Beam Search快速理解及代码解析(下)
Beam Search的问题
先解释一下什么要对Beam Search进行改进。因为Beam Search虽然比贪心强了不少,但还是会生成出空洞、重复、前后矛盾的文本。如果你有文本生成经验,一定对这些现象并不陌生。在语言模型还不像如今的BERT、GPT这么厉害的时候,这种现象更加明显。
没有经验也没关系,我们来看一个论文里面的例子。输入模型的引文(context)
"The study, published in the Proceedings of the They were cattle called Bolivian Cavalleros; they live in a National Academy of Sciences of the United States of remote desert uninterrupted by town, and they speak huge, America (PNAS), was conducted by researchers from the beautiful, paradisiacal Bolivian linguistic thing. They say, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM) and
GPT-2模型, Beam Search, num_beams=32的生成结果:
'Lunch, marge.' They don't tell what the lunch is," director the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Professor Chuperas Omwell told Sky News. "They've only (UNAM/Universidad Nacional Autónoma de been talking to scientists, like we're being interviewed by TV México/Universidad Nacional Autónoma de reporters. We don't even stick around to be interviewed by México/Universidad Nacional Autónoma de TV reporters. Maybe that's how they figured out that they're México/Universidad Nacional Autónoma de ...”
可以发现即使是如今最顶级的语言模型加上足够长的引文输入,还是无法得到高质量的生成结果。
论文认为这种问题是由于这种试图最大化序列条件概率的解码策略从根上就有问题。他们对比了给定同样引文的情况下人类续写和机器生成的词用语言模型计算出来的概率。如下图所示,人类选择的词(橙线)并不是像机器选择的(蓝线)那样总是那些条件概率最大的词。从生成的结果也可以看出,机器生成的结果有大量重复。
机器选词和人类选词的概率对比图
解决对策
人们其实尝试了各种办法对Beam Search进行改进,其实都很好理解,这篇论文总结的也比较到位。
随机采样
第一种方法是用随机采样(sampling)代替取概率最大的词。采样的依据就是解码器输出的词典中每个词的概率分布。相比于按概率“掐尖”,这样会增大所选词的范围,引入更多的随机性。当时那篇论文的结论就是这种随机采样的方法远好于Beam Search。但这其实也是有条件的,随机采样容易产生前后不一致的问题。而在开放闲聊领域,生成文本的长度都比较短,这种问题就被自然的淡化了。
采样的时候有一个可以控制的超参数,称为温度(temperature, )。解码器的输出层后面通常会跟一个softmax函数来将输出概率归一化,通过改变 可以控制概率分布的形貌。softmax的公式如下,当 大的时候,概率分布趋向平均,随机性增大;当 小的时候,概率密度趋向于集中,即强者愈强,随机性降低,会更多地采样出“放之四海而皆准”的词汇。
top-k采样
这个方法就是在采样前将输出的概率分布截断,取出概率最大的k个词构成一个集合,然后将这个子集词的概率再归一化,最后从新的概率分布中采样词汇。这个办法据说可以获得比Beam Search好很多的效果,但也有一个问题,就是这个k不太好选。
While top-k sampling leads to considerably higher quality text than either beam search or sampling from the full distribution, the use of a constant k is sub-optimal across varying contexts.
为啥呢?因为这个概率分布变化比较大,有时候可能很均匀(flat),有的时候比较集中(peaked)。对于集中的情况还好说,当分布均匀时,一个较小的k容易丢掉很多优质候选词。但如果k定的太大,这个方法又会退化回普通采样。
两种分布,左边是均匀的,右边是集中的
核采样(Nucleus sampling)
首先表示我不确定这个翻译是不是对的。
这是这篇论文提出的方式,也是相比前面那些都更好的采样方式,这个方法不再取一个固定的k,而是固定候选集合的概率密度和在整个概率分布中的比例。也就是构造一个最小候选集V ,使得
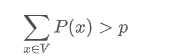
选出来这个集合之后也和top-k采样一样,重新归一化集合内词的概率,并把集合外词的概率设为0。这种方式也称为top-p采样。
论文有一个图,对比了这几种采样方式的效果。
效果对比图,红字是前后不符,蓝字是重复。Nucleus效果拔群。
惩罚重复
为了解决重复问题,还可以通过惩罚因子将出现过词的概率变小或者强制不使用重复词来解决。惩罚因子来自于同样广为流传的《CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation》[2]。如果大家感兴趣的话后面可以专门写一期可控文本生成方向的解读。
代码解析
其实上述各种采样方式在HuggingFace的库里都已经实现了(感动!),我们来看一下代码。
先看top-k和top-p采样
1 # 代码输入的是logits,而且考虑很周全(我感觉漏了考虑k和p都给了的情况,这应该是不合适的)
2 # 巧妙地使用了torch.cumsum
3 # 避免了一个词都选不出来的尴尬情况
4 def top_k_top_p_filtering(logits, top_k=0, top_p=1.0, filter_value=-float("Inf"), min_tokens_to_keep=1):
5 """ Filter a distribution of logits using top-k and/or nucleus (top-p) filtering
6 Args:
7 logits: logits distribution shape (batch size, vocabulary size)
8 if top_k > 0: keep only top k tokens with highest probability (top-k filtering).
