快速排序—三路快排 vs 双基准
快速排序被公认为是本世纪最重要的算法之一,这已经不是什么新闻了。对很多语言来说是实际系统排序,包括在Java中的Arrays.sort。
那么快速排序有什么新进展呢?
好吧,就像我刚才提到的那样(Java 7发布两年后)快速排序实现的Arrays.sort被双基准(dual-pivot)排序的一种变体取代了。这篇文章不仅展示了为什么这个变化如此优秀,而且让我们看到Jon Bentley和Joshua Bloch的谦逊。
我当时做了什么?
与所有人一样,我想实现这个算法并且对一千万个数值排序(随机数据和重复数据)。奇怪的是,我得到了下面的结果:
随机数据:
- 基本排序:1222ms。
- 三路(Three-way)快速排序:1295ms(我是认真的!)。
- 双基准快速排序:1066ms。
重复数据:
- 基本排序:378ms。
- 三路快速排序:15ms。
- 双基准快速排序:6ms。
愚蠢的问题1
我担心自己在实现三路快速排序的时候遗漏了什么。在多次执行随机输入一千万个数值后,可以看到单点排序始终运行更良好。尽管在执行一千万个数值的时候差距小于100ms。
我现在明白了,用三路快速排序作为默认排序工具的目的。因为在重复数值时,它的时间复杂度没有0(n2)。当我在输入重复值数据时,结果非常明显。但是真的为了处理重复数据的缘故,三路快速排序会受到性能损失吗?或者是我实现方式有问题?
愚蠢的问题2
我的双基准快速排序在实现重复数据的时候并没有处理好,它执行时耗费了0(n2)的时间复杂度。有什么好的办法可以避免吗?实现数组排序时我发现,在实际排序前升序序列和重复就已经能得到很好地消除。所以,作为一种应急的办法,如果定位的数字与比较的数字相等,则增长lowerIndex 去比较下一位数直到与pivot2不相等为止。这种实现会没有问题吗?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
else if (pivot1==pivot2){ while (pivot1==pivot2 && lowIndex<highIndex){ lowIndex++; pivot1=input[lowIndex]; } } |
这就是所有内容吗?我究竟做了哪些?
我一直觉得算法跟踪很有趣,但是双基准快速排序中出现的变量个数让我眼花缭乱。所以,接下来我在(三种)实现中都加入了调试信息,这样就可以看出实际运行中不同。
这些可跟踪的类只负责追踪数组下方的指针。希望你能发现这些类是很有用的。
例如一个双基准迭代器:

你可以从哪里下载代码?
整个项目(连同一些蹩脚的DSA实现)的实现可以在GitHub上找到。快速排序类就可以在这里找到。
这是我的实现单基准(Hoare),三路快排(Sedgewick)和新双基准(Yaroslavskiy)。
单基准:
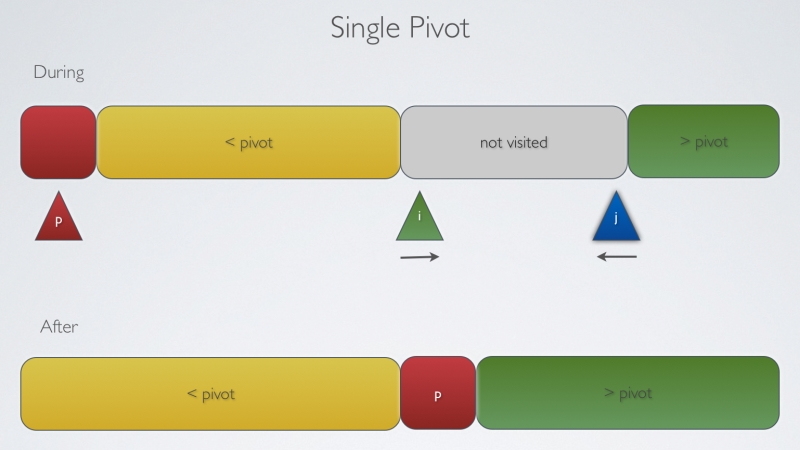
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
package basics.sorting.quick;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.exchange;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.less;import basics.shuffle.KnuthShuffle;public class QuickSortBasic { public void sort (int[] input){ //KnuthShuffle.shuffle(input); sort (input, 0, input.length-1); } private void sort(int[] input, int lowIndex, int highIndex) { if (highIndex<=lowIndex){ return; } int partIndex=partition (input, lowIndex, highIndex); sort (input, lowIndex, partIndex-1); sort (input, partIndex+1, highIndex); } private int partition(int[] input, int lowIndex, int highIndex) { int i=lowIndex; int pivotIndex=lowIndex; int j=highIndex+1; while (true){ while (less(input[++i], input[pivotIndex])){ if (i==highIndex) break; } while (less (input[pivotIndex], input[--j])){ if (j==lowIndex) break; } if (i>=j) break; exchange(input, i, j); } exchange(input, pivotIndex, j); return j; }} |
