AQS底层原理分析
J.U.C 简介
Lock
Lock 简介
Lock 的实现
Lock 的类关系图
Lock 有很多的锁的实现,但是直观的实现是 ReentrantLock 重入锁
 |
 void lock() // 如果锁可用就获得锁,如果锁不可用就阻塞直到锁释放
void lockInterruptibly() // 和lock()方法相似, 但阻塞的线程 可 中 断 , 抛 出java.lang.InterruptedException 异常
boolean tryLock() // 非阻塞获取锁;尝试获取锁,如果成功返回 true
boolean tryLock(longtimeout, TimeUnit timeUnit)//带有超时时间的获
取锁方法
void unlock() // 释放锁
|
ReentrantLock 重入锁
重入锁的设计目的
public class ReentrantDemo{
public synchronized void demo(){
System.out.println("begin:demo");
demo2();
}
public void demo2(){
System.out.println("begin:demo1");
synchronized (this){
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantDemo rd=new ReentrantDemo();
new Thread(rd::demo).start();
}
}
public class AtomicDemo {
private static int count=0;
static Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
public static void inc(){
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
lock.unlock();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
new Thread(()->{AtomicDemo.inc();}).start();;
}
Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("result:"+count);
}
}
ReentrantReadWriteLock
public class LockDemo {
static Map<String,Object> cacheMap=new HashMap<>();
static ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl=new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
static Lock read=rwl.readLock();
static Lock write=rwl.writeLock();
public static final Object get(String key) {
System.out.println("开始读取数据");
read.lock(); //读锁
try {
return cacheMap.get(key);
}finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
public static final Object put(String key,Object value){
write.lock();
System.out.println("开始写数据");
try{
return cacheMap.put(key,value);
}finally {
write.unlock();
}
}
}
ReentrantLock 的实现原理
AQS 是什么
AQS 的内部实现
static final class Node {
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
volatile int waitStatus;
volatile Node prev;//前驱节点
volatile Node next;//后驱节点
volatile Thread thread;//当前线程
Node nextWaiter;//存储在condition 队列中的后继节点
final boolean isShared() {//是否为共享锁
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter 将线程构造一个节点,添加队列
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