9 if top_p < 1.0: keep the top tokens with cumulative probability >= top_p (nucleus filtering).
10 Nucleus filtering is described in Holtzman et al. (http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09751)
11 Make sure we keep at least min_tokens_to_keep per batch example in the output
12 From: https://gist.github.com/thomwolf/1a5a29f6962089e871b94cbd09daf317
13 """
14 if top_k > 0:
15 top_k = min(max(top_k, min_tokens_to_keep), logits.size(-1)) # Safety check
16 # Remove all tokens with a probability less than the last token of the top-k
17 indices_to_remove = logits < torch.topk(logits, top_k)[0][..., -1, None]
18 logits[indices_to_remove] = filter_value
19
20 if top_p < 1.0:
21 sorted_logits, sorted_indices = torch.sort(logits, descending=True)
22 cumulative_probs = torch.cumsum(F.softmax(sorted_logits, dim=-1), dim=-1)
23
24 # Remove tokens with cumulative probability above the threshold (token with 0 are kept)
25 sorted_indices_to_remove = cumulative_probs > top_p
26 if min_tokens_to_keep > 1:
27 # Keep at least min_tokens_to_keep (set to min_tokens_to_keep-1 because we add the first one below)
28 sorted_indices_to_remove[..., :min_tokens_to_keep] = 0
29 # Shift the indices to the right to keep also the first token above the threshold
30 sorted_indices_to_remove[..., 1:] = sorted_indices_to_remove[..., :-1].clone()
31 sorted_indices_to_remove[..., 0] = 0
32
33 # scatter sorted tensors to original indexing
34 indices_to_remove = sorted_indices_to_remove.scatter(1, sorted_indices, sorted_indices_to_remove)
35 logits[indices_to_remove] = filter_value
36 return logits
再看看重复惩罚
1 # 输入的同样是logits(lprobs)
2 # 同时输入了之前出现过的词以及惩罚系数(大于1的)
3 # 考虑到了logit是正和负时处理方式应该不一样
4 def enforce_repetition_penalty_(self, lprobs, batch_size, num_beams, prev_output_tokens, repetition_penalty):
5 """repetition penalty (from CTRL paper https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858). """
6 for i in range(batch_size * num_beams):
7 for previous_token in set(prev_output_tokens[i].tolist()):
8 # if score < 0 then repetition penalty has to multiplied to reduce the previous token probability
9 if lprobs[i, previous_token] < 0:
10 lprobs[i, previous_token] *= repetition_penalty
11 else:
12 lprobs[i, previous_token] /= repetition_penalty
最后是重复词去除
1 # 这个函数将会返回一个不可使用的词表
2 # 生成n-gram的巧妙方式大家可以借鉴一下
3 # 下面是一个3-gram的例子
4 # a = [1,2,3,4,5]
5 # for ngram in zip(*[a[i:] for i in range(3)]):
6 # print(ngram)
7 def calc_banned_tokens(prev_input_ids, num_hypos, no_repeat_ngram_size, cur_len):
8 # Copied from fairseq for no_repeat_ngram in beam_search"""
9 if cur_len + 1 < no_repeat_ngram_size:
10 # return no banned tokens if we haven't generated no_repeat_ngram_size tokens yet
11 return [[] for _ in range(num_hypos)]
12 generated_ngrams = [{} for _ in range(num_hypos)]
13 for idx in range(num_hypos):
14 gen_tokens = prev_input_ids[idx].numpy().tolist()
15 generated_ngram = generated_ngrams[idx]
16 # 就是这巧妙的一句
17 for ngram in zip(*[gen_tokens[i:] for i in range(no_repeat_ngram_size)]):
18 prev_ngram_tuple = tuple(ngram[:-1])