三基准
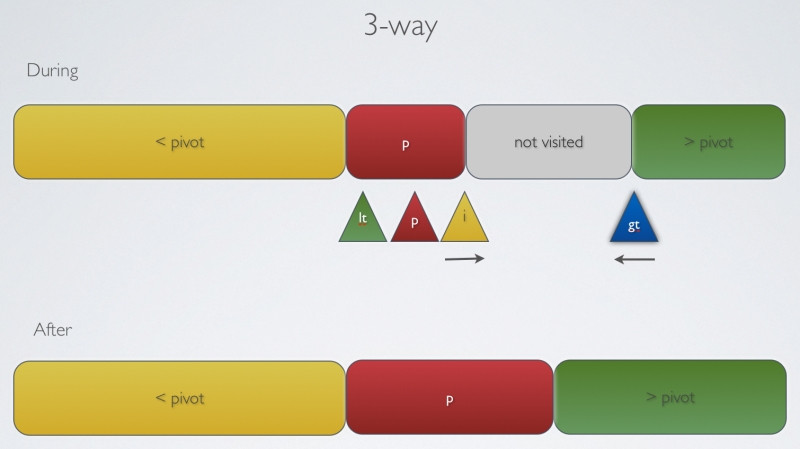
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
package basics.sorting.quick;import static basics.shuffle.KnuthShuffle.shuffle;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.exchange;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.less;public class QuickSort3Way { public void sort (int[] input){ //input=shuffle(input); sort (input, 0, input.length-1); } public void sort(int[] input, int lowIndex, int highIndex) { if (highIndex<=lowIndex) return; int lt=lowIndex; int gt=highIndex; int i=lowIndex+1; int pivotIndex=lowIndex; int pivotValue=input[pivotIndex]; while (i<=gt){ if (less(input[i],pivotValue)){ exchange(input, i++, lt++); } else if (less (pivotValue, input[i])){ exchange(input, i, gt--); } else{ i++; } } sort (input, lowIndex, lt-1); sort (input, gt+1, highIndex); }} |
双基准
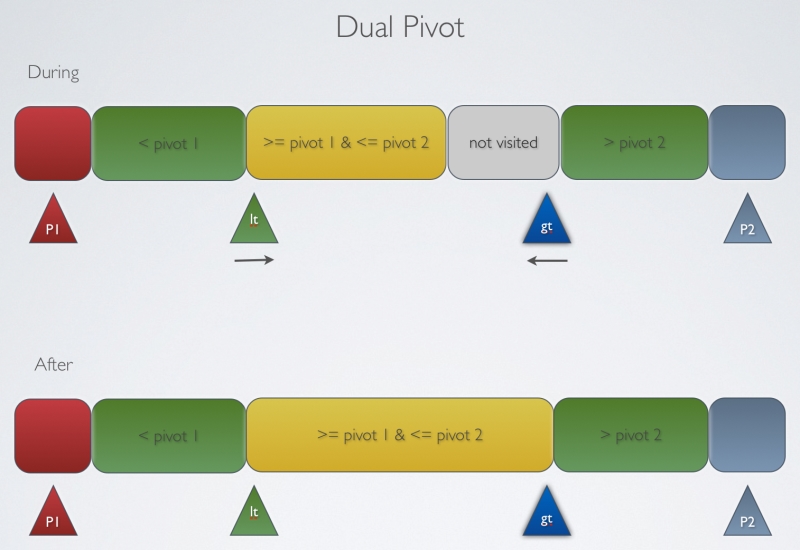
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
package basics.sorting.quick;import static basics.shuffle.KnuthShuffle.shuffle;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.exchange;import static basics.sorting.utils.SortUtils.less;public class QuickSortDualPivot { public void sort (int[] input){ //input=shuffle(input); sort (input, 0, input.length-1); } private void sort(int[] input, int lowIndex, int highIndex) { if (highIndex<=lowIndex) return; int pivot1=input[lowIndex]; int pivot2=input[highIndex]; if (pivot1>pivot2){ exchange(input, lowIndex, highIndex); pivot1=input[lowIndex]; pivot2=input[highIndex]; //sort(input, lowIndex, highIndex); } else if (pivot1==pivot2){ while (pivot1==pivot2 && lowIndex<highIndex){ lowIndex++; pivot1=input[lowIndex]; } } int i=lowIndex+1; int lt=lowIndex+1; int gt=highIndex-1; while (i<=gt){ if (less(input[i], pivot1)){ exchange(input, i++, lt++); } else if (less(pivot2, input[i])){ exchange(input, i, gt--); } else{ i++; } } exchange(input, lowIndex, --lt); exchange(input, highIndex, ++gt); sort(input, lowIndex, lt-1); sort (input, lt+1, gt-1); sort(input, gt+1, highIndex); }} |
http://www.importnew.com/8445.html
快速排序—三路快排 vs 双基准的更多相关文章
- 快速排序 java实现 (原理-优化) 三路快排
一.基本的快速排序 在数组中选取一个元素为基点,然后想办法把这个基点元素移动到它在排好序后的最终位置,使得新数组中在这个基点之前的元素都小于这个基点,而之后的元素都大于这个基点,然后再对前后两部分数组 ...