释放锁以及添加线程对于队列的变化
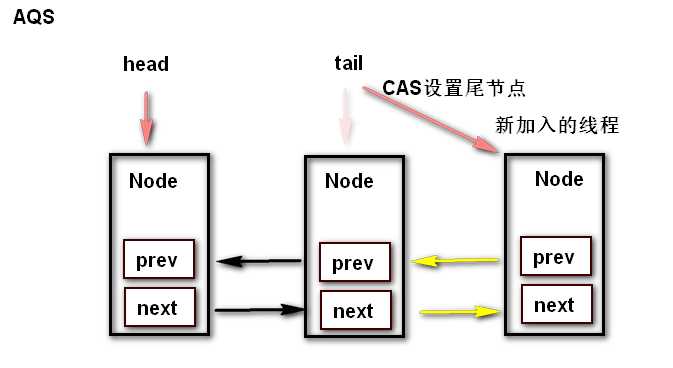
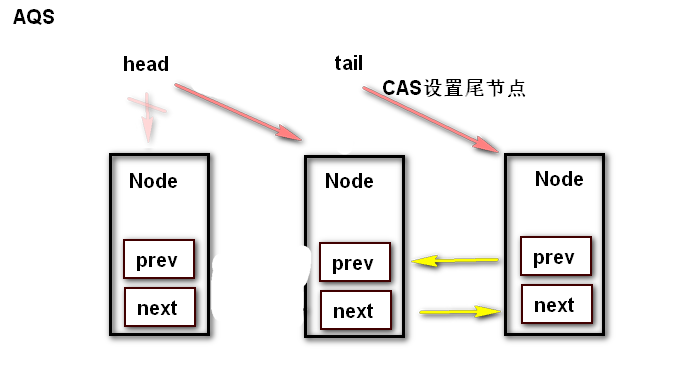
ReentrantLock 的源码分析
ReentrantLock 的时序图
调用 ReentrantLock 中的 lock()方法,源码的调用过程我使用了时序图来展现。
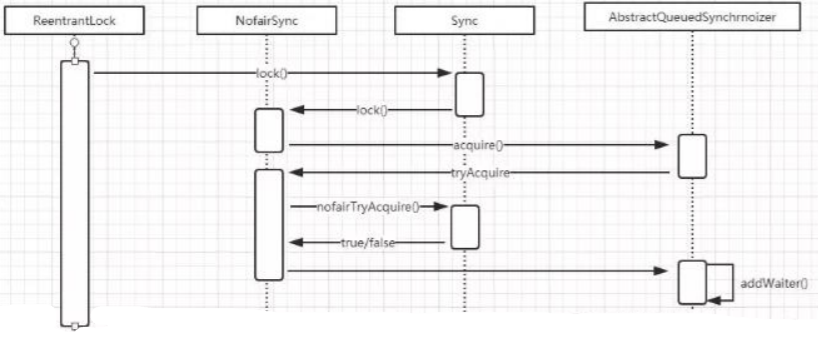
ReentrantLock.lock()
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
NofairSync.lock
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
CAS 的实现原理
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this,stateOffset, expect, update);
}
Unsafe 类
stateOffset
compareAndSwapInt
UNSAFE_ENTRY(jboolean, Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt(JNIEnv *env, jobject unsafe, jobject obj, jlong offset, jint e, jint x))
UnsafeWrapper("Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt");
oop p = JNIHandles::resolve(obj); //将 Java 对象解析成 JVM 的 oop(普通对象指针),
jint* addr = (jint *) index_oop_from_field_offset_long(p, offset); //根据对象 p和地址偏移量找到地址
return (jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e; //基于 cas 比较并替换, x 表示需要更新的值,addr 表示 state 在内存中的地址,e 表示预期值
UNSAFE_END
AQS.accquire
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))selfInterrupt();
}
NonfairSync.tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
ReentrantLock.nofairTryAcquire
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前执行的线程
int c = getState();//获得 state 的值
if (c == ) {//表示无锁状态
if (compareAndSetState(, acquires)) {//cas 替换 state 的值,cas 成功表示获取锁成功
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);//保存当前获得锁的线程,下次再来的时候不要再尝试竞争锁
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//如果同一个线程来获得锁,直接增加重入次数
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < ) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
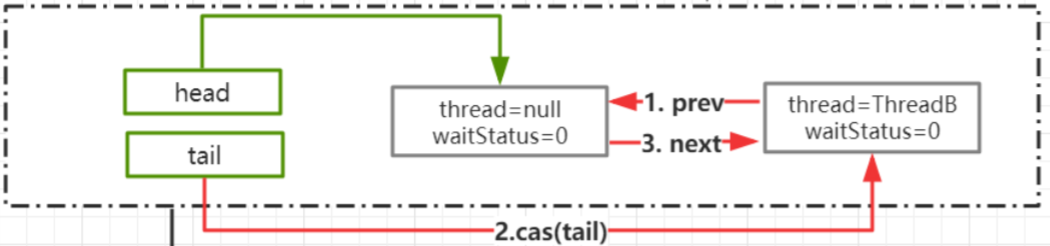
AQS.addWaiter
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);//把当前线程封装为 Node
Node pred = tail; //tail 是 AQS 中表示同比队列队尾的属性,默认是 null
if (pred != null) {//tail 不为空的情况下,说明队列中存在节点
node.prev = pred;//把当前线程的 Node 的 prev 指向 tail
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {//通过 cas 把 node加入到 AQS 队列,也就是设置为 tail
pred.next = node;//设置成功以后,把原 tail 节点的 next指向当前 node
return node;
}
}
