WSGI、mini-web框架
阅读目录:
一.服务器动态资源请求
1. 浏览器请求动态页面过程
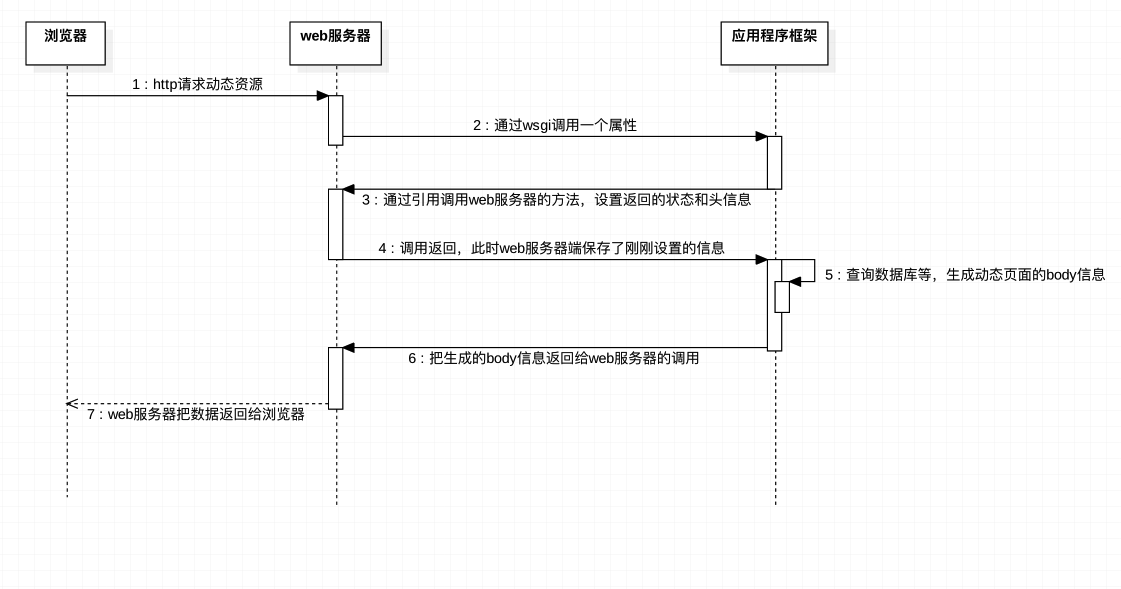
2. WSGI
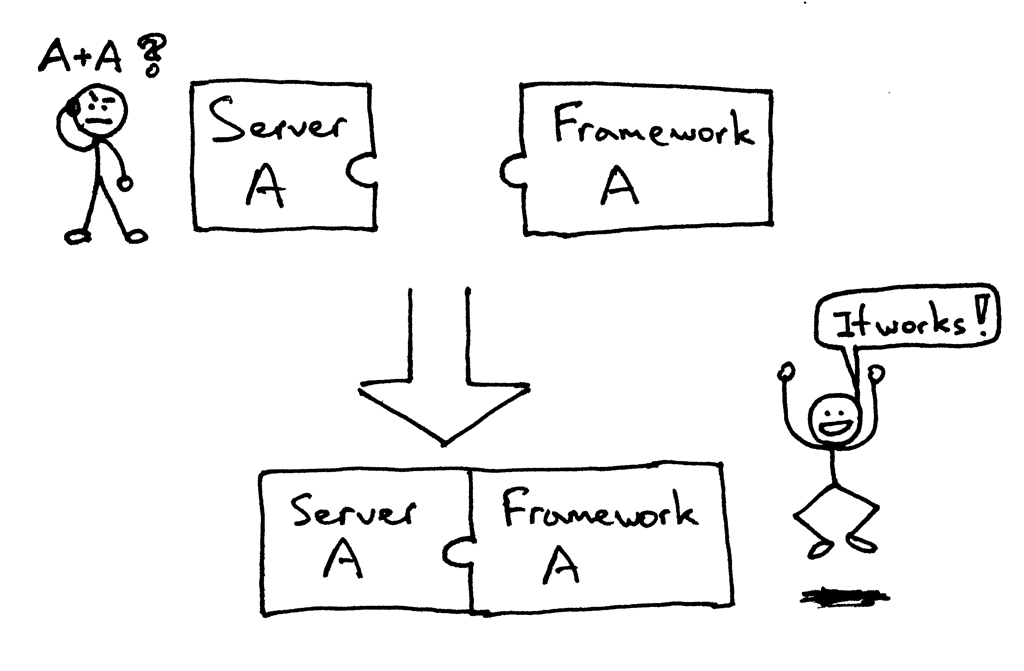
怎么在你刚建立的Web服务器上运行一个Django应用和Flask应用,如何不做任何改变而适应不同的web架构呢?
