linux系统编程之文件与IO(六):实现ls -l功能
本文利用以下系统调用实现ls -l命令的功能:
1,lstat:获得文件状态,
2,getpwuid:
#include <pwd.h>
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);
描述:
The getpwuid() function returns a pointer to a structure containing the broken-out fields of the record in the password database that matches the user ID uid.
返回值:
The passwd structure is defined in <pwd.h> as follows:
struct passwd {
char *pw_name; /* username */
char *pw_passwd; /* user password */
uid_t pw_uid; /* user ID */
gid_t pw_gid; /* group ID */
char *pw_gecos; /* real name */
char *pw_dir; /* home directory */
char *pw_shell; /* shell program */
};
示例:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pwd.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while() int main(void)
{
uid_t uid;
struct passwd *pw;
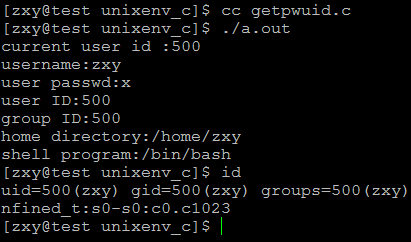
uid = getuid();
printf("current user id :%d\n",uid);
if((pw = getpwuid(uid)) == NULL)
ERR_EXIT("getpwuid error");
printf("username:%s\n",pw->pw_name);
printf("user passwd:%s\n",pw->pw_passwd);
printf("user ID:%d\n",pw->pw_uid);
printf("group ID:%d\n",pw->pw_gid);
//printf("real name:%s\n",pw->pw_gecos);
printf("home directory:%s\n",pw->pw_dir);
printf("shell program:%s\n",pw->pw_shell);
return ;
}
运行结果:
3,getgrgid:
#include <grp.h>
struct group *getgrnam(const char *name);//根据组名获得组信息
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);//根据组ID获得组信息
描述:
The getgrnam() function returns a pointer to a structure containing the broken-out fields of the record in the group database (e.g., the local group file /etc/group, NIS, and LDAP) that matches the group name name.
The getgrgid() function returns a pointer to a structure containing the broken-out fields of the record in the group database that matches thegroup ID gid.
返回值:
The group structure is defined in <grp.h> as follows:
struct group {
char *gr_name; /* group name */
char *gr_passwd; /* group password */
gid_t gr_gid; /* group ID */
char **gr_mem; /* group members */
};
4,readlink:读取软链接文件的内容
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t readlink(const char *path, char *buf, size_t bufsiz);
描述:
DESCRIPTION
readlink() places the contents of the symbolic link path in the buffer
buf, which has size bufsiz. readlink() does not append a null byte to
buf. It will truncate the contents (to a length of bufsiz characters),
in case the buffer is too small to hold all of the contents.
RETURN VALUE
On success, readlink() returns the number of bytes placed in buf. On
error, -1 is returned and errno is set to indicate the error.
示例:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while()
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
if(argc != ){