19 generated_ngram[prev_ngram_tuple] = generated_ngram.get(prev_ngram_tuple, []) + [ngram[-1]]
20 def _get_generated_ngrams(hypo_idx):
21 # Before decoding the next token, prevent decoding of ngrams that have already appeared
22 start_idx = cur_len + 1 - no_repeat_ngram_size
23 ngram_idx = tuple(prev_input_ids[hypo_idx, start_idx:cur_len].numpy().tolist())
24 return generated_ngrams[hypo_idx].get(ngram_idx, [])
25 banned_tokens = [_get_generated_ngrams(hypo_idx) for hypo_idx in range(num_hypos)]
26 return banned_tokens
以上这些代码应该在哪里调用相信看上一篇文章的朋友都应该知道了,这里就放出来最核心的差异。
1 if do_sample:
2 # 这是今天的采样方式
3 _scores = scores + beam_scores[:, None].expand_as(scores) # (batch_size * num_beams, vocab_size)
4 # Top-p/top-k filtering,这一步重建了候选集
5 _scores = top_k_top_p_filtering(
6 _scores, top_k=top_k, top_p=top_p, min_tokens_to_keep=2
7 ) # (batch_size * num_beams, vocab_size)
8 # re-organize to group the beam together to sample from all beam_idxs
9 _scores = _scores.contiguous().view(
10 batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size
11 ) # (batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size)
12
13 # Sample 2 next tokens for each beam (so we have some spare tokens and match output of greedy beam search)
14 probs = F.softmax(_scores, dim=-1)
15 # 采样
16 next_tokens = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=2 * num_beams) # (batch_size, num_beams * 2)
17 # Compute next scores
18 next_scores = torch.gather(_scores, -1, next_tokens) # (batch_size, num_beams * 2)
19 # sort the sampled vector to make sure that the first num_beams samples are the best
20 next_scores, next_scores_indices = torch.sort(next_scores, descending=True, dim=1)
21 next_tokens = torch.gather(next_tokens, -1, next_scores_indices) # (batch_size, num_beams * 2)
22 else:
23 # 这是昨天的beam search方式
24 # 直接将log概率相加求条件概率
25 next_scores = scores + beam_scores[:, None].expand_as(scores) # (batch_size * num_beams, vocab_size)
26
27 # re-organize to group the beam together (we are keeping top hypothesis accross beams)
28 next_scores = next_scores.view(
29 batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size
30 ) # (batch_size, num_beams * vocab_size)
31
32 next_scores, next_tokens = torch.topk(next_scores, 2 * num_beams, dim=1, largest=True, sorted=True)
OK,谢谢各位看到这里,祝大家生成出高质量的文本!
参考资料
[1]
The Curious Case of Neural Text Degeneration: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09751
[2]
CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation: https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858
Beam Search快速理解及代码解析(下)的更多相关文章
- Beam Search快速理解及代码解析
目录 Beam Search快速理解及代码解析(上) Beam Search 贪心搜索 Beam Search Beam Search代码解析 准备初始输入 序列扩展 准备输出 总结 Beam Sea ...
- Beam Search快速理解及代码解析(上)
Beam Search 简单介绍一下在文本生成任务中常用的解码策略Beam Search(集束搜索). 生成式任务相比普通的分类.tagging等NLP任务会复杂不少.在生成的时候,模型的输出是一个时 ...
- eclipse快速复制一行代码(向下/向上)快捷键修改设置
eclipse快速复制一行代码(向下/向上)快捷键修改设置 2015年10月05日 17:46:57 xiaoguanglgc 阅读数:20906 标签: eclipse快速复制一行快捷键冲突英特尔 ...
- 《轻量级Java Web整合开发入门SSH》 - 快速理解Java框架的又一积木
学习JAVA不难,难的是没有多余的时间给你仔细学习. 伴随着项目的不断跟进,责任重于泰山,必须快速提升. 我不能期望把一本书或者一个项目完全吃透,只希望能用数量去 ...