在以前,选择 Python web 架构会受制于可用的web服务器,反之亦然。如果架构和服务器可以协同工作,那就好了:
但有可能面对(或者曾有过)下面的问题,当要把一个服务器和一个架构结合起来时,却发现他们不是被设计成协同工作的:
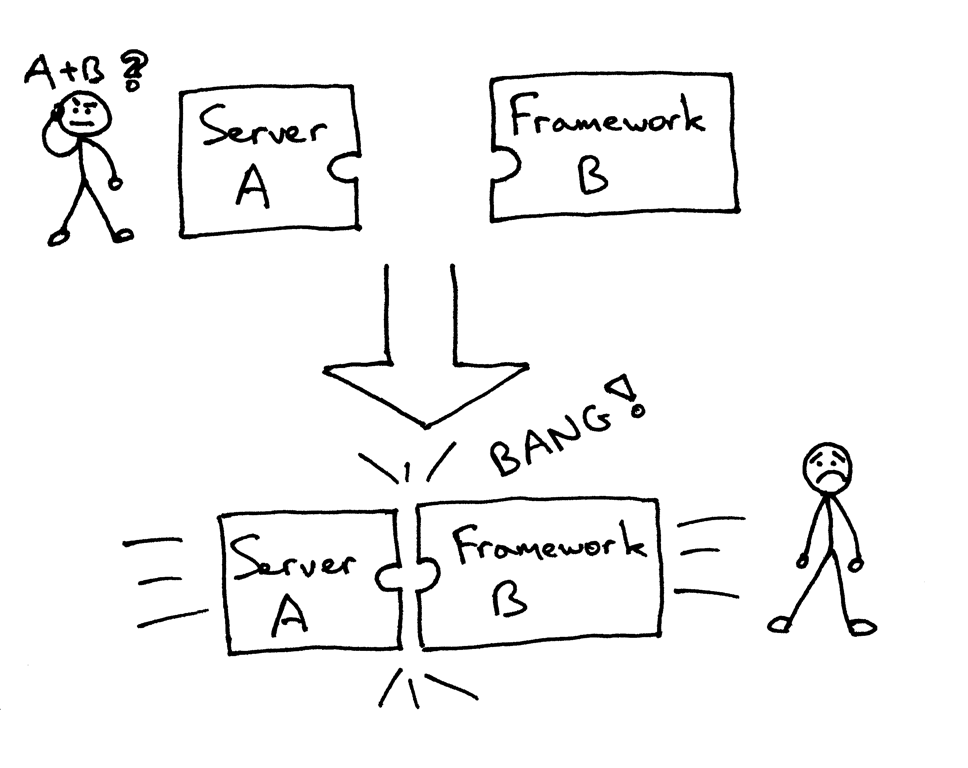
那么,怎么可以不修改服务器和架构代码而确保可以在多个架构下运行web服务器呢?答案就是 Python Web Server Gateway Interface (或简称 WSGI,读作“wizgy”)。
WSGI允许开发者将选择web框架和web服务器分开。可以混合匹配web服务器和web框架,选择一个适合的配对。比如,可以在Gunicorn 或者 Nginx/uWSGI 或者 Waitress上运行 Django, Flask, 或 Pyramid。真正的混合匹配,得益于WSGI同时支持服务器和架构:

web服务器必须具备WSGI接口,所有的现代Python Web框架都已具备WSGI接口,它让你不对代码作修改就能使服务器和特点的web框架协同工作。
WSGI由web服务器支持,而web框架允许你选择适合自己的配对,但它同样对于服务器和框架开发者提供便利使他们可以专注于自己偏爱的领域和专长而不至于相互牵制。其他语言也有类似接口:java有Servlet API,Ruby 有 Rack。
3.定义WSGI接口
WSGI接口定义非常简单,它只要求Web开发者实现一个函数,就可以响应HTTP请求。我们来看一个最简单的Web版本的“Hello World!”:
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return 'Hello World!'