enq(node);//tail=null或者compareAndSetTail(pred, node)=false,把 node 添加到同步队列
return node;
}
enq
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
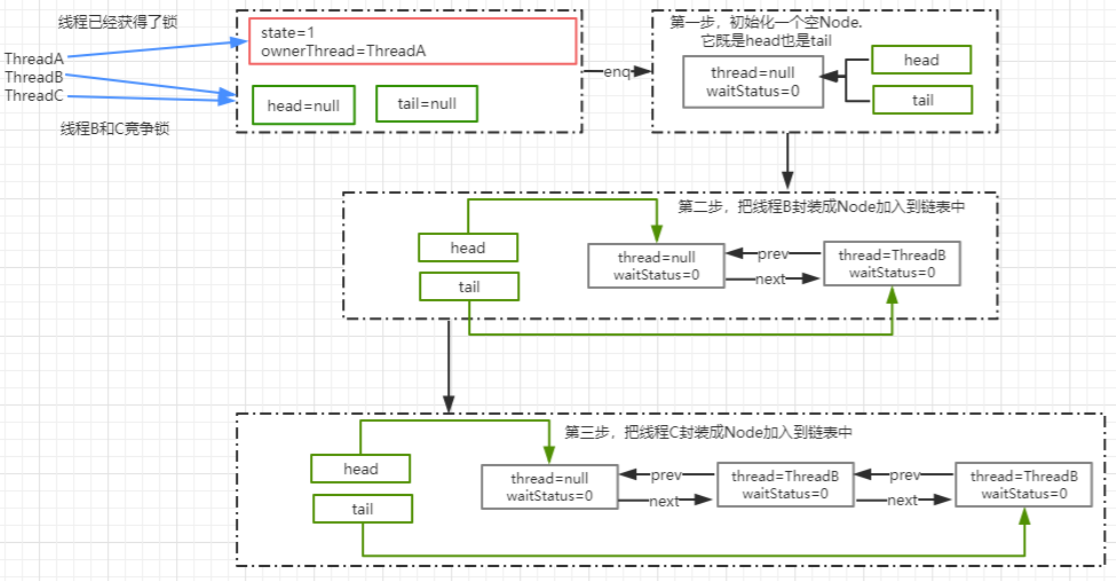
AQS.acquireQueued
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//获取当前节点的 prev 节点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//如果是 head 节点,说明有资格去争抢锁
setHead(node);//获取锁成功,也就是ThreadA 已经释放了锁,然后设置 head 为 ThreadB 获得执行权限
p.next = null; //把原 head 节点从链表中移除
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//ThreadA 可能还没释放锁,使得 ThreadB 在执行 tryAcquire 时会返回 false
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p,node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true; //并且返回当前线程在等待过程中有没有中断过。
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
NofairSync.tryAcquire
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;//前置节点的waitStatus
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)//如果前置节点为 SIGNAL,意味着只需要等待其他前置节点的线程被释放,
return true;//返回 true,意味着可以直接放心的挂起了
if (ws > 0) {//ws 大于 0,意味着 prev 节点取消了排队,直接移除这个节点就行
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;//相当于: pred=pred.prev;
node.prev=pred;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0); //这里采用循环,从双向列表中移除 CANCELLED 的节点
pred.next = node;
} else {//利用 cas 设置 prev 节点的状态为 SIGNAL(-1)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws,Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
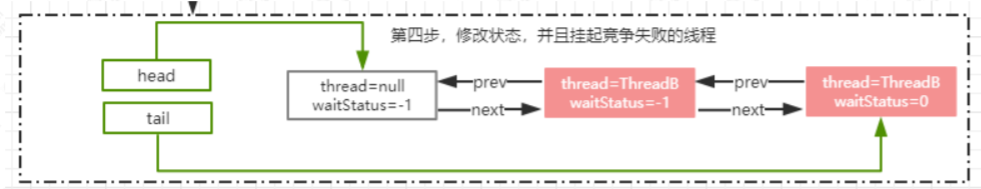
LockSupport
锁的释放流程
ReentrantLock.unlock
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) { //释放锁成功
Node h = head; //得到 aqs 中 head 节点
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)//如果 head 节点不为空并且状态!=0.调用 unparkSuccessor(h)唤醒后续节点
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases){
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() !=getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
unparkSuccessor
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;//获得 head 节点的状态
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);// 设置 head 节点状态为 0
Node s = node.next;//得到 head 节点的下一个节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
//如果下一个节点为 null 或者 status>0 表示 cancelled 状态.
