I2C协议背景知识简介与FTDI的FT4232H配成USB to I2C(MPSSE)使用实例
MPSSE Application Example:
http://ftdichip.cn/Support/SoftwareExamples/MPSSE.htm
MPSSE: AN_129 FTDI USB To JTAG TAP Example
MPSS: AN_114 FTDI USB to SPI Example
MPSSE: AN_113 FTDI USB to I2C Example
MPSS: AN_113 FTDI USB to I2C Example
Acronyms and Abbreviations
| Terms | Description |
|---|---|
| MPSSE | Multi Purpose Synchronous Serial Engine |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| JTAG | Joint Test Action Group |
| SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| SPI Master | A SPI device that initiates and manages serial communication to all devices connected to its SPI bus. |
| SPI Slave | A SPI device that responds to commands sent to it by the SPI master. |
| MISO | Master In, Slave Out |
| MOSI | Master Out, Slave In |
| Serial EEPROM | A programmable memory chip that uses a bitwise serial interface such as I2C or SPI. |
| USB | Universal Serial bus |
FTDI MPSSE(Multi-Protocol Synchronous Serial Engine)
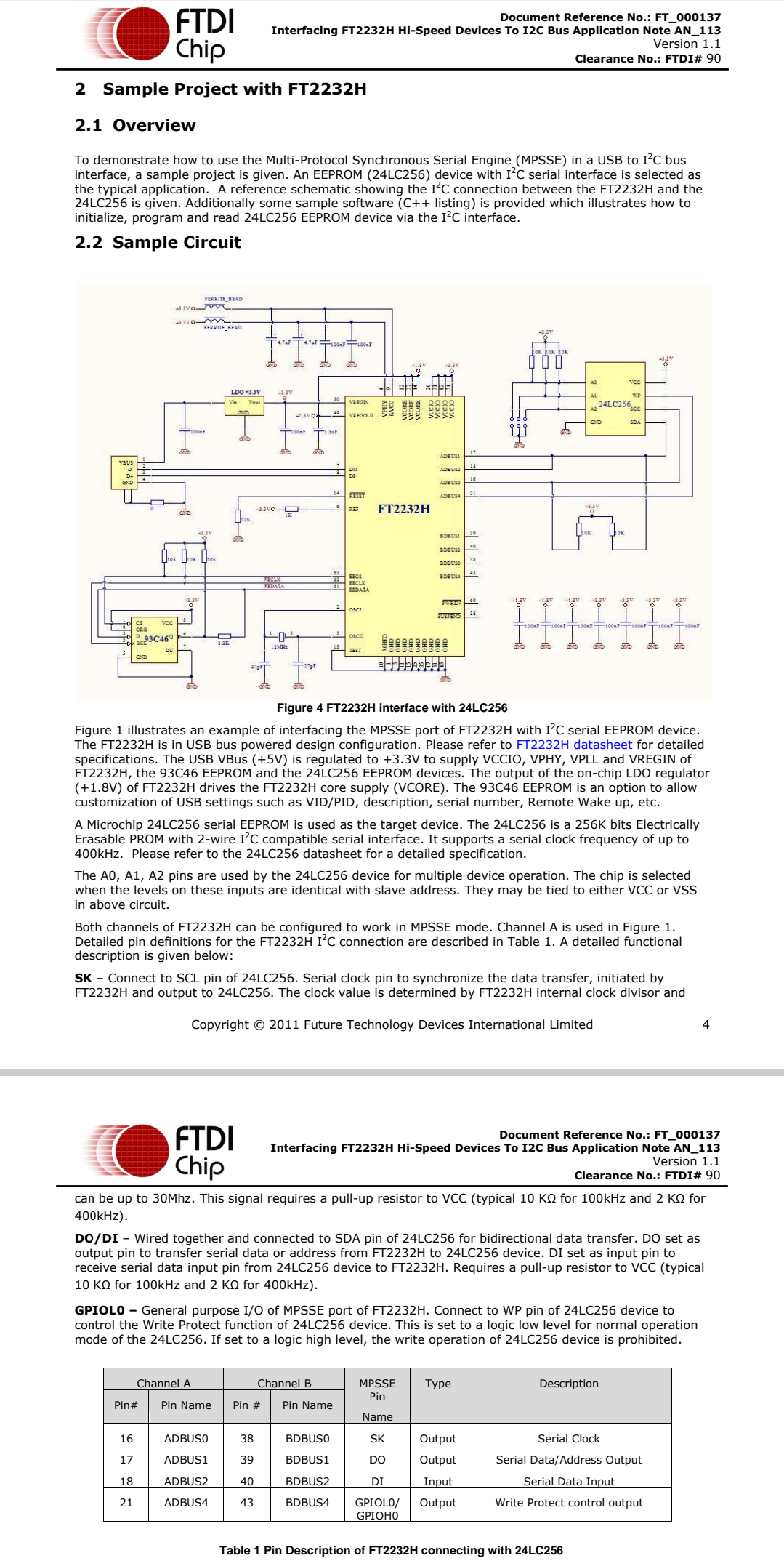
Using the MPSSE can simplify the synchronous serial protocol (USB to SPI, I2C, JTAG, etc.) design. This application note illustrates how to use the MPSSE of the FT2232H to interface with the I2C bus. The FT232H and FT4232H can also be used with the example in this document, though pin-out and port selection will need to match the respective part.