上面的application()函数就是符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,它接收两个参数:
- environ:一个包含所有HTTP请求信息的dict对象;
- start_response:一个发送HTTP响应的函数。
整个application()函数本身没有涉及到任何解析HTTP的部分,也就是说,把底层web服务器解析部分和应用程序逻辑部分进行了分离,这样开发者就可以专心做一个领域了
不过,等等,这个application()函数怎么调用?如果我们自己调用,两个参数environ和start_response我们没法提供,返回的str也没法发给浏览器。
所以application()函数必须由WSGI服务器来调用。有很多符合WSGI规范的服务器。而我们此时的web服务器项目的目的就是做一个既能解析静态网页还可以解析动态网页的服务器
4. web服务器-----WSGI协议---->web框架 传递的字典
{
'HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE': 'zh-cn',
'wsgi.file_wrapper': <built-infunctionuwsgi_sendfile>,
'HTTP_UPGRADE_INSECURE_REQUESTS': '1',
'uwsgi.version': b'2.0.15',
'REMOTE_ADDR': '172.16.7.1',
'wsgi.errors': <_io.TextIOWrappername=2mode='w'encoding='UTF-8'>,
'wsgi.version': (1,0),
'REMOTE_PORT': '40432',
'REQUEST_URI': '/',
'SERVER_PORT': '8000',
'wsgi.multithread': False,
'HTTP_ACCEPT': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
'HTTP_HOST': '172.16.7.152: 8000',
'wsgi.run_once': False,
'wsgi.input': <uwsgi._Inputobjectat0x7f7faecdc9c0>,
'SERVER_PROTOCOL': 'HTTP/1.1',
'REQUEST_METHOD': 'GET',
'HTTP_ACCEPT_ENCODING': 'gzip,deflate',
'HTTP_CONNECTION': 'keep-alive',
'uwsgi.node': b'ubuntu',
'HTTP_DNT': '1',
'UWSGI_ROUTER': 'http',
'SCRIPT_NAME': '',
'wsgi.multiprocess': False,
'QUERY_STRING': '',
'PATH_INFO': '/index.html',
'wsgi.url_scheme': 'http',
'HTTP_USER_AGENT': 'Mozilla/5.0(Macintosh;IntelMacOSX10_12_5)AppleWebKit/603.2.4(KHTML,likeGecko)Version/10.1.1Safari/603.2.4',
'SERVER_NAME': 'ubuntu'
}
二.应用程序示例
import time def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
三.Web动态服务器-基本实现
文件结构
├── web_server.py
├── web
│ └── my_web.py
└── html
└── index.html
.....
