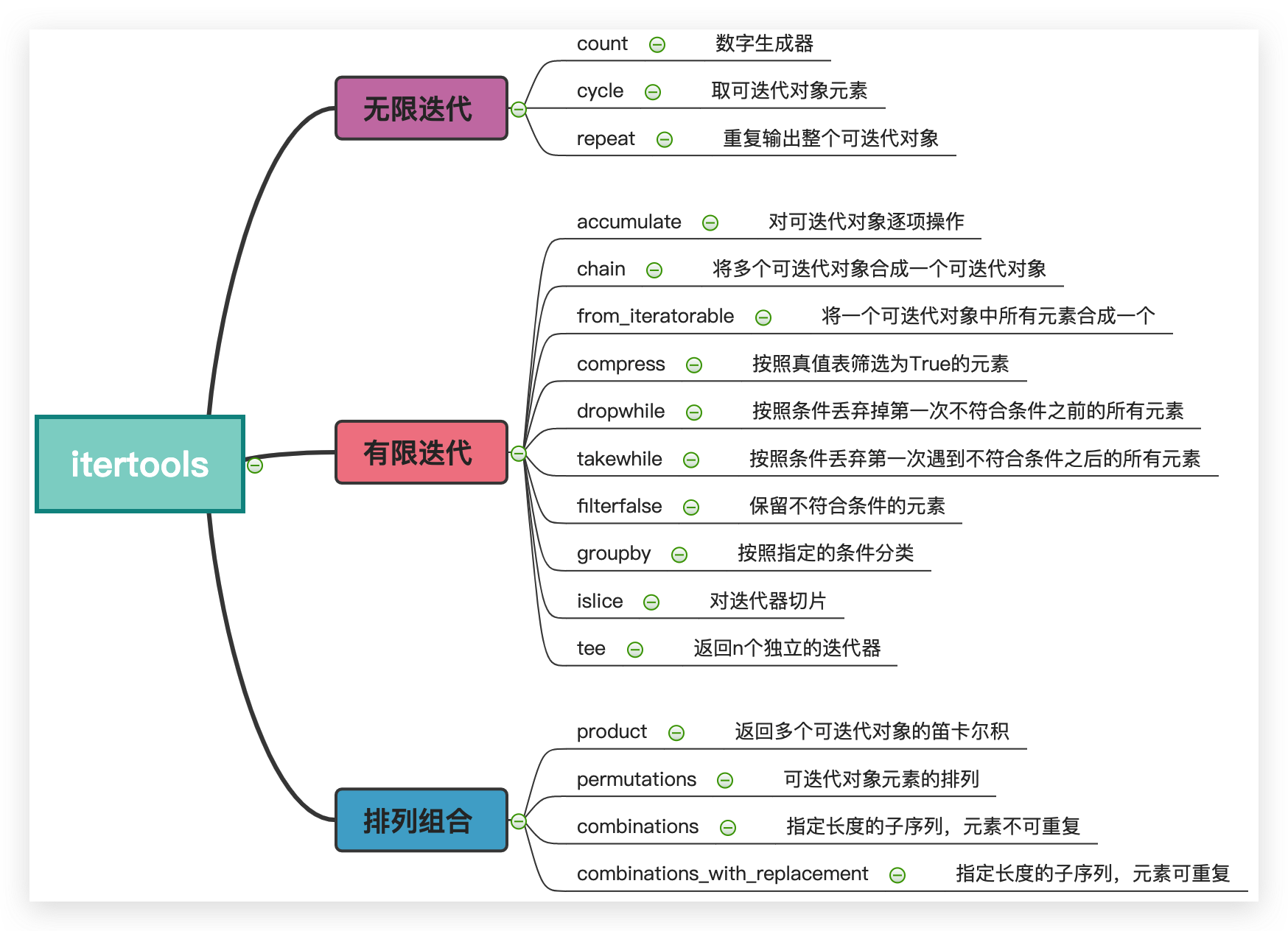
python自带性能强悍的标准库 itertools
可迭代对象就像密闭容器里的水,有货倒不出
itertools是python内置的标准模块,提供了很多简洁又高效的专用功能,使用得当能够极大的简化代码行数,同时所有方法都是实现了生成器函数,这就意味着极大的节省内存。
itertools提供的功能主要分为三大块,以最新版本的3.10为例:
- 对可迭代对象无限迭代,无限输出
- 对可迭代对象有限迭代
- 对可迭代对象排列组合
方法如下:
导入包
>>> from iteratortools import *
无限迭代
iteratortools.count(start=0, step=1)
数值生成器,可以指定起始位置和步长,并且步长可以为浮点数。无限输出,一直累加,在例子中需要边睡眠1s边输出。
>>> import time
>>> iterator = count(4, 0.5)
>>> for i in iterator:
... print(i)
... time.sleep(1)
...