Users can use the example schematic (refer to Figure 3) and software code (section 3) to begin their design.
Note that software code listing is provided as an illustration only and not supported by FTDI.
provided as an illustration only and not supported by FTDI.
1.1 I2C Bus Introduction
I2C is a low- to medium-data-rate master/slave communication bus.:
- Two wires: SCL(serial clock) and SDA(serial data), carry information between the devices connected to the bus.
- Each device is recognized by a unique address and can operate as either a transmitter or receiver, depending on the function of the device.
- In addition to transmitters and receivers, devices can also be considered as masters or slaves when performing data transfers. A master is the device whic h initiates a data transfer on the bus. At that time, any device addressed is considered a slave.
The physical layer of I2C bus is a simple handshaking protocol that relies upon open collector outputs on the bus devices and the device driving or releasing the bus lines, so a pull-up resistor is needed on each wire of the bus.
I2C bus is a true multi-master bus including collision detection and arbitration to prevent data corruption, if two or more masters simultaneously initiate data transfer Serial, 8-bit oriented, bi-directional data transfers can be made at:
- Standard-mode: up to 100 kbit/s,
- Fast-mode: up to 400 kbit/s,
- High-speed mode: up to 3.4 Mbit/s.
Figure 1 shows typical data transfers on the I2C bus.
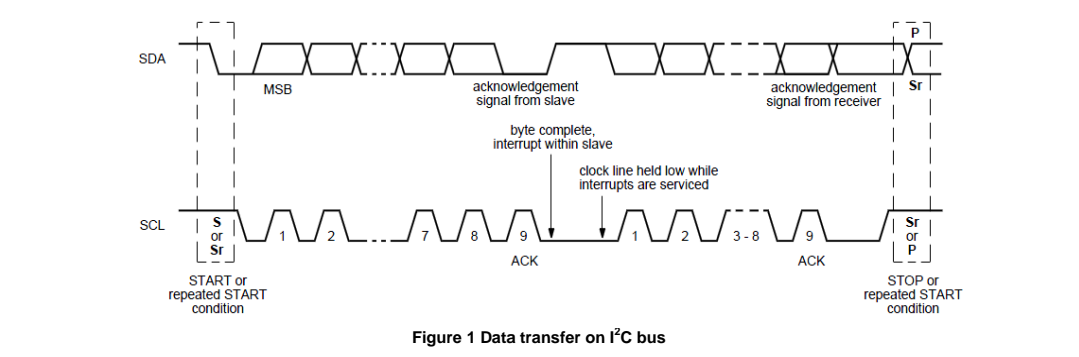
The master supplies the clock; it initiates and terminates transactions and the intended slave (based upon the address provided by the master) acknowledges the master by driving or releasing the bus. The slave cannot terminate the transaction but can indicate a desire to by a "NAK" or not-acknowledge.