web/my_web.py
import time def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py
import select
import time
import socket
import sys
import re
import multiprocessing class WSGIServer(object):
"""定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 2. 绑定本地信息
self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.server_socket.bind(("", port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径
self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象)
self.app = app def run_forever(self):
"""运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接
while True:
new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept()
# 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务
new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s
new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,))
new_process.start()
new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket):
"""以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True:
try:
request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
except Exception as ret:
print("========>", ret)
client_socket.close()
return # 判断浏览器是否关闭
if not request:
client_socket.close()
return request_lines = request.splitlines()
for i, line in enumerate(request_lines):
print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html)
# GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1
ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1))
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2))
file_name = ret.group(2)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件
if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据
try:
f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb")
except:
response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else:
content = f.read()
f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面
else:
# 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据
env = {}
# 存web返回的数据
response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0])
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body)
for temp_head in self.headers[1]:
response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n"
response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers):
"""这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用"""
response_header_default = [
("Data", time.ctime()),
("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server")
] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来
# [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]]
self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers] # 设置静态资源访问的路径
g_static_document_root = "./html"
# 设置动态资源访问的路径
g_dynamic_document_root = "./web" def main():
"""控制web服务器整体"""
# python3 xxxx.py 7890
if len(sys.argv) == 3:
# 获取web服务器的port
port = sys.argv[1]
if port.isdigit():
port = int(port)
# 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字
web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2]
else:
print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:application")
return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了
sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name)
if ret:
# 获取模块名
web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1)
# 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称
app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块
web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name)
# 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象)
app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器
http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app)
# 运行http服务器
http_server.run_forever() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行
1. 打开终端,输入以下命令开始服务器
python3 web_server.py my_web:application
2. 打开浏览器

四.mini web框架-1-文件结构
文件结构
├── dynamic ---存放py模块
│ └── my_web.py
