JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(格式化相关类)
一:格式化相关类
(一)java.text包java.text.Format的子类
–NumberFormat:数字格式化,抽象类
DecimalFormat
–MessageFormat:字符串格式化
–DateFormat:日期/时间格式化,抽象类
SimpleDateFormat
(二)java.time.format包下
–DateTimeFormatter
二:相关类的使用
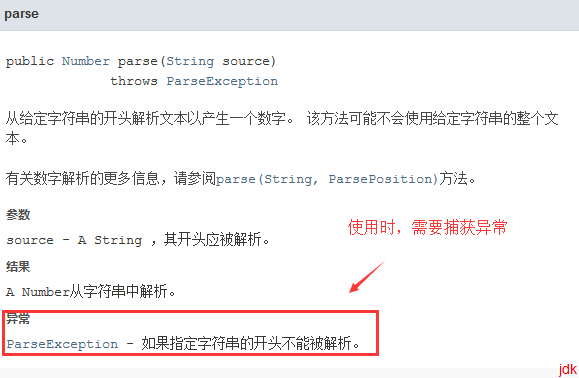
(一)NumberFormat的使用

NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
System.out.println(nf.format());
String name="";
try {
System.out.println(nf.parse(name));
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
,
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
¥,000.00
String name="100d000";
try {
System.out.println(nf.parse(name));
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
String name="d100000";
try {
System.out.println(nf.parse(name));
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
Unparseable number: "d100000"
(二)DecimalFormat的使用
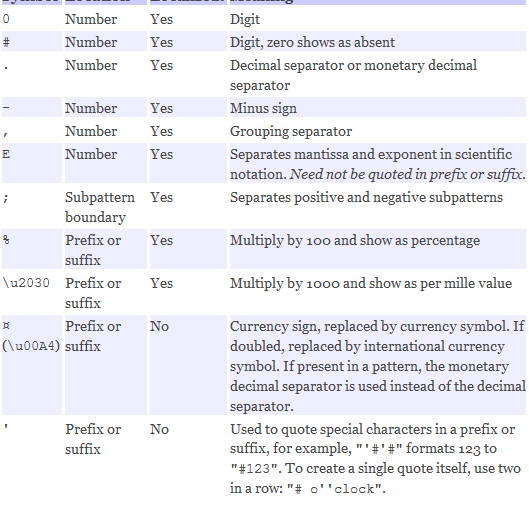
DecimalFormat df1,df2;
System.out.println("整数部分为0的情况,0/#的区别");
// 整数部分为0 , #认为整数不存在,可不写; 0认为没有,但至少写一位,写0
df1 = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
df2 = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
System.out.println(df1.format(0.1)); // .10
System.out.println(df2.format(0.1)); // 0.10
System.out.println("小数部分0/#的区别");
//#代表最多有几位,0代表必须有且只能有几位,同C中的域宽,当域宽小于整数部分,整数部分会失效,全部显示
df1 = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
df2 = new DecimalFormat("0.##");
System.out.println(df1.format(0.1)); // 0.10
System.out.println(df2.format(0.1)); // 0.1
System.out.println(df1.format(0.006)); // 0.01
System.out.println(df2.format(0.006)); // 0.01
System.out.println("整数部分有多位");
//0和#对整数部分多位时的处理是一致的 就是有几位写多少位
df1 = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
df2 = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
System.out.println(df1.format()); // 2.00
System.out.println(df2.format()); // 2.00
System.out.println(df1.format()); // 20.00
System.out.println(df2.format()); // 20.00
System.out.println(df1.format()); // 200.00
System.out.println(df2.format()); // 200.00
整数部分为0的情况,/#的区别
.