- 快速理解web语义化
什么是Web语义化 Web语义化是指使用恰当语义的html标签.class类名等内容,让页面具有良好的结构与含义,从而让人和机器都能快速理解网页内容.语义化的web页面一方面可以让机器在更少的人类干预 ...
- [代码]解析nodejs的require,吃豆人的故事
最近在项目中需要对nodejs的require关键字做解析,并且替换require里的路径.一开始我希望nodejs既然作为脚本语言,内核提供一个官方的parser库应该是一个稳定可靠又灵活的渠道,然 ...
- 字符编码那点事:快速理解ASCII、Unicode、GBK和UTF-8
原作者:阮一峰(ruanyifeng.com),现重新整理发布,感谢原作者的无私分享. 1.引言 今天中午,我突然想搞清楚 Unicode 和 UTF-8 之间的关系,就开始查资料. 这个问题比我想象 ...
- 前端系列——快速理解babel6配置过程
繁琐的配置? 你能快速读懂babel的官方文档吗? 你能根据官方文档快速配置好babelrc吗? 你能明白自己需要哪些插件吗? 没有搞明白这3个问题,请往下看. 快速理解babel 6 来看一张让人颤 ...
- Solutions:如何运用Elastic App Search快速建立出色的React搜索体验
建立搜索体验是一项艰苦的工作. 乍一看似乎很容易:建立一个搜索栏,将数据放入数据库,然后让用户输入对该数据库的查询. 但是,在数据建模,底层逻辑以及(当然)总体设计和用户体验方面,有很多事情要考虑. ...
随机推荐
- 编译原理-翻译程序(Translator)
分为编译程序(compiler)和解释程序(interpreter) 编译程序:把源程序(高级语言编写)转换成目标程序(汇编语言或机器语言编写). 解释程序:对源程序边翻译边执行. 编译型语言 优点: ...
- 二、创建测试JSP页面
root@web1 ~]# rm -rf /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/* 1.创建测试网页 [root@web1 ROOT]# vim /usr/local/tomc ...
- JVM面试题(史上最强、持续更新、吐血推荐)
文章很长而且持续更新,建议收藏起来,慢慢读! 高并发 发烧友社群:疯狂创客圈(总入口) 奉上以下珍贵的学习资源: 疯狂创客圈 经典图书 : 极致经典 + 社群大片好评 < Java 高并发 三部 ...
- 天天写order by,你知道Mysql底层如何执行吗?
在实际的开发中一定会碰到根据某个字段进行排序后来显示结果的需求,但是你真的理解order by在 Mysql 底层是如何执行的吗? 假设你要查询城市是苏州的所有人名字,并且按照姓名进行排序返回前 10 ...
- WPF使用 INotifyPropertyChanged 实现数据驱动
如下图,有这么一个常见需求,在修改表单明细的苹果价格时,总价会改变,同时单据总和也随之改变. 按照Winfrom事件驱动的思想来做的话,我们就需要在将UI的修改函数绑定到CellEdit事件中来实现. ...
- Python基础之:Python的数据结构
目录 简介 列表 列表作为栈使用 列表作为队列使用 列表推导式 del 元组 集合 字典 循环 简介 不管是做科学计算还是编写应用程序,都需要使用到一些基本的数据结构,比如列表,元组,字典等. 本文将 ...
- vue+element表格
效果图 备注:前后端分离实现效果 接下来是代码环节 <template> <div class="comprehensive-table-container" ...
- Docker 优雅终止方案
作为一名系统工程师,你可能经常需要重启容器,毕竟Kubernetes的优势就是快速弹性伸缩和故障恢复,遇到问题先重启容器再说,几秒钟即可恢复,实在不行再重启系统,这就是系统重启工程师的杀手锏.然而现实 ...
- Windows10 上Docker 安装运行Consul
背景简介 Consul是一种服务网格解决方案,提供具有服务发现,配置和分段功能的全功能控制平面. 这些功能中的每一个都可以根据需要单独使用,也可以一起使用以构建全服务网格. Consul需要数据平面并 ...
- linux命令-------find命令之exec
p.p1 { margin: 0; font: 18px "Hannotate SC"; color: rgba(4, 51, 255, 1); -webkit-text-stro ...