- 快速排序详解(lomuto划分快排,hoare划分快排,classic经典快排,dualpivot双轴快排源码)
目录 快速排序(lomuto划分快排,hoare划分快排,classic经典快排,dualpivot双轴快排) 一.快速排序思想 二.划分思想 三.测试用例 快速排序(lomuto划分快排,hoare ...
- LeetCode 75. Sort Colors (颜色分类):三路快排
Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the ...
- javascript高级排序算法之快速排序(快排)
javascript高级排序算法之快速排序(快排)我们之前讨论了javascript基本排序算法 冒泡排序 选择排序 插入排序 简单复习: 冒泡排序: 比较相邻的两个元素,如果前一个比后一个大,则交换 ...
- 普林斯顿大学算法课 Algorithm Part I Week 3 重复元素排序 - 三路快排 Duplicate Keys
很多时候排序是为了对数据进行归类,这种排序重复值特别多 通过年龄统计人口 删除邮件列表里的重复邮件 通过大学对求职者进行排序 若使用普通的快排对重复数据进行排序,会造成N^2复杂度,但是归并排序和三路 ...
- leetcode 75 Sort Colors 计数排序,三路快排
解法一:计数排序:统计0,1,2 的个数 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(k) k为元素的取值范围, 此题为O(1) class Solution { public: void sortC ...
- LeetCode 75. Sort Colors (python一次遍历,模拟三路快排)
LeetCode 75. Sort Colors (python一次遍历,模拟三路快排) 题目分析: 本题需要实现数字只包含0,1,2的排序,并且要求一次遍历. 由于只用把数字隔离开,很容易想到快排的 ...
- luogu_P1177 【模板】快速排序 (快排和找第k大的数)
[算法] 选取pivot,然后每趟快排用双指针扫描(l,r)区间,交换左指针大于pivot的元素和右指针小于pivot的元素,将区间分成大于pivot和小于pivot的 [注意] 时间复杂度取决于pi ...
- 【C语言编程入门笔记】排序算法之快速排序,一文轻松掌握快排!
排序算法一直是c语言重点,各个算法适应不用的环境,同时,在面试时,排序算法也是经常被问到的.今天我们介绍下快速排序,简称就是快排. 1.快速排序思想: 快排使用 分治法 (Divide and con ...
随机推荐
- C#四舍五入说明
string.Format("{0:N2}", d) 与 Math.Round(d, 2).ToString() 不总是相等 string.Format("{0:N2}& ...
- python -m
影响sys.path python xxx.py python -m xxx.py 这是两种加载py文件的方式:1叫做直接运行2把模块当作脚本来启动 直接启动是把脚本所在的目录放到了sys.path属 ...
- 清理数据库errorlog
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\LOGERRORLOGERRORLOG.1ERRORLOG.2ERRORLOG.3ERRORLO ...
- Required String parameter ' ' is not present
Required String parameter ' ' is not present 报错原因: url中的参数错误. 解决方法: 1.修正url中的参数的值. 2.在Controller层中的@ ...
- 慕课网access_token的获取
access_token的接口是微信公众号一个基础接口,access_token接口微信公众号一个非常重要的接口 access_token是微信公众号的全局唯一票据,公众号的所有接口的调用都需要使用到 ...
- hdoj1251-统计难题 【字典树】
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1251 统计难题 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory ...
- 【校招面试 之 C/C++】第29题 C/C++ 关键字extern
1.extern "C" extern "C"的主要作用就是为了能够正确实现C++代码调用其他C语言代码.加上extern "C"后,会指示 ...
- 【校招面试 之 C/C++】第16题 C++ new和delete的实现原理
1.new new操作针对数据类型的处理,分为两种情况: (1)简单数据类型(包括基本数据类型和不需要构造函数的类型) 代码实例: int* p = new int; 汇编码如下: int* p = ...
- Java多线程超详细总结
目录(?)[-] 一扩展javalangThread类 二实现javalangRunnable接口 三Thread和Runnable的区别 四线程状态转换 五线程调度 六常用函数说明 使用方式 为什么 ...
- js string 字符串
mutil lines string 多行字符串, 由于多行字符串用\n写起来比较费事,所以最新的ES6标准新增了一种多行字符串的表示方法,用...表示,是单撇号, 不是单引号. 这是一个 多行 字符 ...