0.10
小数部分0/#的区别
0.10
0.1
0.01
0.01
整数部分有多位
2.00
2.00
20.00
20.00
200.00
200.00
df1 = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
df2 = new DecimalFormat("0.##");
System.out.println(df1.format(10.1)); // 0.10
System.out.println(df2.format(10.1)); // 0.1
10.10
10.1
(三)MessageFormat的使用(字符串格式化)
–支持多个参数-值对位复制文本
–支持变量的自定义格式
int planet = ;
String event = "a disturbance in the Force"; String result = MessageFormat.format(
"At {1,time} on {1,date}, there was {2} on planet {0,number,integer}.",
planet, new Date(), event); //planet对应0处,new Date()对应1,event对应2 System.out.println(result);
At 下午3:: on 2019年1月3日, there was a disturbance in the Force on planet .
int fileCount = ;
String diskName = "MyDisk";
Object[] testArgs = {new Long(fileCount), diskName}; MessageFormat form = new MessageFormat(
"The disk \"{1}\" contains {0} file(s)."); //\转义 System.out.println(form.format(testArgs));
The disk "MyDisk" contains , file(s).
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat("{0,number,#.##}, {0,number,#.#}");
Object[] objs = {new Double(3.1415)};
String result = mf.format( objs );
System.out.println(result);
3.14, 3.1
String message = "{0}{1}{2}{3}{4}{5}{6}{7}{8}{9}{10}{11}{12}{13}{14}{15}{16}";
Object[] array = new Object[]{"A","B","C","D","E","F","G","H","I","J","K","L","M","N","O","P","Q"};
String value = MessageFormat.format(message, array);
System.out.println(value);
message = "oh, {0,number,#.##} is a good number";
array = new Object[]{new Double(3.1415)};
value = MessageFormat.format(message, array);
System.out.println(value);
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQ
oh, 3.14 is a good number
parse的使用(重点):按照格式解析字符串,返回数组对象
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat("{0,number,#.##}, {0,number,#.#}");
Object[] objs = {new Double(3.1415)};
String result = mf.format( objs );
// result now equals "3.14, 3.1"
objs = null;
objs = mf.parse(result, new ParsePosition());
for(int i=;i<objs.length;i++) {
System.out.println(objs[i]);
}
3.1
ParsePosition设置访问起始下标,0表示从{0}开始全部获取,1表示从{1}开始索引,但是顺序不变0,1,...
MessageFormat mf2 = new MessageFormat("{0}, {2}, {1}");
String forParsing = "x, y, z";
Object[] obj2 = mf2.parse(forParsing, new ParsePosition());
// result now equals {new String("z")}
for(int i=;i<obj2.length;i++) {
System.out.println(obj2[i]);
}
x
z
y
(四)DateFormat的使用(时间格式化,抽象类)
–SimpleDateFormat 工厂模式
–parse:将字符串格式化为时间对象
–format:将时间对象格式化为字符串
–如将当前时间转为化YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS
String strDate = "2008-10-19 10:11:30.345" ;
// 准备第一个模板,从字符串中提取出日期数字
String pat1 = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS" ;
// 准备第二个模板,将提取后的日期数字变为指定的格式
String pat2 = "yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒SSS毫秒" ;
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat(pat1) ; // 实例化模板对象
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat(pat2) ; // 实例化模板对象
Date d = null ;
try{
d = sdf1.parse(strDate) ; // 将给定的字符串中的日期提取出来
}catch(Exception e){ // 如果提供的字符串格式有错误,则进行异常处理
e.printStackTrace() ; // 打印异常信息
}
System.out.println(sdf2.format(d)) ; // 将日期变为新的格式
–parse:将字符串格式化为时间对象
–format:将时间对象格式化为字符串
三:格式化练习
(一)验证身份证号码是否正确
输入一个字符串,请判断是否满足身份证基本要求,并返回具体的生日yyyy-mm-dd。如果输入数据有误,请输出0000--。基本要求是:
a)必须是18位;
b) 前面位数必须是数字,最后一位可以是数字或小写字母;
c) 日期是存在的。
输入格式:
一个身份证号码,18位字符串 输出格式:
yyyy-mm-dd 输入样例:
53010219200508011x 输出样例:
--
import java.text.*;
import java.util.*; public class ClasslibTest {
public static int judge(String iden) {
if(iden.length() != ) {
