.Fi ...
- Pipelines - .NET中的新IO API指引(一)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39223648 原文:Pipelines - a guided tour of the new IO API in .NET, part 1 ...
- Java——新IO 通道
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.ch ...
- 新IO建立的聊天程序
服务端: package com.net.scday3; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import j ...
- java 1.7 新io 实践 NIO2
Files 类使用 package com.xinyu.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import jav ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode——Next Permutation
1. Question Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next gre ...
- 快递100API接口调用代码示例
package com.util; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.MalformedU ...
- 将 R 整合到 markdown 中
markdown 易于写入和读取,具有编写报告的必要功能,例如简单的文本格式,嵌入图片.链接.表.引用.数学公式以及代码块.虽然在 markdown 中编写纯文本很容易,但是创建具有许多图片和表格的报 ...
- 重塑 data.table
在前面的章节中,我们已经学习了如何使用 reshape2 扩展包对 data.frame 进行塑形.其实,data.table 扩展包为 data.table 对象提供了更快更强的 dcast( ) ...
- a href 属性
两种用法: 页面跳转时使用 url (部分浏览器会阻止新窗口弹出页面),其他情况一律遵循 ‘结构样式行为分离’ 1. url href="#" 文档顶部 ...
- UVA-10603 Fill (BFS)
题目大意:有三个已知体积但不知刻度的杯子,前两个杯子中初始时没有水,第三个装满水,问是否可以倒出d升水,如果倒不出,则倒出一个最大的d’,使得d’<=d,并且在这个过程中要求总倒水量最少. 题目 ...
- URAL 1040 Airline Company 构造,思路 难度:2
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1040 题目要求在一个联通无向图中找出一种方法给边标号使得任意一个有多条边的点,边的号码的最大公约数 ...
- 前序+中序->后序 中序+后序->前序
前序+中序->后序 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node { char elem; node* l; n ...
- Python+Flask+MysqL的web建设技术过程
一.前言(个人学期总结) 个人总结一下这学期对于Python+Flask+MysqL的web建设技术过程的学习体会,Flask小辣椒框架相对于其他框架而言,更加稳定,不会有莫名其妙的错误,容错性强,运 ...
- Openlayers4中地图的导出
概述: 本文讲述Openlayers4中地图的导出,包括调用天地图切片跨域.Geoserver11 WMS跨域等. 效果: 导出图片 页面展示 实现代码: document.getElementByI ...
