SciTech-Mathmatics-Taylor Equation泰勒公式: 用幂级数(幂函数的和) 去无穷拟合 N阶可导函数(连续可导有N阶导数)
https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/taylor-series.html
https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Calculus/Calculus_3e_(Apex)/08%3A_Sequences_and_Series/8.08%3A_Taylor_Series
Derivative and Slope
Quick review: a \(derivative\) gives us the \(\text{slope of a function}\) at \(any\ point\).
These derivative rules can help us:
- The derivative of \(a\ constant\) is 0
- The derivative of \(a x\) is \(a\) (example: the derivative of \(2x\) is \(2\))
- The derivative of \(x^n\) is \(nx^{n-1}\) (example: \(\text{the derivative of }x^3\text{ is }3x^2\))
- We will use the little mark \(’\) to denote "\(\text{derivative of}\)" (example: \(f'(x)\) denote the \(\text{derivative of } f(x)\)).
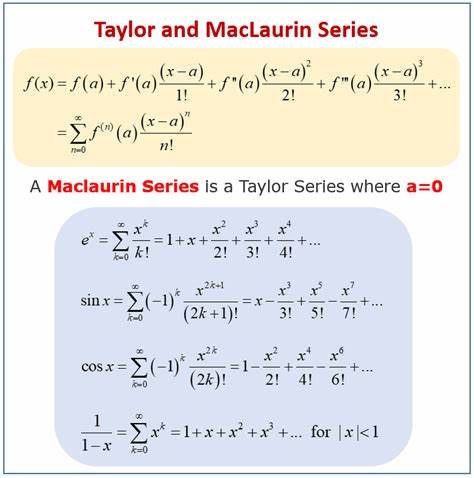
Taylor Series:
\(\large \text{First define } f^{(0)} (x) = f(x) \text{ and } 0! = 1\) :
Formula:
\(\large \begin{array}{rll} \\
f(x) &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}{\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} (x-x_0)^n} \\
&=& f(x_0) +\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}{\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} (x-x_0)^n} \\
\end{array}\)Examples:
\(\begin{array}{rll} \\
e^x &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} {\frac{x^n}{n!}} \\
&=& 1 + x + \frac{x^2}{2!} + \frac{x^3}{3!} + \frac{x^4}{4!} + \frac{x^5}{5!} + \cdots + \frac{x^n}{n!} \\
\cos (x) &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} {\frac{(-1)^{(n)}}{(2n)!} {x^{(2n)}} } \\
&=& 1 + \frac{(-1)x^{2}}{2!} + \frac{(+1)x^{4}}{4!} + \cdots + \frac{(-1)^{(n)}}{(2n)!} {x^{(2n)}} \\
\sin (x) &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} {\frac{(-1)^{n}}{(2n+1)!} {x^{(2n+1)}} } \\
&=& x + \frac{(-1)x^{3}}{3!} + \frac{(+1)x^{5}}{5!} + \cdots + \frac{(-1)^{n}}{(2n+1)!} {x^{(2n+1)}} \\
\end{array}\)
Let $\large \ x=i \cdot y $ and \(\large i^2=-1\):
\(\begin{array}{rll} \\
e^x = e^{i \cdot y} &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} {\frac{(i \cdot y)^n}{n!}} \\
&=& 1 + i \cdot y + \frac{-1 \cdot y^2}{2!} + i \cdot \frac{-1 \cdot y^3}{3!} + \frac{+1 \cdot y^4}{4!} + i \cdot \frac{+1 \cdot y^5}{5!} + \cdots + i^{n} \cdot \frac{(y^n}{n!} \\
&=& (1 + \frac{-1 \cdot y^2}{2!} + \frac{+1 \cdot y^4}{4!} + \cdots ) + i ( y + \frac{-1 \cdot y^3}{3!} + \frac{+1 \cdot y^5}{5!} + \cdots ) \\
&=& \cos y + i \sin y \\
\therefore e^{ix} &=& \cos x + i \sin x\ , \text{ Euler's Equation} \\
\end{array}\)
So \(the\ Taylor's\ Equation,\ Euler's\ Equation \text{ are unified in }Complex\ Space\) with $ the\ Trigonometry\ Functions and \(\ Natural\ Exponential\ Functions\)Applications of Taylor Series
The uses of the Taylor series are:- Taylor series is used to evaluate the value of a whole function in each point,
if the functional values and derivatives are identified at a single point. - The representation of Taylor series reduces many mathematical proofs.
The sum of partial series can be used as an approximation of the whole series. - Multivariate Taylor series is used in many optimization techniques.
This series is used in the power flow analysis of electrical power systems.
