Spring Boot 异常处理
Spring Boot 异常处理
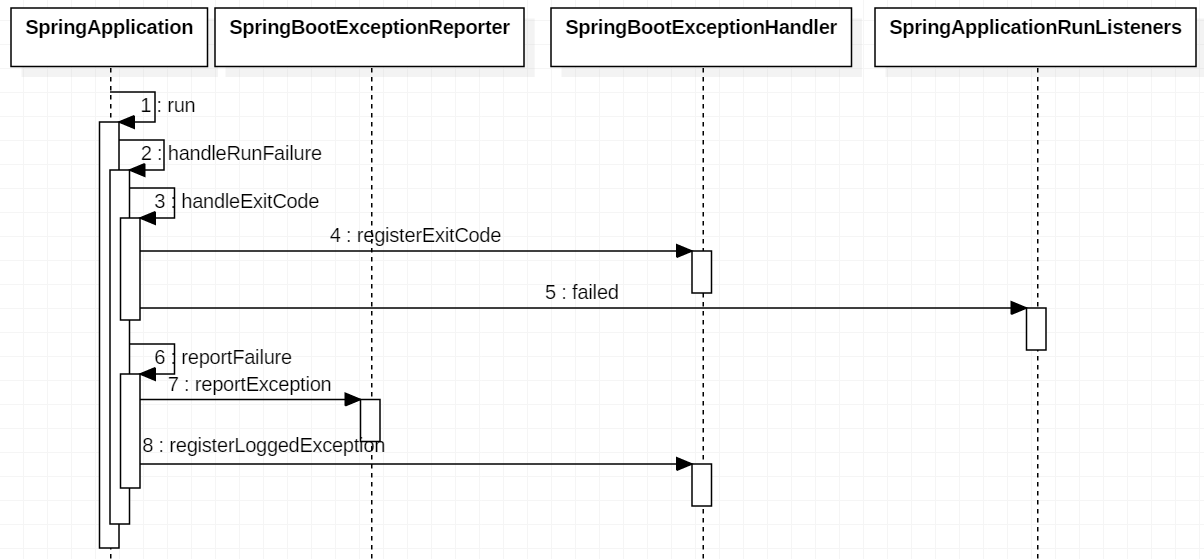
本节介绍一下 Spring Boot 启动时是如何处理异常的?核心类是 SpringBootExceptionReporter 和 SpringBootExceptionHandler。
一、Spring Boot 异常处理流程
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
try {
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 处理异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
run 方法中的异常处理都交给 handleRunFailure 完成。
private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception,
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) {
try {
try {
// 1. ExitCodeGenerators 根据异常获取是正常不是异常退出
handleExitCode(context, exception);
if (listeners != null) {
listeners.failed(context, exception);
}
} finally {
// 2. SpringBootExceptionReporter 处理异常报告
reportFailure(exceptionReporters, exception);
if (context != null) {
context.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Unable to close ApplicationContext", ex);
}
// 3. 重新报出异常,由 SpringBootExceptionHandler 处理
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
handleRunFailure 中主要依赖了三个组件完成异常的处理:
SpringBootExceptionReporter生成错误报告并处理,主要是用于输出日志。SpringBootExceptionHandler实现了 Thread#UncaughtExceptionHandler 接口,可以在线程异常关闭的时候进行回调。主要用于退出程序 System.exit(xxx)SpringApplicationRunListenersSpring Boot 事件机制
1.1 handleExitCode
handleExitCode 根据异常的类型决定如何退出程序,并将 exitCode(0 或 1) 退出码注册到 SpringBootExceptionHandler 上。
private void handleExitCode(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception) {
// 根据异常判断是正常退出还是异常退出
int exitCode = getExitCodeFromException(context, exception);
if (exitCode != 0) {
if (context != null) {
context.publishEvent(new ExitCodeEvent(context, exitCode));
}
SpringBootExceptionHandler handler = getSpringBootExceptionHandler();
if (handler != null) {
// 正常退出或异常退出,System.exit(exitCode) 用
handler.registerExitCode(exitCode);
}
}
}
getExitCodeFromException 根据异常判断是正常退出还是异常退出,委托给了 ExitCodeGenerators,最后将退出码注册到 SpringBootExceptionHandler 上。
1.2 reportFailure
private void reportFailure(Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters,
Throwable failure) {
try {
for (SpringBootExceptionReporter reporter : exceptionReporters) {
if (reporter.reportException(failure)) {
registerLoggedException(failure);
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
}
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Application run failed", failure);
registerLoggedException(failure);
}
}
reportFailure 委托 SpringBootExceptionReporter 处理异常,并将异常注册到 SpringBootExceptionHandler 上。
二、ExitCodeGenerators
private int getExitCodeFromException(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception) {
// ExitCodeGenerators 处理异常
int exitCode = getExitCodeFromMappedException(context, exception);
// 如果没有分析出来,则判断这个异常本身是实现了 ExitCodeGenerator 接口,继续分析
if (exitCode == 0) {
exitCode = getExitCodeFromExitCodeGeneratorException(exception);
}
return exitCode;
}
// 从 context 中获取所有的 ExitCodeExceptionMapper 来分析异常