├── templates ---存放模板文件
│ ├── center.html
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── location.html
│ └── update.html
├── static ---存放静态的资源文件
│ ├── css
│ │ ├── bootstrap.min.css
│ │ ├── main.css
│ │ └── swiper.min.css
│ └── js
│ ├── a.js
│ ├── bootstrap.min.js
│ ├── jquery-1.12.4.js
│ ├── jquery-1.12.4.min.js
│ ├── jquery.animate-colors.js
│ ├── jquery.animate-colors-min.js
│ ├── jquery.cookie.js
│ ├── jquery-ui.min.js
│ ├── server.js
│ ├── swiper.jquery.min.js
│ ├── swiper.min.js
│ └── zepto.min.js
└── web_server.py ---mini web服务器
my_web.py
import time def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py
import select
import time
import socket
import sys
import re
import multiprocessing class WSGIServer(object):
"""定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 2. 绑定本地信息
self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.server_socket.bind(("", port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径
self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象)
self.app = app def run_forever(self):
"""运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接
while True:
new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept()
# 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务
new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s
new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,))
new_process.start()
new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket):
"""以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True:
try:
request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
except Exception as ret:
print("========>", ret)
client_socket.close()
return # 判断浏览器是否关闭
if not request:
client_socket.close()
return request_lines = request.splitlines()
for i, line in enumerate(request_lines):
print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html)
# GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1
ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1))
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2))
file_name = ret.group(2)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件
if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据
try:
f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb")
except:
response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else:
content = f.read()
f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面
else:
# 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据
env = dict()
# 存web返回的数据
response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0])
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body)
for temp_head in self.headers[1]:
response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n"
response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers):
"""这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用"""
response_header_default = [
("Data", time.time()),
("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server")
] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来
# [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]]
self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers] # 设置静态资源访问的路径
g_static_document_root = "./static"
# 设置动态资源访问的路径
g_dynamic_document_root = "./dynamic" def main():
"""控制web服务器整体"""
# python3 xxxx.py 7890
if len(sys.argv) == 3:
# 获取web服务器的port
port = sys.argv[1]
if port.isdigit():
port = int(port)
# 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字
web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2]
else:
print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:application")
return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了
sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name)
if ret:
# 获取模块名
web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1)
