Spring Boot 启动(二) Environment 加载
Spring Boot 启动(二) Environment 加载
Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698.html)
上一节中讲解了 SpringApplication 启动的整个流程,本节关注第二步 prepareEnvironment,尤其是配置文件的加载。
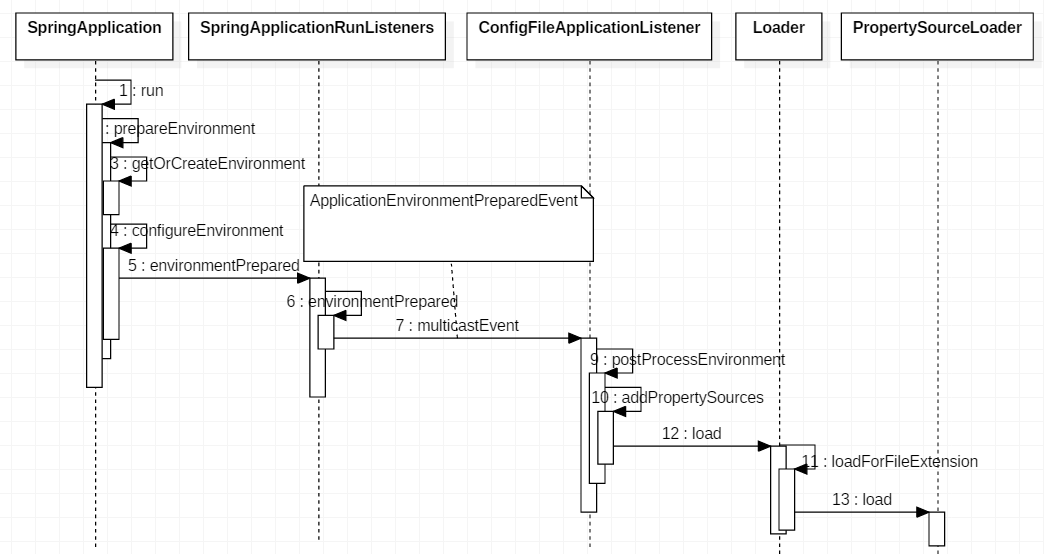
一、prepareEnvironment 加载流程分析
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 1. listeners 用户监听容器的运行,默认实现为 EventPublishingRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 2. 初始化环境变量 environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 1. 根据 webApplicationType 创建相应的 Environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 2. 配置 Environment,主要有三点:一是 ConversionService;二是数据源,包括命令行参数;三是 Profiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 3. 激活 environmentPrepared 事件,主要是加载 application.yml 等配置文件
// ConfigFileApplicationListener#ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// ??? 以后再研究
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
根据 webApplicationType 类型创建相应的 Environment,分为 StandardEnvironment、StandardServletEnvironment、StandardReactiveWebEnvironment。
configureEnvironment 主要有三点:一是 ConversionService;二是数据源,包括命令行参数;三是 Profiles
激活 environmentPrepared 事件,主要是加载 application.yml 等配置文件
2.1 getOrCreateEnvironment
对于 StandardServletEnvironment 的 servletContextInitParams 和 servletConfigInitParams 两个 web 的数据源,会先用 StubPropertySource 占位,等初始化 web 容器时再替换。详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10291323.html
2.2 configureEnvironment
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
String[] args) {
// 1. 设置 ConversionService
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
// 2. 加载 defaultProperties 和 CommandLinePropertySource(main 参数) 信息
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 3. 设置 environment 的 Profiles(additionalProfiles + spring.profile.active/default)
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
configurePropertySources 添加在 Spring Framework 基础上添加了两个新的据源,一是自定义的 defaultProperties;二是 CommandLinePropertySource(main 参数)
configureProfiles 在原有的剖面上添加自定义的剖面 additionalProfiles,注意 additionalProfiles 在前,Spring Framework 默认的剖面在后。
2.3 environmentPrepared
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment) 主要是加载配置文件,其中 listeners 是通过 spring.factories 配置的 SpringApplicationRunListener,默认实现是 EventPublishingRunListener。
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));
}
environmentPrepared 触发了 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件,这个事件是在 spring.factories 配置的监听器 ConfigFileApplicationListener 处理的。
二、ConfigFileApplicationListener
2.1 ConfigFileApplicationListener 处理流程
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener
implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 1. Environment 加载完成触发 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
// 2. ApplicationContext 加载完成触发 ApplicationPreparedEvent
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
}
本例中触发了 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件。
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 1. 委托给 EnvironmentPostProcessor 处理,也是通过 spring.factories 配置
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
// 2. ConfigFileApplicationListener 本身也实现了 EnvironmentPostProcessor 接口
postProcessors.add(this);
// 3. spring 都都通过 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator 控制执行顺序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
// 4. 执行 EnvironmentPostProcessor
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
在 spring.factories 配置文件中默认定义了三个 EnvironmentPostProcessor 的实现类:
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
优先级 SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor > SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor对 systemEnvironment 属性进行了包装。SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor解析 spring.application.json 或 SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON 配置的 json 字符串。
同时 ConfigFileApplicationListener 也实现了 EnvironmentPostProcessor 接口。我们重点关注的是 ConfigFileApplicationListener 是如何加载配置文件的,其它的 EnvironmentPostProcessor 暂时忽略。跟踪 ConfigFileApplicationListener#postProcessEnvironment 方法,最终加载配置文件委托给了其内部类 Loader 完成。
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// 1. 加载随机数据源 ${random.int} ${random.long} ${random.uuid}
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
// 2. 加载配置文件
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
三、Loader 加载配置文件
3.1 Spring Boot 默认目录及配置文件名
Spring Boot 默认的配置文件的目录及配置文件名称如下:
// 1. 配置文件默认的目录,解析时会倒置,所以 Spring Boot 默认 jar 包的配置文件会覆盖 jar 中的配置文件
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
public static final String INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.include";
// 2. 配置文件默认的文件名
private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "application";
public static final String CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY = "spring.config.name";
3.2 profiles 解析配置文件的顺序
先了解一起 Spring FrameWork 和 Spring Boot 的 profiles 的概念。
| 配置 | Spring | 类 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| spring.profiles.active | Spring FrameWork | AbstractEnvironment | 激活的剖面 |
| spring.profiles.default | Spring FrameWork | AbstractEnvironment | 默认剖面 |
| additionalProfiles | Spring Boot | SpringApplication | 自定义激活的剖面 |
| spring.profiles.include | Spring Boot | ConfigFileApplicationListener | 自定义激活的剖面 |
在启动 SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment 时已经激活了 additionalProfiles + Spring FrameWork 剖面,注意剖面的顺序。 ConfigFileApplicationListener 引入 spring.profiles.include
private void initializeProfiles() {
// 1. null
this.profiles.add(null);
// spring.profiles.include + spring.profiles.active 配置的剖面
Set<Profile> activatedViaProperty = getProfilesActivatedViaProperty();
// 2. environment.getActiveProfiles() 过滤 activatedViaProperty 之后的剖面
// 目前看只有 SpringApplication 配置的 additionalProfiles
this.profiles.addAll(getOtherActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty));
// 3. spring.profiles.include + spring.profiles.active
// addActiveProfiles 方法只能调用一次,前提是 activatedViaProperty 不为空
addActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty);
// 4. spring.profiles.default
if (this.profiles.size() == 1) {
for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) {
Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true);
this.profiles.add(defaultProfile);
}
}
}
Spring Boot 配置文件 Profiles(application-dev.properties) 的解析顺序如下:
- 首先解析 null,也就是 application.properties 或 application.yml 文件
- spring.profiles.include/active 属性配置之外的剖面先解析,一般是 activatedViaProperty 或其它编程式配置的 Profiles
- spring.profiles.include 定义的剖面,第三和第四的顺序在 getProfilesActivatedViaProperty 中定义
- spring.profiles.active 定义的剖面
- spring.profiles.default 如果没有激活的剖面,默认 default,即没有 2、3、4 项
注意:实际读取配置文件的顺序和解析的相反,下面会详细说明。
还有一种情况是在配置文件 application.properties 中定义了 spring.profiles.include/active 属性的情况。加载到配置文件后需要判断是否定义了以上两个属性,如果定义了,也需要加载该剖面对应的配置文件。
private void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile,
DocumentFilter filter, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
// 省略...
