python的super深入了解(转)
1、python的继承以及调用父类成员
python子类调用父类成员有2种方法,分别是普通方法和super方法
假设Base是基类
class Base(object):
def __init__(self):
print("Base init")
普通方法如下
class Leaf(Base):
def __init__(self):
Base.__init__(self)
print “Leaf init”
super方法如下
class Leaf(Base):
def __init__(self):
super(Leaf, self).__init__()
print “Leaf init”
在上面的简单场景下,两种方法的效果一致
>>> leaf = Leaf() Base init Leaf init
2、钻石继承遇到的难题
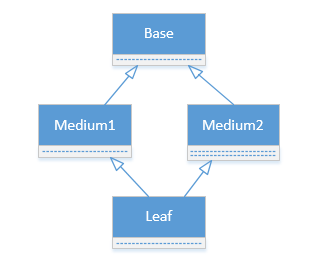
如果我们还是用普通方法调用父类成员,代码如下
class Base(object):
def __init__(self):
print “Base init” class Medium1(Base):
def __init__(self):
Base.__init__(self)
print “Medium1 init” class Medium2(Base):
def __init__(self):
Base.__init__(self)
print “Medium2 init” class Leaf(Medium1, Medium2):
def __init__(self):
Medium1.__init__(self)
Medium2.__init__(self)
print “Leaf init”
当我们实例化Leaf对象时,结果如下
>>> leaf = Leaf() Base init Medium1 init Base init Medium2 init Leaf init
可以看到Base被初始化了两次,这是由于Medium1和Medium2各自调用了Base的初始化函数导致的
3、python的解决方法
python使用的是super来解决这个问题
我们把上面的钻石继承用super重写一下,看一下输出结果
class Base(object):
def __init__(self):
print “Base init” class Medium1(Base):
def __init__(self):
super(Medium1, self).__init__()
print “Medium1 init” class Medium2(Base):
def __init__(self):
super(Medium2, self).__init__()
print “Medium2 init” class Leaf(Medium1, Medium2):
def __init__(self):
super(Leaf, self).__init__()
print “Leaf init”
我们生成Leaf对象:
>>> leaf = Leaf() Base init Medium2 init Medium1 init Leaf init
可以看到整个初始化过程符合我们的预期,Base只被初始化了1次。而且重要的是,相比原来的普通写法,super方法并没有写额外的代码,也没有引入额外的概念
4、super的内核:mro
要理解super的原理,就要先了解mro,mro是method resolution order的缩写,表示了类继承体系中的成员解析顺序
在python中,每个类都有一个mro的类方法,我们来看一下钻石继承中,Leaf类的mro是什么样子的
>>> Leaf.mro() [<class '__main__.Leaf'>, <class '__main__.Medium1'>, <class '__main__.Medium2'>, <class '__main__.Base'>, <type 'object'>]
可以看到mro方法返回的是一个祖先类的列表,Leaf的每个祖先都在其中出现一次,这也是super在父类中查找成员的顺序
通过mro,python巧妙的将多继承的图结构,转变为list的顺序结构,super在继承体系中向上的查找过程,变成了在mro中向右的线性查找过程,任何类都只会被处理一次
通过这个方法,python解决了多继承中的2大难题
1、查找顺序问题,从Leaf的mro顺序可以看出,如果Leaf类通过super来访问父类成员,那么Medium1的成员会在Medium2之前被首先访问到,如果Medium1和Medium2都没有找到,最后再到Base中查找
2、钻石继承的多次初始化问题,在mro的list中,Base类只出现了一次,事实上任何类都只会在mro list中出现一次,这就确保了super向上调用的过程中,任何祖先类的方法都只会被执行一次
至于mro的生成算法,可以参考https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C3_linearization
5、super的具体用法
我们首先来看一下python中的super文档
>>> help(super) Help on class super in module __builtin__: class super(object) | super(type, obj) -> bound super object; requires isinstance(obj, type) | super(type) -> unbound super object | super(type, type2) -> bound super object; requires issubclass(type2, type)
光从字面来看,这可以算是python中最语焉不详的帮助文档之一了。甚至里面还有一些术语误用。那super究竟应该怎么用呢,我们重点来看super中的第1和第3种用法
5.1super(type,obj)
当我们在Leaf的__init__中写这样的super时:
class Leaf(Medium1, Medium2):
def __init__(self):
super(Leaf, self).__init__()
print “Leaf init”
super(Leaf,self).__init__()的意思是说:
1、获取self所属类的mro,也就是[Leaf, Medium1, Medium2, Base]
2、从mro中Leaf右边的一个类开始,依次寻找__init__函数,这是从Medium1开始寻找
3、一旦找到,就把找到的__init__函数绑定到self对象,并返回
从这个执行流程可以看到,如果我们不想调用Medium1的__init__,而想要调用Medium2的__init__,那么
super应该写成:super(Medium1, self)__init__()
5.2super(type,type2)
当我们在Leaf中写类方法的super时
class Leaf(Medium1, Medium2):
def __new__(cls):
obj = super(Leaf, cls).__new__(cls)
print “Leaf new”
return obj
super(Leaf,cls).__new__(cls)的意思是说
1、获取cls这个类的mro,这里也是
2、从mro中Leaf右边的一个类开始,一次寻找__new__函数
3、一旦找到,就返回“”非绑定”的__new__函数
由于返回的是非绑定的函数对象,因此调用时不能省略函数的第一个参数,这也是调用__new__时,需要传入参数cls的原因
同样的,如果我们想从某个mro的某个位置开始查找,只需要修改super的第一个参数就行
6、小结
至此,我们讲解了和super相关的用法及原理,小结一下我们讲过的内容有:
1、python调用父类成员共有2种方法:普通方法,super方法
2、在钻石继承中,普通方法会遇到Base类两次初始化的问题
4、用实例展示了python使用super可以解决此问题
5、讲解了super两种主要的用法及原理
6、Python3.x 和 Python2.x 的一个区别是: Python 3 可以使用直接使用 super().xxx 代替 super(Class, self).xxx :
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/testview/p/4651198.html
python的super深入了解(转)的更多相关文章
- python之super()函数
python之super()函数 python的构造器奇特, 使用魔方. 构造器内对基类对象的初始化同样也很奇特, 奇特到没有半点优雅! 在构造器中使用super(class, instance)返回 ...