private int getExitCodeFromMappedException(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception) {
if (context == null || !context.isActive()) {
return 0;
}
ExitCodeGenerators generators = new ExitCodeGenerators();
Collection<ExitCodeExceptionMapper> beans = context
.getBeansOfType(ExitCodeExceptionMapper.class).values();
// 将 exception 和 ExitCodeExceptionMapper 封装成 ExitCodeGenerator 注册到 generators 中
generators.addAll(exception, beans);
return generators.getExitCode();
}
// 异常本身实现了 ExitCodeGenerator 接口
private int getExitCodeFromExitCodeGeneratorException(Throwable exception) {
if (exception == null) {
return 0;
}
if (exception instanceof ExitCodeGenerator) {
return ((ExitCodeGenerator) exception).getExitCode();
}
return getExitCodeFromExitCodeGeneratorException(exception.getCause());
}
ExitCodeGenerator 和 ExitCodeExceptionMapper 接口如下,ExitCodeGenerators 管理多个 ExitCodeGenerator。Spring 将 exception 和 ExitCodeExceptionMapper 封装成 ExitCodeGenerator 注册到 ExitCodeGenerators 中便于统一处理。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ExitCodeGenerator {
int getExitCode();
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ExitCodeExceptionMapper {
int getExitCode(Throwable exception);
}
三、SpringBootExceptionReporter
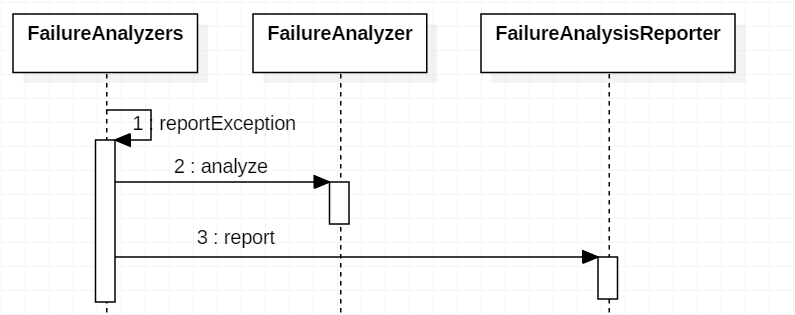
SpringBootExceptionReporter 也是在 spring.factories 中配置的,默认实现为 FailureAnalyzers。FailureAnalyzers 持有多个 FailureAnalyzer 来分析异常生成 FailureAnalysis 报告,由 FailureAnalysisReporter 处理。这些类都位于 org.springframework.boot.diagnostics 包下。具体的配置如下:
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer
# FailureAnalysisReporters
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
FailureAnalyzers 处理流程也非常简单。
四、SpringBootExceptionHandler
Thread#UncaughtExceptionHandler 处理线程异常关闭时未处理的异常:https://www.cnblogs.com/jadic/p/3532580.html
SpringBootExceptionHandler 实现了 Thread#UncaughtExceptionHandler 接口,在线程关闭时退出程序。
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable ex) {
try {
if (isPassedToParent(ex) && this.parent != null) {
this.parent.uncaughtException(thread, ex);
}
} finally {
this.loggedExceptions.clear();
if (this.exitCode != 0) {
System.exit(this.exitCode);
}
}
}
那 SpringBootExceptionHandler 是怎么注册到线程上的呢?实际上在初始化类的时候就注册到线程上了。
// 初始化类的时候就实例了 SpringBootExceptionHandler
private static LoggedExceptionHandlerThreadLocal handler = new LoggedExceptionHandlerThreadLocal();
private static class LoggedExceptionHandlerThreadLocal
extends ThreadLocal<SpringBootExceptionHandler> {
@Override
protected SpringBootExceptionHandler initialValue() {
SpringBootExceptionHandler handler = new SpringBootExceptionHandler(
Thread.currentThread().getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
// 将 SpringBootExceptionHandler 注册到当前线程上
Thread.currentThread().setUncaughtExceptionHandler(handler);
return handler;
}
}
获取 SpringBootExceptionHandler 实例:
static SpringBootExceptionHandler forCurrentThread() {
return handler.get();
}
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!