List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
if (filter.match(document)) {
// 1. spring.profiles.active,如果已经定义了该方法就不会再执行了
addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles());
// 2. spring.profiles.include
addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles());
loaded.add(document);
}
}
}
// 毫无疑问,如果配置文件中定义了 spring.profiles.include 则需要先解析这些剖面,再解析其余的剖面
private void addIncludedProfiles(Set<Profile> includeProfiles) {
LinkedList<Profile> existingProfiles = new LinkedList<>(this.profiles);
this.profiles.clear();
// 1. 先解析配置文件中定义的 spring.profiles.include,当然如果已经解析了则需要排除
this.profiles.addAll(includeProfiles);
this.profiles.removeAll(this.processedProfiles);
// 2. 再解析剩余的剖面
this.profiles.addAll(existingProfiles);
}
总结,(1) 剖面最终的读取顺序如下:
- spring.profiles.active 配置的剖面
- spring.profiles.include 配置的剖面
- 编程式配置的剖面,如 SpringApplicaiton#etAdditionalProfiles 或 environment#addActiveProfile
- 如果未定义激活的剖面,则 spring.profiles.default
- 默认的配置文件,如 application.properties
- 如果 1-5 项定义了多个,则后面定义的剖面覆盖前面的剖面,如 spring.profiles.active=dev,test 则 test 覆盖 dev
(2) 文件名定义的读取顺序如下:
- spring.config.name 定义了配置文件名,默认为 applicaiton,可以定义多个,如果有多个则后面的覆盖前面的
(3) 目录定义的读取顺序如下:
spring.config.location 定义配置文件所在目录,默认为
classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/也就是后面的覆盖前面的配置,也就是 jar 包外的配置覆盖 jar 包内的配置。注意 spring.config.location 如果指定了文件名则 spring.config.name 不会生效。spring.config.additional-location 上面的配置会覆盖 Spring Boot 的默认配置目录,而本配置项则是在默认配置项上追加,先读取 spring.config.additional-location 再读取默认的目录。当然如果显示的定义了 spring.config.location 就只会读取这一项。
3.3 配置文件解析
public void load() {
// 所有的要解析的 profiles,注意读取配置文件的时候可以会增加
// 因为配置文件中可能又定义了 spring.profiles.include 属性
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
// 已经解析过的 profiles,可以避免循环解析
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 1. this.profiles 集合定义了 profile 解析顺序
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (profile != null && !profile.isDefaultProfile()) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
// 2. 具体解析配置文件到 this.loaded 中
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter,
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
// 3. 解析后 environment#getActiveProfles 可能和配置文件的顺序 processedProfiles 不一致
resetEnvironmentProfiles(this.processedProfiles);
// 4. 默认的配置文件中定义了剖面,则要看这个配置文件定义的剖面是否激活
// 即 application.properties 定义了 spring.profile=dev,dev 如果被激活则加载
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter,
addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
// 5. 加载配置文件到 environment 中,注意读取配置文件的顺序和解析的相反
addLoadedPropertySources();
}
- initializeProfiles 加载所有的剖面,解析时会按上面提到的顺序进行解析
- load 具体解析配置文件到 this.loaded 中
- addLoadedPropertySources 加载配置文件到 environment 中,注意读取配置文件的顺序和解析的相反
配置文件属性那一种剖面有三种定义方式:
- 文件名指定:application-dev.properties 属于 dev 剖面
- 文件名为 application.properties 但文件配置了 spring.profile=dev 属性也属于 dev 剖面
- 以上两种都指定了,即文件名为 application-dev.properties 的同时文件配置属性 spring.profile=dev
Spring Boot 针对以上三种情况均有支持。load 方法加载配置文件,最终调用 loadForFileExtension 方法。
private void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix,
String fileExtension, Profile profile,
DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null);
DocumentFilter profileFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile);
// 1. application-dev.properties
if (profile != null) {
String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension;
// application-dev.properties 这二个 load 最多只可能有一个生效 (gh-340)
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer);
// application-dev.properties && spring.profile=dev
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
// Try profile specific sections in files we've already processed
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile
+ fileExtension;
load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
}
}
// 2. application.properties && spring.profile=dev
load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
DocumentFilter 判断文件中是否定义了 spring.profile 的剖面
private DocumentFilter getPositiveProfileFilter(Profile profile) {
return (Document document) -> {
// profile==null 则文件中不能定义 spring.profile
if (profile == null) {
return ObjectUtils.isEmpty(document.getProfiles());
}
// profile!=null 则配置文件中定义的 spring.profile 包含该 profile
// 且该配置文件定义的 spring.profile 被激活了
return ObjectUtils.containsElement(document.getProfiles(), profile.getName())
&& this.environment.acceptsProfiles(Profiles.of(document.getProfiles()));
};
}
另外这里的 PropertySourceLoader 也是通过 spring.factories 定义的,默认为 PropertiesPropertySourceLoader 和 YamlPropertySourceLoader 两种。
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!