# 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称
app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块
web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name)
# 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象)
app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器
http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app)
# 运行http服务器
http_server.run_forever() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
五.mini web框架-2-显示页面
dynamic/my_web.py (更新)
import time
import os template_root = "./templates" def index(file_name):
"""返回index.py需要的页面内容"""
# return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题
try:
file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html")
f = open(template_root + file_name)
except Exception as ret:
return "%s" % ret
else:
content = f.read()
f.close()
return content def center(file_name):
"""返回center.py需要的页面内容"""
# return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题
try:
file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html")
f = open(template_root + file_name)
except Exception as ret:
return "%s" % ret
else:
content = f.read()
f.close()
return content def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]
start_response(status, response_headers) file_name = environ['PATH_INFO']
if file_name == "/index.py":
return index(file_name)
elif file_name == "/center.py":
return center(file_name)
else:
return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py (更新)
import select
import time
import socket
import sys
import re
import multiprocessing class WSGIServer(object):
"""定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字
self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 2. 绑定本地信息
self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.server_socket.bind(("", port))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径
self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象)
self.app = app def run_forever(self):
"""运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接
while True:
new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept()
# 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务
new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s
new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,))
new_process.start()
new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket):
"""以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True:
try:
request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
except Exception as ret:
print("========>", ret)
client_socket.close()
return # 判断浏览器是否关闭
if not request:
client_socket.close()
return request_lines = request.splitlines()
for i, line in enumerate(request_lines):
print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html)
# GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1
ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1))
print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2))
file_name = ret.group(2)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件
if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据
try:
print(self.documents_root+file_name)
f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb")
except:
response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else:
content = f.read()
f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body))
response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器
client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面
else:
# 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据
env = dict()
# ----------更新---------
env['PATH_INFO'] = file_name # 例如 index.py # 存web返回的数据
response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0])
response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n"
response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body.encode("utf-8"))