I2C specification defines unique situations as S(START) and P(STOP) conditions(Figure 2):
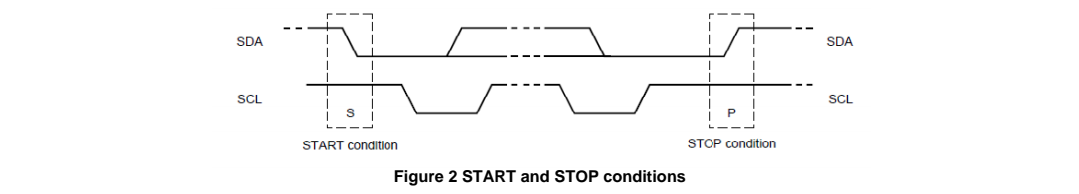
- START and STOP conditions are always generated by the master.
- START condition: A HIGH to LOW transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH.
- STOP condition: A LOW to HIGH transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH.
- Every byte put on the SDA line must be 8-bits long. The number of bytes can be transmitted per transfer is unrestricted.
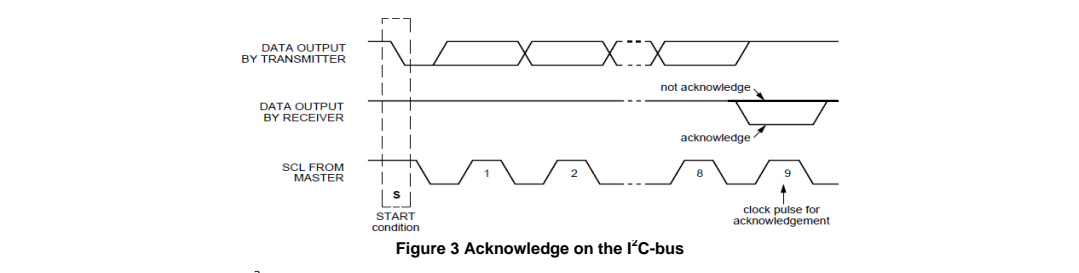
- Each byte is followed by an acknowledge bit. In most cases, data transfer with acknowledge is obligatory. The acknowledge-related clock pulse is generated by the master.
- Data is transferred with the MSB(most significant bit) first.
- The transmitter releases the SDA line (HIGH) during the acknowledge clock pulse. The receiver must pull down the SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse so that it remains stable LOW during the HIGH period of this clock pulse (see Figure 3). Also, set-up and hold times must also be taken into account.
Data transfers of I2C specification should follow the format. After the START condition (S), a slave address should be sent first. This address is 7 bits long followed by an eighth bit which is a data direction bit (R/ ) – a "zero" indicates a transmission (WRITE), a "one" indicates a request for data (READ). After the slave address byte is sent, master can continue its data transfer by writing or reading data byte as defined format. The data transfer is always terminated by a STOP condition generated by the master.
I2C协议背景知识简介与FTDI的FT4232H配成USB to I2C(MPSSE)使用实例的更多相关文章
- Http协议基本知识简介
HTTP协议是指超文本传输协议,位于应用层,HTTP规定数据格式,然后用tcp进行传输. 请求响应模式:简单理解为客户端对服务器发起请求,服务器响应客户端. 主要特点 无连接:无连接的含义是限制每次连 ...
- 很清晰的解读i2c协议
很清晰的解读i2c协议 转载:http://dpinglee.blog.163.com/blog/static/14409775320112239374615/ 1.I2C协议 2条双向串行线,一条数 ...
- I2C协议简介
主从芯片如何传输数据 AT24C02是一个存储芯片,需要把数据从ARM板发给AT24C02,也需要从AT24C02读取数据. I2C是一个主从结构,Master发起传输,slave接收或回应 一主多从 ...
- 『Python基础-1 』 编程语言Python的基础背景知识
#『Python基础-1 』 编程语言Python的基础背景知识 目录: 1.编程语言 1.1 什么是编程语言 1.2 编程语言的种类 1.3 常见的编程语言 1.4 编译型语言和解释型语言的对比 2 ...
- i2c协议简要分析(转载)
声明 本文大部分内容为转载,因此标定为转载 源地址: http://www.cnblogs.com/zym0805/archive/2011/07/31/2122890.html http://blo ...