fprintf(stderr,"usage:%s linkfile", argv[]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} char buf[]; if(readlink(argv[],buf,) ==-)
ERR_EXIT("readlink error");
printf("the content of %s are: %s\n",argv[],buf);
return ;
}
运行结果:

现在利用相关的系统调用实现ls –l功能:
程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <libgen.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do\
{\
perror(m);\
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);\
}while()\ void lsdir(char *dirname);
void lsfile(char *filename);
void lsfile(char *filename);
char getFileType(struct stat *fstat);
void getFilePerm(struct stat *st, char *perm); int main(int argc,char **argv)
{ if(argc != ){
fprintf(stderr,"usage:%s [filepath]\n",argv[]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct stat fstat;
if(lstat(argv[],&fstat) == -)
ERR_EXIT("STAT ERROR"); if(S_ISDIR(fstat.st_mode))
{
lsdir(argv[]);
}
else{
lsfile(argv[]);
}
return ;
} void lsdir(char *dirname)
{
DIR *dir;
char filename[] = {};
dir =opendir(dirname);
if(dir == NULL)
ERR_EXIT("opendir error");
struct dirent *dentry;
while((dentry = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
{ char *fname;
fname = dentry->d_name;
if(strncmp(fname,".",) == )
continue;
sprintf(filename,"%s/%s",dirname,fname);
lsfile(filename);
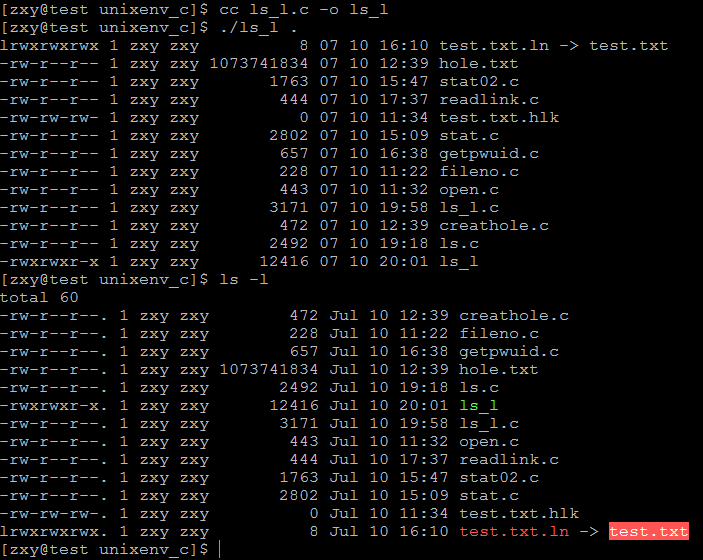
} closedir(dir); } //-rw-r--r--. 1 zxy zxy 2586 Jul 10 17:00 ls.c
//类型及权限 硬链接数 拥有者 所属组 文件大小 创建时间 文件名
void lsfile(char *filename)
{
struct stat tmpstat;
if(lstat(filename,&tmpstat) == -)
ERR_EXIT("STAT ERROR");
char buf[]= {};
strcpy(buf,"----------");
char type;
type = getFileType(&tmpstat);
char *bname = basename(filename);
buf[] = type;
if(type == 'l'){
char content[];
if(readlink(filename,content,) == -)
ERR_EXIT("readlink error");
sprintf(bname,"%s -> %s",bname,content); }
getFilePerm(&tmpstat,buf);
struct tm *ftime;
ftime = localtime(&tmpstat.st_mtime); printf("%s %d %s %s %10ld %02d %02d %02d:%02d %s\n",
buf,tmpstat.st_nlink,
getpwuid(tmpstat.st_uid)->pw_name,
getgrgid(tmpstat.st_gid)->gr_name,
tmpstat.st_size,
ftime->tm_mon+,
ftime->tm_mday,
ftime->tm_hour,
ftime->tm_min,
bname); } //获得文件类型
char getFileType(struct stat *st)
{
char type = '-';
switch (st->st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFSOCK:
type = 's';
break;
case S_IFLNK:
type = 'l';
break;
case S_IFREG:
type = '-';
break;
case S_IFBLK:
type = 'b';
break;
case S_IFDIR:
type = 'd';
break;
case S_IFCHR:
type = 'c';
break;
case S_IFIFO:
type = 'p';
break;
}
return type;
} //获得文件访问权限
void getFilePerm(struct stat *st, char *perm)
{
mode_t mode = st->st_mode;
if (mode & S_IRUSR)
perm[] = 'r';
if (mode & S_IWUSR)
perm[] = 'w';
if (mode & S_IXUSR)
perm[] = 'x';
if (mode & S_IRGRP)
perm[] = 'r';
if (mode & S_IWGRP)
perm[] = 'w';
if (mode & S_IXGRP)