4
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
7.5
iteratortools.cycle(iteratorable)
无限循环取出可迭代对象里的元素
>>> a = cycle("ABCD")
>>> import time
>>> for i in a:
... print(i)
... time.sleep(1)
...
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
iteratortools.repeat(object[, times])
不断重复输出整个object,如果指定了重复次数,则输出指定次数,否则将无限重复。
>>> iterator = repeat('hello world', 10)
>>>
>>> for i in iterator:
... print(i)
...
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
有了这个神器,对输出10次hello world这种问题又有一种新解法
有限迭代
iteratortools.accumulate(iteratorable[, func, *, initial=None])
返回对列表中元素逐项的操作,操作有:
- 累加,返回累加到每一项的列表
- 累乘,返回累乘到每一项的列表
- 最小值,返回到当前项的最小值
- 最大值,返回到当前项的最大值
>>> [2, 4, 8, 1, 3, 5]
[2, 4, 8, 1, 3, 5]
>>> arr = [2, 4, 8, 1, 3, 5]
>>>
>>> add = accumulate(arr)
>>>
>>> list(add)
[2, 6, 14, 15, 18, 23]
>>>
>>> max = accumulate(arr, max)
>>> list(max)
[2, 4, 8, 8, 8, 8]
>>>
>>> import operator
>>> mul = accumulate(arr, operator.mul)
>>> list(mul)
[2, 8, 64, 64, 192, 960]
>>>
>>> min = accumulate(arr, min)
>>> list(min)
[2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1]
iteratortools.chain(*iteratorables)
将多个可迭代对象构建成一个新的可迭代对象,统一返回。类似于将多个对象链成一条串
>>> iterator = chain([1,2,3],['a','b','c'],(5,6,7))
>>> list(iterator)
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c', 5, 6, 7]
优点:可以将多个可迭代对象整合成一个,避免逐个取值
chain.from_iteratorable(iteratorable)
将一个迭代对象中将所有元素类似于chain一样,统一返回。
>>> chain.from_iteratorable(['abc','def'])
<iteratortools.chain object at 0x1083ae460>
>>> iterator = chain.from_iteratorable(['abc','def'])
>>> list(iterator)
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
iteratortools.compress(data, selectors)
按照真值表筛选元素
>>> arr = [1,2,3,4]
>>> selectors = [1,0,1,0]
>>>
>>> iterator = compress(arr, selectors)
>>>
>>> list(iterator)
[1, 3]
iteratortools.dropwhile(predicate, iteratorable)
按照条件筛选,丢弃掉第一次不符合条件时之前的所有元素
>>> arr = [1,2,3,2,1,2,1]
>>> iterator = dropwhile(lambda x: x<3, arr)
>>> list(iterator)
[3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
iteratortools.takewhile(predicate, iteratorable)
根据predicate条件筛选可迭代对象中的元素,只要元素为真就返回,第一次遇到不符合的条件就退出。
按照条件筛选,丢弃第一次遇到不符合条件之后的元素。行为类似于上一个dropwhile,区别在于丢弃的选择不同。
iteratortools.filterfalse(predicate, iteratorable)
保留不符合条件的元素,返回迭代器
>>> arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> iterator = filterfalse(lambda x:x<3, arr)
>>> list(iterator)
[3, 4, 5]
iteratortools.groupby(iteratorable, key=None)
按照指定的条件分类。输出条件和符合条件的元素
>>> iterator = groupby(arr, lambda x: x>3)
>>> for condition ,numbers in iterator:
... print(condition, list(numbers))
...