- Mozilla研究—深入理解mozilla所需的背景知识
mozilla是一个以浏览器为中心的软件平台,它在我们平台中占有重要地位.我们用它来实现WEB浏览器.WAP浏览器.邮件系统.电子书和帮助阅读器等应用程序.为此,我最近花了不少时间去阅读mozilla ...
- Tomcat(一):背景知识和安装tomcat
Tomcat系列文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/7576137.html 1. 基础背景知识 1.1 java和jdk概念 无论是何种程序,要能在计算机 ...
- jenkins X实践系列(1) —— 背景知识
本文介绍jenkins X(以下简称jx)相关的背景技术. jenkins X 简介 Jenkins X 是一个高度集成化的CI/CD平台,基于Jenkins和Kubernetes实现,旨在解决微服务 ...
- {Python之进程} 背景知识 什么是进程 进程调度 并发与并行 同步\异步\阻塞\非阻塞 进程的创建与结束 multiprocess模块 进程池和mutiprocess.Poll
Python之进程 进程 本节目录 一 背景知识 二 什么是进程 三 进程调度 四 并发与并行 五 同步\异步\阻塞\非阻塞 六 进程的创建与结束 七 multiprocess模块 八 进程池和mut ...
- http协议与url简介(转)
一 知识简介 HTTP:(Hypertext transfer protocol)超文本传输协议,是用于从万维网(WWW:World Wide Web)服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送协议. URL ...
随机推荐
- 3.4K star!全能PDF处理神器开源!文档转换/OCR识别一键搞定
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 PDF-Guru 是一款开箱即用的全能型PDF处理工具,支持跨平台文档转换.智能OCR识别. ...
- JSP (二) -- JSP与HTML集成开发
目录 脚本 普通脚本 声明脚本 输出脚本 JSP注释 语法规则 JSP指令 page指令 include指令 taglib指令 动作标签 include useBean setProperty get ...
- 【HUST】网安|编译原理|期末复习概念梳理笔记
纯自用,仅概念无题型,配合课本<编译原理 第4版>(ISBN: 978-7-121-31930-3)理解. 参考文献:刘铭. 编译原理 第4版. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2018.06. ...
- 将查询集SQL-存为物理 OR 临时表
最近的BI项目, 就是会涉及大量的 sql, 后台处理也全是 sql 来拼接成一张物理宽表, 然后前台也是用 sql 来做各种图形骚操作. 尤其是后台处理部分, 大量的sql, 有点尴尬的事情是, s ...
- BP算法完整推导 2.0 (下)
上篇主要阐述 BP算法的过程, 以及 推导的 4 大公式的结论, 现在呢要来逐步推导出这写公式的原理. 当理解到这一步, 就算真正理解 BP算法了. 也是先做一个简单的回顾一下, 不是很细, 重点在推 ...
- 推荐一个Elasticsearch ES可视化客户端工具:ES-King,支持win、mac、linux
ES-King:开源免费,一个现代.实用的ES GUI客户端,支持多平台. 下载地址:https://github.com/Bronya0/ES-King 我之前开源的kafka客户端kafka-ki ...
- Mimikatz 常用命令
以肉去蚁蚁愈多,以鱼驱蝇蝇愈至. 导航 1 工具介绍 2 基本用法 2.1 执行方式 2.2 帮助命令 3 模块用法 3.1 Standard 模块 3.2 Privilege 模块 3.3 Toke ...
- Qt 图片轮播
最近研究了一下图片轮播,主要是用到了QPropertyAnimation这个类,具体代码示例如下: main.cpp #include <QApplication> #include &q ...
- 「Log」NOIP 2023 游记
Day 0 打了大半天板子,然后开摆. 打块,快下班的时候玩了猜词游戏. 回家睡大觉. Day 1 早上起床状态良好,收拾收拾就出门了,跟爸妈吃了肯德基,然后坐车到三校区. 才看到 cc0000 之前 ...
- CRD的简单介绍
介绍 Custom Resource Define 简称 CRD,是 Kubernetes(v1.7+)为提高可扩展性,让开发者去自定义资源的一种方式. CRD 资源可以动态注册到集群中,注册完毕后, ...