for temp_head in self.headers[1]:
response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n"
response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers):
"""这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用"""
response_header_default = [
("Data", time.time()),
("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server")
] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来
# [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]]
self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers] # 设置静态资源访问的路径
g_static_document_root = "./static"
# 设置动态资源访问的路径
g_dynamic_document_root = "./dynamic" def main():
"""控制web服务器整体"""
# python3 xxxx.py 7890
if len(sys.argv) == 3:
# 获取web服务器的port
port = sys.argv[1]
if port.isdigit():
port = int(port)
# 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字
web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2]
else:
print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:app")
return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了
sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name)
if ret:
# 获取模块名
web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1)
# 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称
app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块
web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name)
# 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象)
app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器
http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app)
# 运行http服务器
http_server.run_forever() if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
浏览器打开看效果
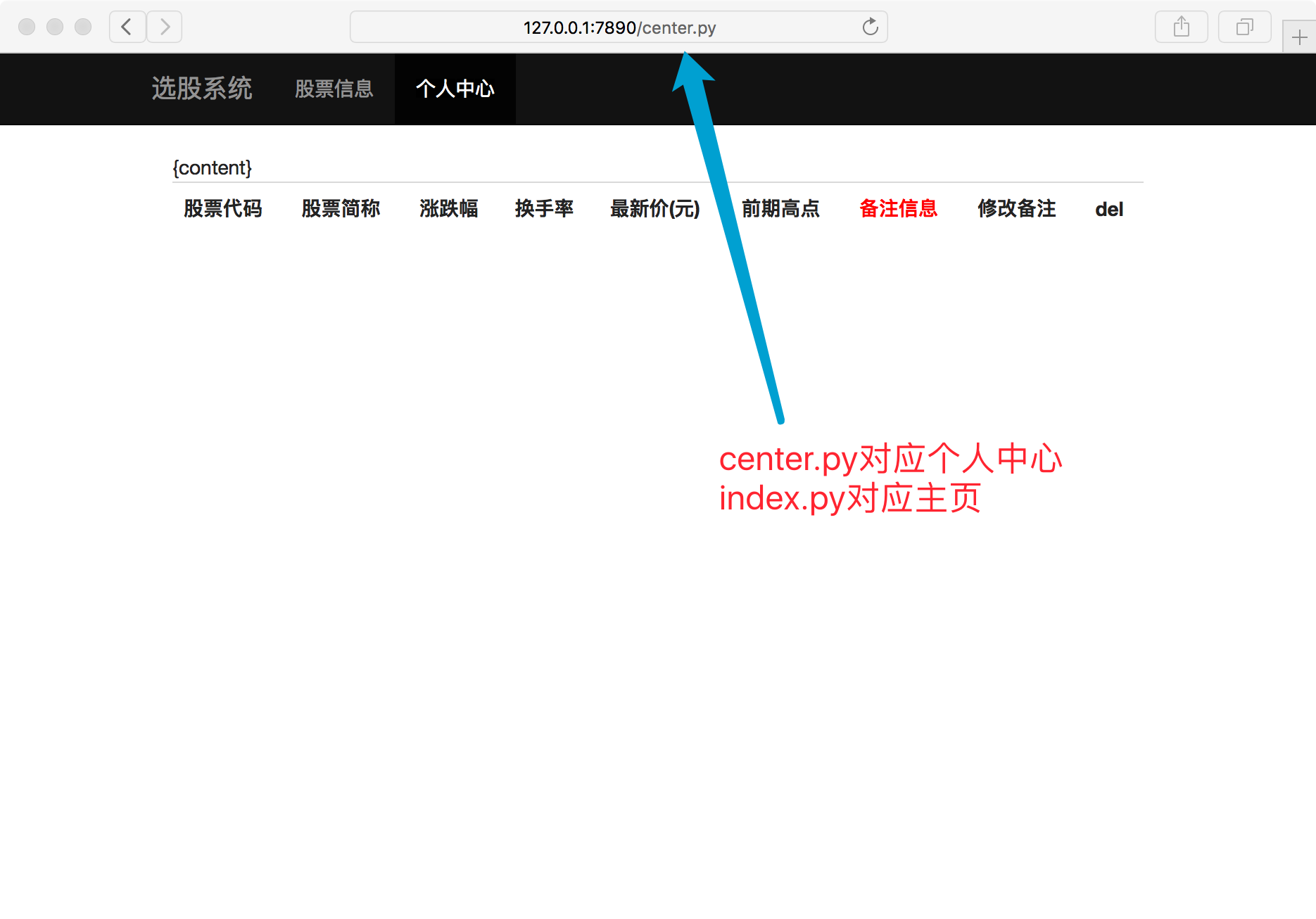
六.mini web框架-3-替换模板
dynamic/my_web.py
import time
import os
import re template_root = "./templates" def index(file_name):
"""返回index.py需要的页面内容"""
# return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题
try:
file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html")
f = open(template_root + file_name)
except Exception as ret:
return "%s" % ret
else:
content = f.read()
f.close() # --------更新-------
data_from_mysql = "数据还没有敬请期待...."
content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", data_from_mysql, content) return content def center(file_name):
"""返回center.py需要的页面内容"""
# return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题
try:
file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html")
f = open(template_root + file_name)
except Exception as ret:
return "%s" % ret
else:
content = f.read()
f.close() # --------更新-------
data_from_mysql = "暂时没有数据,,,,~~~~(>_<)~~~~ "
content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", data_from_mysql, content) return content def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]
start_response(status, response_headers) file_name = environ['PATH_INFO']
if file_name == "/index.py":
return index(file_name)
elif file_name == "/center.py":
return center(file_name)
else:
return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
浏览器打开看效果
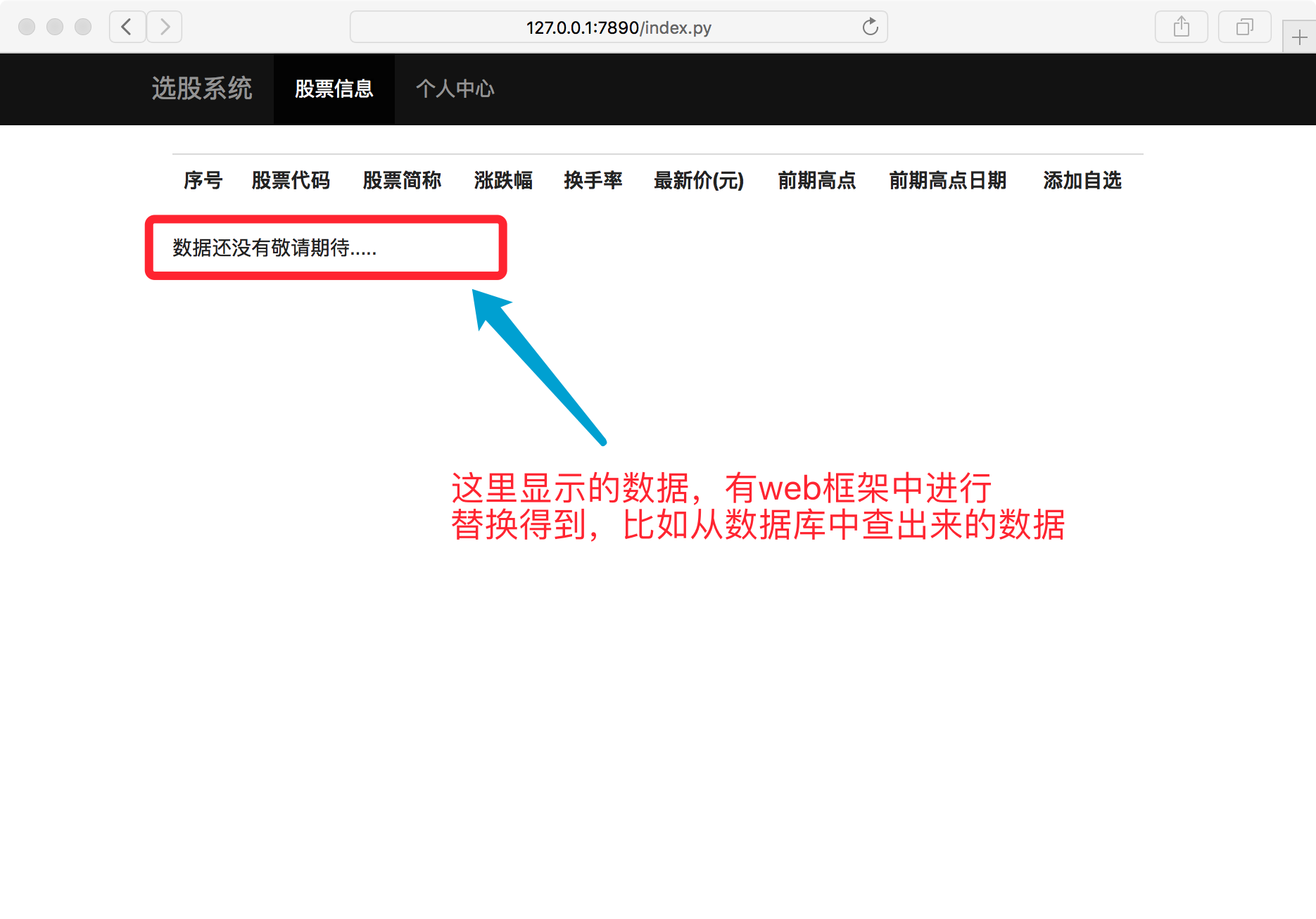
WSGI、mini-web框架的更多相关文章
- [Python之路] 实现简易HTTP服务器与MINI WEB框架(利用WSGI实现服务器与框架解耦)
本文描述如果简单实现自定义Web服务器与自定义简易框架,并且不断进行版本迭代,从而清晰的展现服务器与Web框架之间是如何结合.如何配合工作的.以及WSGI是什么. 本文帖的代码有点多,但基本每次迭代修 ...
- Wsgi的web框架实例
建立server服务端: from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server import time def f1(request): return [b'&l ...
- [Python之路] 使用装饰器给Web框架添加路由功能(静态、动态、伪静态URL)
一.观察以下代码 以下来自 Python实现简易HTTP服务器与MINI WEB框架(利用WSGI实现服务器与框架解耦) 中的mini_frame最后版本的代码: import time def in ...
- python学习之路web框架
WEB框架的本质 python的WEB框架分为两大类: 1.自己写socket,自己处理请求 2.基于wsgi(Web Server Gateway Interface WEB服务网关接口),自己处理 ...
- [py]彻底细究web框架的wsgi+逻辑处理模块
wsgi逻辑结构初探 参考: 这里图很精彩,wsgi写的不错 web框架 = wsgi+逻辑处理app 接收请求,返回对应的内容 python wsgiref实现了wsgi规范. from wsgir ...