False [1, 2, 3]
True [4, 5]
iteratortools.islice(iteratorable, start, stop[, step])
对迭代器进行切片,老版本中不能指定start和stop以及步长,新版本可以。
>>> iterator = count()
>>> slice_iterator = islice(iterator, 10, 20, 2)
>>> list(slice_iterator)
[10, 12, 14, 16, 18]
iteratortools.starmap(function, iteratorable)
将function作用于可迭代对象上,类似于map函数
iteratortools.tee(iteratorable, n=2)
从一个可迭代对象中返回 n 个独立的迭代器
>>> iterator = tee(arr)
>>> for i in iterator:
... print(type(i), list(i))
...
<class 'iteratortools._tee'> [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
<class 'iteratortools._tee'> [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
iteratortools.zip_longest(*iteratorables, fillvalue=None)
创建一个迭代器,从每个可迭代对象中收集元素。如果可迭代对象的长度未对齐,将根据 fillvalue 填充缺失值。
迭代持续到耗光最长的可迭代对象。大致相当于:
>>> iterator = zip_longest("ABCD", "xy", fillvalue="-")
>>> list(iterator)
[('A', 'x'), ('B', 'y'), ('C', '-'), ('D', '-')]
排列组合迭代
iteratortools.product(*iteratorables, repeat=1)
生成多个可迭代对象的笛卡尔积
大致相当于生成器表达式中的嵌套循环。例如, product(A, B) 和 ((x,y) for x in A for y in B) 返回结果一样。
>>> iterator = product("123", "abc")
>>> list(iterator)
[('1', 'a'), ('1', 'b'), ('1', 'c'), ('2', 'a'), ('2', 'b'), ('2', 'c'), ('3', 'a'), ('3', 'b'), ('3', 'c')]
将可选参数 repeat 设定为要重复的次数。例如,product(A, repeat=4) 和 product(A, A, A, A) 是一样的
iteratortools.permutations(iteratorable, r=None)
由 iteratorable 元素生成长度为 r 的排列。元素的排列,类似于给一个[1,2,3],选取其中两个元素,一共有多少种组合方法?不要求元素排列之后的位置。
>>> iter = permutations([1,2,3], r=3)
>>> list(iterator)
[(1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), (3, 2, 1)]
这个方法能够完美解决算法中的全排列问题,简直是量身定做。如果早知道这么简单,当年考算法也不会。。,哎
可参见leetcode46题:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/
iteratortools.combinations(iteratorable, r)
返回由输入 iteratorable 中元素组成长度为 r 的子序列。元素不可重复使用。子序列是要求元素在排列之后和之前的相对位置不变的。1,2,3中3在1的后面,子序列中3也一定在1的后面。
>>> iterator = combinations([1,2,3,4], r = 3)
>>> list(iterator)
[(1, 2, 3), (1, 2, 4), (1, 3, 4), (2, 3, 4)]
>>> iterator = combinations([1], r = 3)
>>> list(iterator)
[]
这个方法可以曲线解决组合总数问题
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/
iteratortools.combinations_with_replacement(iteratorable, r)
返回由输入 iteratorable 中元素组成的长度为 r 的子序列,允许每个元素可重复出现
>>> iter = combinations_with_replacement([1,2,3,4], r=2)
>>> list(iter)
[(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 3), (3, 4), (4, 4)]
>>> iterator = combinations_with_replacement([1], r=3)
>>> list(iterator)
[(1, 1, 1)]
python自带性能强悍的标准库 itertools的更多相关文章
- python协程(yield、asyncio标准库、gevent第三方)、异步的实现
引言 同步:不同程序单元为了完成某个任务,在执行过程中需靠某种通信方式以协调一致,称这些程序单元是同步执行的. 例如购物系统中更新商品库存,需要用"行锁"作为通信信号,让不同的更新 ...
- Python学习笔记011_模块_标准库_第三方库的安装
容器 -> 数据的封装 函数 -> 语句的封装 类 -> 方法和属性的封装 模块 -> 模块就是程序 , 保存每个.py文件 # 创建了一个hello.py的文件,它的内容如下 ...