return -;
} int i=;
int flag = ; for(i=;i<iden.length()-;i++) {
if(!(iden.charAt(i)>=''&&iden.charAt(i)<='')) {
flag=;
break;
}
} if(!((iden.charAt(i)>=''&&iden.charAt(i)<='')||(iden.charAt(i)>='a'&&iden.charAt(i)<='z'))) {
flag=;
} if(flag==) {
return -;
} return flag;
} public static String getDate(String iden) {
String sub=iden.substring(, );
return sub;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner inp = new Scanner(System.in);
String strDate = inp.next() ;
int flag = judge(strDate); if(flag!=) {
return ;
} String substr=getDate(strDate); String part1 = "yyyyMMdd";
String part2 = "yyyy-MM-dd"; SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat(part1);
SimpleDateFormat sf2 = new SimpleDateFormat(part2); Date d=null; try {
d = sf.parse(substr); //获取时间
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
} System.out.println(sf2.format(d)); }
}
实现代码
53010219200508011x
--
(二)验证身份证号码是否正确(带校验算法)
输入一个字符串,请判断是否满足身份证基本要求,并返回具体的生日yyyy-mm-dd。
如果输入数据有误,请输出0000--。基本要求是:
a)必须是18位;
b) 前面位数必须是数字,最后一位可以是数字或小写字母;
c) 日期是存在的;
d)最后一位校验码检查。
校验码规则如下: 、将前面的身份证号码17位数分别乘以不同的系数。从第一位到第十七位的系数分别为:----------------。 、将这17位数字和系数相乘的结果相加。 、用加出来和除以11,看余数是多少? 、余数只可能有0----------10这11个数字。其分别对应的最后一位身份证的号码为1--X--------。 、通过上面得知如果余数是3,就会在身份证的第18位数字上出现的是9。如果对应的数字是10,身份证的最后一位号码就是罗马数字x。
import java.text.*;
import java.util.*; public class ClasslibTest {
public static int judge(String iden) {
if(iden.length() != ) {
return -;
} int i=;
int flag = ; for(i=;i<iden.length()-;i++) {
if(!(iden.charAt(i)>=''&&iden.charAt(i)<='')) {
flag=;
break;
}
} if(!((iden.charAt(i)>=''&&iden.charAt(i)<='')||(iden.charAt(i)>='a'&&iden.charAt(i)<='z'))) {
flag=;
} if(flag==) {
return -;
} return flag;
} public static String getDate(String iden) {
String sub=iden.substring(, );
return sub;
} public static void printDate(String strDate) { String substr=getDate(strDate); String part1 = "yyyyMMdd";
String part2 = "yyyy-MM-dd"; SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat(part1);
SimpleDateFormat sf2 = new SimpleDateFormat(part2); Date d=null; try {
d = sf.parse(substr); //获取时间
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
} System.out.println(sf2.format(d));
} public static int checkIden(String strDate) {
int flag = judge(strDate); if(flag!=) {
return -;
} int everPos[]= {,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,};
int LastPos[]= {,,-,,,,,,,,}; //-1表示X
int n=;
for(int i=;i<strDate.length()-;i++) {
n+=(strDate.charAt(i)-'')*everPos[i];
} n %= ; if((LastPos[n]==-&&strDate.charAt()=='x')||(LastPos[n]==(strDate.charAt()-'')))
return ;
else
return -;
} public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner inp = new Scanner(System.in);
String strDate = inp.next() ;
int flag = checkIden(strDate); if(flag==) {
printDate(strDate);
}else {
System.out.println("0000-00-00");
}
}
}
实现代码
23402613390168801x
-- 53010219200508011x
--
JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(格式化相关类)的更多相关文章
- 《Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10》学习笔记 第5章 继承
<Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10>学习笔记 第5章 继承 目录 <Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10>学习笔记 第5章 继承 5.1 类.超类和子类 5.1 ...
- Java核心技术 卷1 基础知识-第一天
基本数据类型 java是一种强数据类的的语言 共有8种基本数据类型 其中: 整型4种 int(4字节) short(2字节) long(8字节) byte(1字节) java中整型的范围与机器无关 长 ...
- Java基础-日期格式化DateFormat类简介
Java基础-日期格式化DateFormat类简介 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.DateFormat类概述 DateFormat 是日期/时间格式化子类的抽象 ...