- Taylor series is used to evaluate the value of a whole function in each point,
Maclaurin Series:
- \(\text{First define } f^{(0)} (x) = f(x) \text{ and } 0! = 1\) :
- Formula: \(\begin{array}{ccc} \\
f(x) &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}{\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} (x-x_0)^n} \\
&=& f(0) +\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}{\frac{f^{(n)}(0)}{n!} x^n} \\
\\ \end{array}\)
幂级数拟合:
幂函数: \(\large x^n\ ,\ n \in N\ ,\ x \in R\) 这类函数, 例如 \(x^2\ ,\ x^3\ ,\ ...\)
其优点:
- 容易计算及实现:
计算上, 只要对 x 及系数\((+\ ,\ -\ ,\ \times\ ,\ \div)\)就可快速高性能求值; 甚至 口/心/笔 算可得出结果;
实现上, 对硬件没特别要求, 嵌入式设备上都可快速实现, 并已有许多可直接使用的成熟软硬件库); - 任意拟合精度: 预先确定可拟合至任意精度, 并可根据需要设置:
- 幂函数的特点(properties)为人熟知使用:
例如:
\(y = a \cdot x^2 + bx + c\) 的 U形图, 有极值以及求解极值.
\(y = a \cdot x^3 + b x^2 + c x + d\) 的 两个极值以及求解极值 .
...
Taylor Series幂级数(Taylor Series)证明
\(\text{First define } f^{(0)} (x) = f(x) \text{ and } 0! = 1\) :
\(\begin{array}{lll} \\
\text{hypothesis: } \\
\text{ 1. the function } f(x) \text{ has }derivatives\ of\ \ every\ order \text{ and that we can in fact find them all. } \\
\text{ 2. the function } f(x) \text{ does in fact have }a\ power\ series\ \text{representation about } x=x_0\ . \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{rll} \\
\text{such that:} & \\
\exists\ f(x) &= P(x)\ ,\ \forall\ f(x) \\
\text{where}\ P(x) &= \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}{c_{n}(x-x_0)^n} \\
&= c_{0}(x-x_0)^0 + c_{1}(x-x_0)^1 + c_{2}(x-x_0)^2 + ... + c_{n}(x-x_0)^n +\ ... \\
&= c_{0} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty}{ c_{n}(x-x_0)^n} \\
\ c_0 &= f(x_0) \\
P^{(0)}(x) &= f^{(0)}(x) \\
P^{(1)}(x) &= f^{(1)}(x) \\
P^{(2)}(x) &= f^{(2)}(x) \\
P^{(3)}(x) &= f^{(3)}(x) \\
& ... \\
P^{(n)}(x) &= f^{(n)}(x) \\
\end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{rll} \\
P^{(0)}(x) &=& c_{0} &+& c_{1}(x-x_0)^1 &+& c_{2}(x-x_0)^2 &+& c_{3} (x-x_0)^{3} &+&\ ... &+& c_{n}(x-x_0)^n &+&\ ... \\
P^{(1)}(x) &=& 0 &+& 1! c_{1} &+& 2! c_{2} (x-x_0)^1 &+& 3 c_{3} (x-x_0)^{(3-1)} &+&\ ...\ &+& n c_{n}(x-x_0)^{(n-1)} &+&\ ... \\
P^{(2)}(x) &=& 0 &+& 0 &+& 2! c_{2} &+& 3! c_{3} (x-x_0)^{(3-2)} &+&\ ...\ &+& n(n-1) c_{n}(x-x_0)^{(n-2)} &+&\ ... \\
P^{(3)}(x) &=& 0 &+& 0 &+& 0 &+& 3! c_{3} &+&\ ...\ &+& n(n-1)(n-2) c_{n}(x-x_0)^{(n-3)} &+&\ ... \\
&...& \\
P^{(n)}(x) &=& 0 &+& 0 &+& 0 &+& 0 &+&\ ...\ &+& n! c_{n} &+&\ ... \\
&...& \\
\text{NOW plugin in } x &=& x_0 \text{ , and we have: } & & \\
P^{(0)}(x_0) &=& f^{(0)}(x_0) = 0!c_{0} & & \\
P^{(1)}(x_0) &=& f^{(1)}(x_0) = 1!c_{1} & & \\
P^{(2)}(x_0) &=& f^{(2)}(x_0) = 2!c_{2} & & \\
P^{(3)}(x_0) &=& f^{(3)}(x_0) = 3!c_{3} & & \\
&...& & & \\
P^{(n)}(x_0) &=& f^{(n)}(x_0) = n!c_{n} & & \\
&...& & & \\
\\
c_{n} &=& \frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} \\
\\ \end{array}\)
\(\begin{array}{lll} \\
\text{coefficients} & \\
& where & c_{n}=\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} \\
\\ \end{array}\)
\(\text{First define } f^{(0)} (x) = f(x) \text{ and } 0! = 1\) :
\(\begin{array}{ccc} \\
f(x) &=& \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}{\frac{f^{(n)}(x_0)}{n!} (x-x_0)^n} \\
\\ \end{array}\)
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
- Q1 What is a Taylor series?
Taylor series is a function of an infinite sum of terms in increasing order of degree. Taylor series of polynomial functions is a polynomial. - Q2 What is the use of Taylor series?
Taylor series is used to evaluate the value of a whole function in each point if the functional values and derivatives are identified at a single point. - Q3 What is a Maclaurin series?
A Taylor series is called Maclaurin series when the function is centered at zero point.