Spring Boot 异常处理的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot异常处理详解
在Spring MVC异常处理详解中,介绍了Spring MVC的异常处理体系,本文将讲解在此基础上Spring Boot为我们做了哪些工作.下图列出了Spring Boot中跟MVC异常处理相关的类 ...
- Spring Boot异常处理
一.默认映射 我们在做Web应用的时候,请求处理过程中发生错误是非常常见的情况.Spring Boot提供了一个默认的映射:/error,当处理中抛出异常之后,会转到该请求中处理,并且该请求有一个全局 ...
- Spring boot 异常处理配置
1. 新建Maven项目 exception 2. pom.xml <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0&quo ...
- Spring Boot 异常处理静止trace
概述 在spring boot 2.2 中 默认状态为status 999 private void addStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttribut ...
- spring boot 异常处理(转)
spring boot在异常的处理中,默认实现了一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer并定义了一个错误页面到"/error"中,在ErrorMvc ...
- Spring Boot 知识图谱
最近有意重新学习下SpringBoot知识,特地总结了SpringBoot的知识点,对于想要学习的人来说,够用. SpringBoot学习路径 第一部分:了解 Spring Boot Spring B ...
- 40 篇原创干货,带你进入 Spring Boot 殿堂!
两个月前,松哥总结过一次已经完成的 Spring Boot 教程,当时感受到了小伙伴们巨大的热情. 两个月过去了,松哥的 Spring Boot 教程又更新了不少,为了方便小伙伴们查找,这里再给大家做 ...
- Spring Boot 日志处理你还在用Logback?
▶ Log4j2 性能 https://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/performance.html ▶ Spring Boot 依赖与配置 Maven 依赖 <! ...
- 天天玩微信,Spring Boot 开发私有即时通信系统了解一下
1/ 概述 利用Spring Boot作为基础框架,Spring Security作为安全框架,WebSocket作为通信框架,实现点对点聊天和群聊天. 2/ 所需依赖 Spring Boot 版本 ...
随机推荐
- Excel组合图表快速制作小功能
1. 选中数据区域,插入推荐的图表 2. 然后可以选择快速布局小工具进行布局微调 选中图表 -> 设计(菜单) -> 快速布局(左边) 个人特别喜欢带表格的那个组合图布局,清晰好看
- appium 使用环境安装配置记录
一.安装配置Java (cmd输入java,回车,没有出现“不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序或批处理文件”,即为成功) 二.安装node.js (cmd输入node -v,显示版本号即为成功) ...
- 容器部署解决方案Docker
容器部署解决方案Docker 课程目标 目标1:了解Docker与虚拟机的不同点,相比的优势 目标2:掌握Docker的启动方法 目标3:掌握Docker镜像操作 目标4:掌握Docker容器操作 ...
- 线程之Callable、Future 和FutureTask使用及源码分析
一.Callable 我们知道启动线程有以下两种方式(jdk源码注释中官方定义只有两种启动方式,callable不算线程启动方式) 原文链接:http://www.studyshare.cn/blog ...
- thinkphp5.1的公共函数库 common.php
首先引入Db类 或者是模型 use think\Db; 然后写公共函数 function getUserName($id){ return Db::table('zh_user')->where ...
- idea 设置光标回到上一次位置的快捷键
1. file-->settings,搜索 navigate 这个 蓝色的back和forward分别就是光标后退.前进的快捷键了,全部移除原来冲突的快捷键,然后重新设置成自己的快捷键即可. 然 ...
- getPageNumRange
<script> function getPageNumRange(pagenumstr) { var pages=pagenumstr.split(";"); pag ...
- vs2015下编译duilib的几个问题
duilib下载地址在github 用vs2015打开,提示升级工程,确认后继续. 编译,UIGifAnim.cpp 323行报错 1>Control\UIGifAnim.cpp(324): e ...
- win10x64启动vs2010报错:未能加载C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\microsoft.vsa.tlb
换了新电脑,因为是win10x64系统,可能是兼容性的问题吧. 启动vs2010,在启动画面直接报错:未能加载C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727 ...
- 讨论下茴香逗的茴字有几种写法,javascript字符串数组查找“indexOf"的替代方式。