- 由Python的super()函数想到的
python-super *:first-child { margin-top: 0 !important; } body>*:last-child { margin-bottom: 0 !im ...
- Python: 你不知道的 super
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000007426467 Python: 你不知道的 super 在类的继承中,如果重定义某个方法,该方法会覆盖父类的同名方法,但有时,我 ...
- python中super的理解(转)
原文地址:https://www.zhihu.com/question/20040039 针对你的问题,答案是可以,并没有区别.但是这题下的回答我感觉都不够好. 要谈论 super,首先我们应该无视 ...
- Python面试题之Python的Super方法
我们最常见的,可以说几乎唯一能见到的使用super的形式是: class SubClass(BaseClass): def method(self): super(SubClass, self).me ...
- Python’s super() considered super!
如果你没有被Python的super()惊愕过,那么要么是你不了解它的威力,要么就是你不知道如何高效地使用它. 有许多介绍super()的文章,这一篇与其它文章的不同之处在于: 提供了实例 阐述了它的 ...
- python中super().__init__和类名.__init__的区别
super().__init__相对于类名.__init__,在单继承上用法基本无差 但在多继承上有区别,super方法能保证每个父类的方法只会执行一次,而使用类名的方法会导致方法被执行多次 多继承时 ...
- Python中super的用法【转载】
Python中super的用法[转载] 转载dxk_093812 最后发布于2019-02-17 20:12:18 阅读数 1143 收藏 展开 转载自 Python面向对象中super用法与MRO ...
- 扯下Python的super()
注: Python 2.7.x 环境下 今晚搜东西无意中看到这篇Understanding Python super() with __init__() methods. 其实这篇老早就看过了, 不过 ...
随机推荐
- Oracle 12cR1 RAC集群安装(二)--使用图形界面安装
Oracle 12cR1 RAC集群安装文档:Oracle 12cR1 RAC集群安装(一)--环境准备Oracle 12cR1 RAC集群安装(二)--使用图形界面安装Oracle 12cR1 RA ...
- 如何使用Mojave将APFS卷上的MacOS Catalina Beta安装到双引导
如果你想与macOS Mojave或macOS High Sierra一起运行MacOS Catalina Beta,你可以通过向Mac添加一个新的APFS卷来实现这一点,如果该Macs硬盘被格式化为 ...
- Python_正则表达式语法
1.正则表达式中的操作符: 2.re库的使用: import re #search方法要求只要待匹配的字符串中包含正则表达式中的字符串就可以 match = re.search('python+',' ...
- asp.net 访问局域网共享文件
最近有个项目ASP.NET的项目,要读写一个局域网里的共享文件夹上的文件,记录如下: 1.访问共享文件 在这里我定义了一个方法,SaveFileExist(filesrc,filename),这个方法 ...
- springboot的第一节课
快速开始spring boot应用 官方向导搭建boot应用 地址:http://start.spring.io/ 设置项目属性: 3.解压,拷贝到工作空间,导入maven项目 4.写Controll ...
- 2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第三场)G: Removing Stones(启发式分治)
题意:给定N,表示N堆石子,每堆石子数为a[],问多少个区间,可以满足“石子总和若为偶数,那么可以两两取来自不同堆的石子,直到取完: 如果为奇数,那么排除其中一个,然后可以两两取来自不同堆的石子,直到 ...
- git基本操作及设置
$ git config --global user.name "wstmljf" $ git config --global user.email "wstmljf@1 ...
- 【模板】A*B Problem(FFT快速傅里叶)
题目:给出两个n位10进制整数x和y,你需要计算x*y.($n \leq 60000$) 分析: 两个正整数的相乘可以视为两个多项式的相乘, 例如 $15 \times 16 = 240$, 可写成 ...
- JSON和计算机网络的个人总结
JSON JSON是什么? JSON:JavaScript Object Notation, JS 对象简谱) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范) ...
- LeetCode 741. Cherry Pickup
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/cherry-pickup/ 题目: In a N x N grid representing a field of che ...