- python进阶(26)collections标准库
前言 这个模块实现了特定目标的容器,以提供Python标准内建容器dict ,list ,set , 和tuple 的替代选择. 这个模块提供了以下几个函数 函数 作用 namedtuple() 创建 ...
- Python入门(六):标准库
操作系统接口 os模块提供了不少与操作系统相关联的函数. import os os.getcwd() # 返回当前的工作目录 os.chdir('d:/') # 修改当前的工作目录 os.system ...
- Python标准库——走马观花
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! Python有一套很有用的标准库(standard library).标准库会随着 ...
- Python 标准库一览(Python进阶学习)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jurbo/article/details/52334345 写这个的起因是,还是因为在做Python challenge的时候,有的时候想解决问题,连 ...
- 第十三篇:带缓冲的IO( 标准IO库 )
前言 在之前,学习了 read write 这样的不带缓冲IO函数. 而本文将讲解标准IO库中,带缓冲的IO函数. 为什么要有带缓冲IO函数 标准库提供的带缓冲IO函数是为了减少 read 和 wri ...
- Python模块进阶、标准库、扩展库
模块进阶 Python有一套很有用的标准库(standard library).标准库会随着Python解释器,一起安装在你的电脑中的. 它是Python的一个组成部分.这些标准库是Python为你准 ...
- C++解析(18):C++标准库与字符串类
0.目录 1.C++标准库 2.字符串类 3.数组操作符的重载 4.小结 1.C++标准库 有趣的重载--操作符 << 的原生意义是按位左移,例:1 << 2;,其意义是将整数 ...
随机推荐
- Windows11下的快捷键(win10通用,部分win11独有的不通用)
给大家介绍一下win11下我常用的几个快捷键,在微软官方的文档里面都可以查到,官网链接 https://support.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/windows-%E7% ...
- python实现拉普拉斯图像金字塔
一,定义 二,代码: 要求:拉普拉斯金字塔时,图像大小必须是2的n次方*2的n次方,不然会报错 1 # -*- coding=GBK -*- 2 import cv2 as cv 3 4 5 #高斯金 ...
- [luogu7831]Travelling Merchant
考虑不断找到以下两种类型的边,并维护答案: 1.终点出度为0的边,那么此时即令$ans_{x}=\min(ans_{x},\max(r,ans_{y}-p))$ 2.(在没有"终点出度为0 ...
- [loj3347]有趣的旅途
考虑求出重心,以0为根建树,求出第 $i$个点的子树大小$sz[i]$($a(0,i)$),则满足$n-sz[i]\le \lfloor\frac{n}{2}\rfloor$的$sz[i]$中的最小值 ...
- ICCV 2021口罩人物身份鉴别全球挑战赛冠军方案分享
1. 引言 10月11-17日,万众期待的国际计算机视觉大会 ICCV 2021 (International Conference on Computer Vision) 在线上如期举行,受到全球计 ...
- 网站每日UV数据指标去重统计
package com.iexecloud.cloud.casemanager;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.text.SimpleDate ...
- Redis 很屌,不懂使用规范就糟蹋了
这可能是最中肯的 Redis 使用规范了 码哥,昨天我被公司 Leader 批评了. 我在单身红娘婚恋类型互联网公司工作,在双十一推出下单就送女朋友的活动. 谁曾想,凌晨 12 点之后,用户量暴增,出 ...
- bluetooth sig bluetooth asia-深圳之行
18年5月30日深圳参见蓝牙展会 主要了解下面 使用蓝牙和区块链构建室内导航定位系统和去中心化的MESH网络 -- 核心是通过iBeacon 来广播数据,典型用例是手机对手机的使用蓝牙进行交互,业界称 ...
- UE4之Slate:纯C++工程配置
概述: Slate是UE4提供的UI框架,整个UE4 Editor UI都是使用Slate构建的: Slate的官方文档:[Slate UI框架] Slate底层内容,中文环境下能搜索到的有效资源也不 ...
- 工作学习2-gcc升级引发的崩溃
分享一下调查gcc 8.0下,函数漏写返回值崩溃问题,调查记录. 现在新的硬件,基本操作系统都是redhat 8.0,升级后测试时,发现了一个崩溃问题,记录一下. ================== ...