Spring Boot 启动(二) Environment 加载的更多相关文章
- spring boot 启动 开启注解 加载 bean
业务描述:创建一个cache类然后交给spring 管理. @Component @Scope("singleton") public class Cache { public C ...
- Spring Boot自定义配置与加载
Spring Boot自定义配置与加载 application.properties主要用来配置数据库连接.日志相关配置等.除了这些配置内容之外,还可以自定义一些配置项,如: my.config.ms ...
- Spring:启动项目时加载数据库数据(总结)
在项目中需要启动程序时,要将数据库的用户信息表加载到内存中,找到一下几种方式. 1.实现ApplicationListener接口,重写onApplicationEvent方法,可以在项目启动的时候执 ...
- Spring Boot 2程序不能加载 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 问题
用Spring Boot Starter 向导生成了一个很简单SpringBoot程序, 用到了 MySQL, 总是下面不能加载 Mysql driver class 错误. Cannot load ...
- Spring Boot 静态资源能加载css 不能加载js
Spring Boot 配置拦截器的时候默认 是放行 静态资源 , 也就是说不需要进行配置 registry.addResourceHandler("/**") .addResou ...
- 1.Spring项目启动时,加载相关初始化配置
Spring项目启动时,会加载一些常用的配置: 1.加载spring上下文 SpringApplicationContextUtils.initApplicationContext(event.get ...
- spring容器启动完成后加载自定义逻辑
业务需求中,可能会有一些逻辑需要在应用启动完成后,例如字典缓存,资源池初始化等等,代码如下 public class InitApplication implements ApplicationCon ...
- spring boot的静态资源加载
1.spring boot默认资源处理 Spring Boot 默认为我们提供了静态资源处理,使用 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中的配置各种属性. spring boot默认加载文 ...
- spring boot注解 --@spring-boot-devtools 自动加载修改的文件和类
spriing boot中有一个注解,是自动加载修改后的类或者文件. 使用方法为: spring-boot-devtools=true 需要引入devtools包依赖: <dependency& ...
- spring boot开发 静态资源加载不出来
spring boot 1.5 版本之前 不拦截静态资源 springboot 2.x版本 拦截静态资源 private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURC ...
随机推荐
- 原生js创建模态框(摘自:东窗凝残月 链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/dcncy/p/9076937.html)
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Te ...
- marathon 测试
marathon 初步使用 关闭selinux setenforce 0 Marathon之应用篇 先来了解一下 Marathon 是怎么布署decker的 json shell.json { } ...
- maven打包时报错:-source 1.5 中不支持 diamond 运算符
报错现象: 解决方法: 在pom文件中加入下面依赖 <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.mav ...
- android selector shape 使用
先上效果图 message_toolbar_left_bg_selector <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?& ...
- 实验四:xl命令的常见子命令以及操作
实验名称: xl命令的常见子命令以及操作 实验环境: 这里我们需要正常安装一台虚拟机,如下图: 我们这里以一台busybox为例,来进行这些简单的常见的操作: 实验要求: 这里我们准备了5个常见操作: ...
- DBsever工具连接mysql数据库
当我们安装网DBeaver的时候,怎么通过这个工具来连接Mysql数据库呢 像这个地方就按平时你的数据库信息输入就可以了 接下来配置JDBC的内容 重点说一下驱动包的版本问题,因为我安装的mysql是 ...
- oracle之分析函数解析及其应用场景
ORACLE 分析函数FIRST_VALUE,LAST_VALUE用法sum overavg over first_value overlast_value over...聚合函数结合over就是分析 ...
- 引用全局变量global
lang = Lang.chn def set_lang(lang_type): global lang lang = lang_type
- ATS的curl清除缓存
在/trafficserver/ip_allow.config定义好允许PURGE的IP后 推送: curl -i -X HEAD “url” -x 127.0.0.1:51899 curl -i - ...
- airbnb 开源reAir 工具 用法及源码解析(一)
reAir 有批量复制与增量复制功能 今天我们先来看看批量复制功能 批量复制使用方式: cd reair ./gradlew shadowjar -p main -x test # 如果是本地tabl ...