- 第一天上午——HTML网页基础知识以及相关内容
今天上午学习了HTML基础知识以及相关内容,还有DW的基本使用方法. HTML(HyperText Markup Language):超文本标记语言,超文本:网页中除了包含文本文字之外,还包含了图片, ...
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (76) - 控件(控件基类): Control - 基础知识, 焦点相关, 运行时获取 ControlTemplate 和 DataTemplate 中的元素
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (76) - 控件(控件基类): Control - 基础知识, 焦点相关, 运行时获取 ControlTemplate 和 DataTemplate 中 ...
- Java并发包——线程安全的Collection相关类
Java并发包——线程安全的Collection相关类 摘要:本文主要学习了Java并发包下线程安全的Collection相关的类. 部分内容来自以下博客: https://www.cnblogs.c ...
- Java并发包——线程安全的Map相关类
Java并发包——线程安全的Map相关类 摘要:本文主要学习了Java并发包下线程安全的Map相关的类. 部分内容来自以下博客: https://blog.csdn.net/bill_xiang_/a ...
- JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(工具类Arrays和Collections类)
一:工具类 –不存储数据,而是在数据容器上,实现高效操作 • 排序 • 搜索 –Arrays类 –Collection类 二:Arrays类(处理数组) (一)基本方法 –排序:对数组排序, sort ...
- [Java面试三]JavaWeb基础知识总结.
1.web服务器与HTTP协议 Web服务器 l WEB,在英语中web即表示网页的意思,它用于表示Internet主机上供外界访问的资源. l Internet上供外界访问的Web资源分为: • 静 ...
随机推荐
- Python中的numpy模块解析
numpy 1. 创建对象 维度(dimensions):轴 轴的个数:秩(rank) Numpy最重要的一个特点就是其N维数组对象(即ndarray) 创建数组最简单的函数就是用array函数: ...
- Quartus prime 16.0 signaltap II 使用
前言 由于逻辑分析仪太贵,altera贴心提供signal tap II来观察输出波形,不过使能signaltap II会占用片内ram,毕竟原理就是把数据采样到ram中再通过jtag口上传到quar ...
- 【XSY2753】Lcm 分治 FWT FFT 容斥
题目描述 给你\(n,k\),要你选一些互不相同的正整数,满足这些数的\(lcm\)为\(n\),且这些数的和为\(k\)的倍数. 求选择的方案数.对\(232792561\)取模. \(n\leq ...
- 【JVM】查看JVM加载的类及类加载器的方法
查看JVM加载了哪些类 java -verbose[:class|gc|jni] 在输出设备上显示虚拟机运行信息. java -verbose:class 在程序运行的时候有多少类被加载!你可以用ve ...
- 【Luogu3732】[HAOI2017]供给侧改革(Trie树)
[Luogu3732][HAOI2017]供给侧改革(Trie树) 题面 洛谷 给定一个纯随机的\(01\)串,每次询问\([L,R]\)之间所有后缀两两之间的\(LCP\)的最大值. 题解 一个暴力 ...
- 【转】C++命名空间 namespace的作用和使用解析
一. 为什么需要命名空间(问题提出) 命名空间是ANSIC++引入的可以由用户命名的作用域,用来处理程序中 常见的同名冲突. 在 C语言中定义了3个层次的作用域,即文件(编译单元).函数和复合语句.C ...
- 牛客练习赛43 Tachibana Kanade Loves Review C(最小生成树Kruskal)
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/548/C来源:牛客网 题目描述 立华奏是一个刚刚开始学习 OI 的萌新. 最近,实力强大的 QingyuQingyu 当 ...
- Python3 与 C# 基础语法对比(Function专栏)
Code:https://github.com/lotapp/BaseCode 多图旧版:https://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/9186561.html 在线编程: ...
- Spring Boot 与 OAuth2 官方最详细教程
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU0MDEwMjgwNA==&mid=2247484357&idx=1&sn=73e501de8591e6 ...
- c# 获取机器硬件信息 (硬盘,cpu,内存等)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Globalization; using System.Management; ...