perm[] = 'x';
if (mode & S_IROTH)
perm[] = 'r';
if (mode & S_IWOTH)
perm[] = 'w';
if (mode & S_IXOTH)
perm[] = 'x';
}
运行结果:
linux系统编程之文件与IO(六):实现ls -l功能的更多相关文章
- linux系统编程之文件与io(一)
经过了漫长的学习,C语言相关的的基础知识算是告一段落了,这也是尝试用写博客的形式来学习c语言,回过头来看,虽说可能写的内容有些比较简单,但是个人感觉是有史起来学习最踏实的一次,因为里面的每个实验都是自 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(五)
上一节中已经学习了文件描述符的复制,复制方法有三种,其中最后一种fcntl还并未使用到,关于这个函数,不光只有复制文件描述符的功能,还有其它一些用法,本节就对其进行一一剖析: fcntl常用操作: 这 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与IO(一):文件描述符、open,close
什么是IO? 输入/输出是主存和外部设备之间拷贝数据的过程 设备->内存(输入操作) 内存->设备(输出操作) 高级I/O ANSI C提供的标准I/O库称为高级I/O,通常也称为带缓冲的 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(四)
今天继续学习文件与io,主要是学习文件共享及文件.复制文件描述符,有点抽象,主要是概念上的理解,但是很重要,下面一一来分解: 文件共享: 回顾一下,在linux系统调用中,是通过文件描述符来访问文件的 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(二)
今天继续学习文件与io,话不多说,开始进入正题: 文件的read和write系统调用: 说明:函数中出现在size_t和ssize_t是针对系统定制的数据类型: 下面以一个实现文件简单拷贝的示 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(三)
上次我们利用文件的read和write来实现了简易的cp命令,其中将源文件拷贝到目标文件时,我们给目标文件的权限是写死的,而非根据源文件的权限生成的,如下: 今天就来解决这个问题,来学习获取文件权限相 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与IO(七):时间函数小结
从系统时钟获取时间方式 time函数介绍: 1.函数名称: localtime 2.函数名称: asctime 3.函数名称: ctime 4.函数名称: difftime 5.函数名称: gmtim ...
- linux系统编程之文件与IO(四):目录访问相关系统调用
1. 目录操作相关的系统调用 1.1 mkdir和rmdir系统调用 1.1.1 实例 1.2 chdir, getcwd系统调用 1.2.1 实例 1.3 o ...
- linux系统编程之文件与IO(三):利用lseek()创建空洞文件
一.lseek()系统调用 功能说明: 通过指定相对于开始位置.当前位置或末尾位置的字节数来重定位 curp,这取决于 lseek() 函数中指定的位置 函数原型: #include <sys/ ...
随机推荐
- 索引与like优化
未建索引 mysql> alter table modulestatus drop index imei;Query OK, 457922 rows affected (4.29 sec)Rec ...
- (转) Ringbuffer为什么这么快?
原文地址:http://ifeve.com/ringbuffer/ 最近,我们开源了LMAX Disruptor,它是我们的交易系统吞吐量快(LMAX是一个新型的交易平台,号称能够单线程每秒处理数百万 ...
- 【趣】Python获取变量的变量名
两种不完美的方式: 用locals,globals 用locals获取变量列表,再遍历比较对象. def namestr(obj): ns = globals() return [name for n ...
- TIME_WAIT状态的作用
TIME_WAIT状态: 主动关闭的那端最后经历的状态,一般为2MSL秒(1~4分钟). 两个原因: 保证当最后一个ack丢失后,能收到对端重传的fin包. 保证ack包消失,不会影响下一个连接. 关 ...
- VC小笔记
1.strcpy不需要指定的长度,遇到被复制字符的串结束符’\0’才结束,容易溢出 2.memcpy(k, s, strlen(s)*sizeof(char)+1); // strlen(s) 后 + ...
- c++ 自动对象
转自: https://www.cnblogs.com/geloutingyu/p/8034904.html 1.自动对象默认情况下,局部变量的生命期局限于所在函数的每次执行期间.只有当定义它的函数被 ...
- html5 web 摇一摇切换歌曲
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8&quo ...
- 16款值得一用的iPhone线框图模板 (PSD & Sketch)
在任何网站或移动应用设计的过程中,线框图作为设计元素和功能的图示,它有助于帮助定义和更好地传达信息层次结构,让参与设计和开发的人员更好的理解设计师的思路和设计的功能点. 即使线框图设计是一个比较耗时的 ...
- VC6.0 OpenGL环境配置及编程基础
1.一般情况下VC并不携带glut,需要到opengl官网下载,下载地址 http://www.opengl.org/resources/libraries/glut/glut37.zip 解压后 打 ...
- [精彩] 关于DB2的内存分配
这两天在看DB2的内存管理的内容,看的很是模糊,有以下问题不明白,请教 是不是数据库管理器的共享内存就是DB2能够使用的最大内容呢,然后数据库全局内存从管理器内存那里获得分配的内存,然后应用程序全局内 ...