- python之web框架(3):WSGI之web应用完善
python之web框架(3):WSGI之web应用完善 1.上篇的web框架太low,只能实现回应固定页面.现在将它进行完善.首先将wsgi和web服务器进行分离,并给予它回复静态页面的能力. we ...
- python之web框架(2):了解WSGI接口
python之web框架(2):了解WSGI接口 1.什么是wsgi接口: wsgi:Web Service Gateway Interface.它不是模块,而只是一种规范,方便web服务器和各种框架 ...
- python web框架 django wsgi 理论
django wsgi python有个自带的wsgi模块 可以写自定义web框架 用wsgi在内部创建socket对象就可以了 自己只写处理函数就可以了django只是web框架 他也不负责写soc ...
- 使用Python开发轻量级的Web框架以及基于WSGI的服务器来实现一个网站页面
说明:该篇博客是博主一字一码编写的,实属不易,请尊重原创,谢谢大家! 目录 一丶项目说明 二丶数据准备 三丶使用网络TCP开发一个基于WSGI协议的Web服务器 四丶使用python3开发一个轻量级的 ...
- wsgi Python的WEB框架
Bottle是一个快速.简洁.轻量级的基于WSIG的微型Web框架,此框架只由一个 .py 文件,除了Python的标准库外,其不依赖任何其他模块. pip install bottle easy_i ...
随机推荐
- 从baselines库的common/vec_env/vec_normalize.py模块看方差的近似计算方法
在baselines库的common/vec_env/vec_normalize.py中计算方差的调用方法为: RunningMeanStd 同时该计算函数的解释也一并给出了: https://en. ...
- python中不同方法的按索引读取数组的性能比较——哪种按索引读取数组的性能更好
写python代码这么多年,从来也没有想过不同方式的读取python数组会有什么太大的性能差距,不过这段时间写代码突然发现这个差别还挺大,于是就多研究了一下. 本文研究的是使用不同方式来对python ...
- java多线程之-线程池状态
1.背景 这一节我们来学习一下线程池状态..... 2.线程池状态 状态名称 高3位 是否接受新任务 是否处理队列中的任务 说明 RUNNING 111 是 是 线程池正常运行状态 SHUTDOWN ...
- WhaleStudio 2.6重磅发布!调度模块WhaleScheduler更新78项核心功能
我们很高兴地宣布WhaleStudio 2.6版本的正式发布!新版本中包含了数据调度模块WhaleScheduler和数据集成模块WhaleTunnel的百余项核心功能更新,本文摘选了WhaleSch ...
- 后端开发学习敏捷需求-->干系人分析与识别
干系人分析与识别 5W1H 干系人分析与识别 1. 干系人是什么 直接或者间接影响专题,以及被专题影响的人和组织,用户也是属于干系人,是产品直接或者间接的使用者 又叫利益相关者,指积极参与专题或者在专 ...
- 从头搭建一个嵌入式web服务器-boa服务器
一.什么是boa? BOA是一款非常小巧的Web服务器,源代码开放.性能优秀.支持CGI通用网关接口技术,特别适合应用在嵌入式系统中. BOA服务器主要功能是在互联嵌入式设备之间进行信息交互,达到通过 ...
- Python 开发中,使用bcrypt 或 Passlib 对系统用户密码进行哈希和验证处理
在设计一个系统的时候,肯定都有会有用户身份认证的问题,一般对用户校验的时候,都是对用户存在数据库总的密码哈希值进行判断,从而避免密码泄露和反向解密,那么在Python 开发中,我们可以引入bcrypt ...
- LeetCode300.最长递增子序列
LeetCode300.最长递增子序列 力扣题目链接(opens new window) 给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度. 子序列是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除 ...
- check Str's Character appearence frequence is ge 1
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.IF_ACMPEQ; import java.util.*; public class HackerRa ...
- 禁止 SSH 传递 locale 环境变量
SSH 在连接远程机器时默认会传递一些环境变量,其中就包括你本机的 locale 变量.这会导致远程机器的 locale 配置变成和你本地主机一样.有时候我们不希望这种行为,我们可以通过修改 SSH ...