//通过从尾部节点开始扫描,找到距离 head 最近的一个waitStatus<=0 的节点
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t =t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null) //next 节点不为空,直接唤醒这个线程即可
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
为什么在释放锁的时候是从 tail 进行扫描
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}

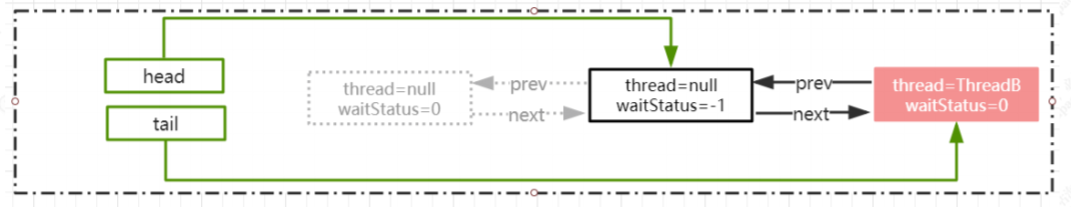
原本挂起的线程继续执行
AQS.acquireQueued
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p,node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
公平锁和非公平锁的区别
FairSync.tryAcquire
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
FairSync.tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
Condition
Condition 的基本使用
ConditionWait
public class ConditionDemoWait implements Runnable{
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public ConditionDemoWait(Lock lock, Condition condition){
this.lock=lock;
this.condition=condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("begin -ConditionDemoWait");
try {
lock.lock();
condition.await();
System.out.println("end - ConditionDemoWait");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
ConditionSignal
public class ConditionDemoSignal implements Runnable{
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public ConditionDemoSignal(Lock lock, Condition condition){
this.lock=lock;
this.condition=condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("begin -ConditionDemoSignal");
try {
lock.lock();
condition.signal();
System.out.println("end - ConditionDemoSignal");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
Condition 源码分析
condition.await
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter(); //创建一个新的节点,节点状态为 condition,采用的数据结构仍然是链表
int savedState = fullyRelease(node); //释放当前的锁,得到锁的状态,并唤醒 AQS 队列中的一个线程
int interruptMode = 0;
//如果当前节点没有在同步队列上,即还没有被 signal,则将当前线程阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {//判断这个节点是否在 AQS 队列上,第一次判断的是 false,因为前面已经释放锁了
LockSupport.park(this); // 第一次总是 park 自己,开始阻塞等待
// 线程判断自己在等待过程中是否被中断了,如果没有中断,则再次循环,会在 isOnSyncQueue 中判断自己是否在队列上.
// isOnSyncQueue 判断当前 node 状态,如果是 CONDITION 状态,或者不在队列上了,就继续阻塞.
// isOnSyncQueue 判断当前 node 还在队列上且不是 CONDITION 状态了,就结束循环和阻塞.
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
// 当这个线程醒来,会尝试拿锁, 当 acquireQueued 返回 false 就是拿到锁了.
// interruptMode != THROW_IE -> 表示这个线程没有成功将 node 入队,但 signal 执行了 enq 方法让其入队了.
// 将这个变量设置成 REINTERRUPT.
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 如果 node 的下一个等待者不是 null, 则进行清理,清理 Condition 队列上的节点.
// 如果是 null ,就没有什么好清理的了.
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 如果线程被中断了,需要抛出异常.或者什么都不做
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively()) //先判断当前线程是否获得了锁
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter; // 拿到 Condition 队列上第一个节点
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
Condition.doSignal
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)// 如果第一个节点的下一个节点是 null, 那么, 最后一个节点也是 null.
lastWaiter = null; // 将 next 节点设置成 null
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
// 如果上一个节点的状态被取消了, 或者尝试设置上一个节点的状态为 SIGNAL失败了(SIGNAL 表示: 他的 next 节点需要停止阻塞),
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws,Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); // 唤醒输入节点上的线程.
return true;
}
AQS.transferForSignal
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
// 如果上一个节点的状态被取消了, 或者尝试设置上一个节点的状态为 SIGNAL失败了(SIGNAL 表示: 他的 next 节点需要停止阻塞),
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws,Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); // 唤醒输入节点上的线程.
return true;
}
Condition 总结
AQS底层原理分析的更多相关文章
- 多线程(四) AQS底层原理分析
J.U.C 简介 Java.util.concurrent 是在并发编程中比较常用的工具类,里面包含很多用来在并发 场景中使用的组件.比如线程池.阻塞队列.计时器.同步器.并发集合等等.并 发包的作者 ...
- HashMap底层原理分析(put、get方法)
1.HashMap底层原理分析(put.get方法) HashMap底层是通过数组加链表的结构来实现的.HashMap通过计算key的hashCode来计算hash值,只要hashCode一样,那ha ...