SciTech-Mathmatics-Taylor Equation泰勒公式: 用幂级数(幂函数的和) 去无穷拟合 N阶可导函数(连续可导有N阶导数)的更多相关文章
- XGBoost 完整推导过程
参考: 陈天奇-"XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System" Paper地址: <https://arxiv.org/abs/1603 ...
- Alink漫谈(十一) :线性回归 之 L-BFGS优化
Alink漫谈(十一) :线性回归 之 L-BFGS优化 目录 Alink漫谈(十一) :线性回归 之 L-BFGS优化 0x00 摘要 0x01 回顾 1.1 优化基本思路 1.2 各类优化方法 0 ...
- 完全搞懂傅里叶变换和小波(1)——总纲<转载>
无论是学习信号处理,还是做图像.音视频处理方面的研究,你永远避不开的一个内容,就是傅里叶变换和小波.但是这两个东西其实并不容易弄懂,或者说其实是非常抽象和晦涩的! 完全搞懂傅里叶变换和小波,你至少需要 ...
- GBDT算法原理深入解析
GBDT算法原理深入解析 标签: 机器学习 集成学习 GBM GBDT XGBoost 梯度提升(Gradient boosting)是一种用于回归.分类和排序任务的机器学习技术,属于Boosting ...
- Gaussian Discriminant Analysis
如果在我们的分类问题中,输入特征$x$是连续型随机变量,高斯判别模型(Gaussian Discriminant Analysis,GDA)就可以派上用场了. 以二分类问题为例进行说明,模型建立如下: ...
- Logistic Regression and Classification
分类(Classification)与回归都属于监督学习,两者的唯一区别在于,前者要预测的输出变量\(y\)只能取离散值,而后者的输出变量是连续的.这些离散的输出变量在分类问题中通常称之为标签(Lab ...
- 支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)—— 线性SVM
支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,简称 SVM)于 1995 年正式发表,由于其在文本分类任务中的卓越性能,很快就成为机器学习的主流技术.尽管现在 Deep Learnin ...
- [再寄小读者之数学篇](2014-06-23 二阶导数估计 [中国科学技术大学2013年高等数学B 考研试题])
设 $f(x)$ 二阶连续可导, $f(0)=f(1)=0$, $\dps{\max_{0\leq x\leq 1}f(x)=2}$. 证明: $$\bex \min_{0\leq x\leq 1}f ...
- oo第一次作业
前言: 这是一篇面向对象作业总结,作业内容是对多项式进行求导,一共有三个阶段,具体要求不详述,第一阶段只要求’+’连接coeff*x^pow的形式,第二次支持*连接的幂函数及三角函数,第三次则需要支持 ...
- BUAAOO P1-P3 Expression Dirivation
目录 1.问题描述 1.1.概念定义 7.程序度量 8.知识点笔记 1.运行 2.1.方法 2.2.检测相等性 2.3.空串与null串 2.4.使用StringBuilder构建字符串 2.5.使用 ...
随机推荐
- IIS—503错误排查
服务器返回503(IIS Service Unavailable HTTP Error 503. The service is unavailable.)+IIS常见优化设置策略 - Yuliang. ...
- EFCore先DBFirst,再CodeFirst(针对老项目迁移)
参照文章: CodeFirst命令介绍:Scaffold-DbContext 命令使用 - 跟着阿笨一起玩.NET - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 整体流程介绍:NetCore 中 EFcor ...
- python相关函数
1.pow()函数 pow()函数解释 pow(x,y):表示x的y次幂. >>> pow(2,4) 16 >>> pow(x,y,z):表示x的y次幂后除以z的余 ...
- 【工具】Zotero|使用Zotero向Word/WPS中插入引用文献(2023年)
版本:Word 2021,Zotero 6.0.30 版本:WPS 教育版,HUST 前言:两年前我找网上插入文献的方式,网上的博客提示让我去官网下个插件然后才能装,非常麻烦,导致我对Zotero都产 ...
- Django REST框架中处理JWT令牌的认证的源码解析
想了解`JWTAuthentication`这个类的源码解析.`JWTAuthentication`是来自`rest_framework_simplejwt.authentication`模块的,它用 ...
- JAVA 24 环境安装与配置
JAVA 24 环境安装与配置 一.Java Downloads Java 下载(Windows x64) https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downl ...
- CUDA原子操作
这节主要涉及到一个多线程情况下存在的数据竞争问题 -- 多个线程同时访问共享数据时,由于没有正确的同步机制,导致数据出现不一致的情况. C/C++ 多线程中,可以通过互斥锁(mutex).原子操作(a ...
- 基于Python运用PyComCAD进行Autocad二次开发实例汇集
本文将对运用Pycomcad库(Pycomcad详见,https://github.com/JohnYang1210/PycomCAD)做的一些项目及其效果图进行展示(欢迎各位老铁pull reque ...
- Python内置库itertools简单学习
该库为满足特定需要的比较高效的迭代器内置库,在数据科学中的应用也不少,故有必要了解一下: import itertools import sys 无限迭代器(Infinite iterators) I ...
- codeup之等腰梯形
Description 请输入高度h,输入一个高为h,上底边长为h 的等腰梯形(例如h=4,图形如下). **** ****** ******** ********** Input 输入第一行表示样例 ...