- AQS工作原理分析
AQS工作原理分析 一.大致介绍1.前面章节讲解了一下CAS,简单讲就是cmpxchg+lock的原子操作:2.而在谈到并发操作里面,我们不得不谈到AQS,JDK的源码里面好多并发的类都是通过Sy ...
- JMM和Volatile底层原理分析
JMM和volatile分析 1.JMM:Java Memory Model,java线程内存模型 JMM:它是一个抽象的概念,描述的是线程和内存间的通信,java线程内存模型和CPU缓存模型类似,它 ...
- springAop:Aop(Xml)配置,Aop注解配置,spring_Aop综合案例,Aop底层原理分析
知识点梳理 课堂讲义 0)回顾Spring体系结构 Spring的两个核心:IoC和AOP 1)AOP简介 1.1)OOP开发思路 OOP规定程序开发以类为模型,一切围绕对象进行,OOP中完成某个任务 ...
- Activiti工作流学习笔记(三)——自动生成28张数据库表的底层原理分析
原创/朱季谦 我接触工作流引擎Activiti已有两年之久,但一直都只限于熟悉其各类API的使用,对底层的实现,则存在较大的盲区. Activiti这个开源框架在设计上,其实存在不少值得学习和思考的地 ...
- AQS实现原理分析——ReentrantLock
在Java并发包java.util.concurrent中可以看到,不少源码是基于AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(以下简写AQS)这个抽象类,因为它是Java并发包的基础工具类, ...
- 基于JAVA Socket的底层原理分析及工具实现
前言 在工作开始之前,我们先来了解一下Socket 所谓Socket,又被称作套接字,它是一个抽象层,简单来说就是存在于不同平台(os)的公共接口.学过网络的同学可以把它理解为基于传输TCP/IP协议 ...
- 从Redis分布式缓存实战入手到底层原理分析、面面俱到覆盖大厂面试考点
概述 官方说明 Redis官网 https://redis.io/ 最新版本6.2.6 Redis中文官网 http://www.redis.cn/ 不过中文官网的同步更新维护相对要滞后不少时间,但对 ...
随机推荐
- 页面中的radio选择适合的非空判断
var cyjb=$('input:radio[name="jcrwModel.cyjb"]:checked').val(); if(cyjb==n ...
- 第K个幸运数(京东2017秋招真题)
题目 4和7是两个幸运数字,我们定义,十进制表示中,每一位只有4和7两个数的正整数都是幸运数字.前几个幸运数字为:4,7,44,47,74,77,444,447... 现在输入一个数字K,输出第K个幸 ...
- sql server for centos7
sql server for centos7 笔者在CENTOS7上面安装SQL SERVER,感觉非常方便. 但有一点要注意,字段是字符串类型的,要使用nvarchar(),不能使用varchar( ...
- React Hooks介绍和环境搭建(一)
React Hooks 简介 2018年底FaceBook的React小组推出Hooks以来,所有的React的开发者都对它大为赞赏.React Hooks就是用函数的形式代替原来的继承类的形式,并且 ...
- hue 登录访问不了HDFS webhdfs_url 调整
Cannot access: /. Note: you are a Hue admin but not a HDFS superuser, "hdfs" or part of HD ...
- (信贷风控九)行为评分卡模型python实现
python信用评分卡建模(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_ca ...
- JFinal-layui极速开发企业应用管理系统
Jfinal-layui 官网:http://www.qinhaisenlin.com/ 项目:https://gitee.com/QinHaiSenLin/Jfinal-layui 介绍 JFina ...
- expandablelistView 可展开的列表
这个东西用法基本固定,不知道能不能做三级的展开. 界面代码 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <L ...
- WPF-支持异步操作的ObservableCollection-AsyncObservableCollection
在进行WPF开发过程中,需要从一个新的线程中操作ObservableCollection,结果程序抛出一个NotSupportedException的错误 public class AsyncObse ...
- error C2061: 语法错误: 标识符“openmode”
今天在一台新机子上编译项目,出现了这个错误,不知如何解决,先记录一下. 1>------ 已启动全部重新生成: 项目: ZERO_CHECK, 配置: Debug x64 ------1> ...
