关于json格式字符串解析并用mybatis存入数据库
园子里面找了很多关于json解析后存入数据库的方法,不是太乱,就是没有写完,我下面的主题代码多是受下面两位的启发,请按顺序查看
http://www.cnblogs.com/tian830937/p/6364622.html,我沿用了这个例子中的json数据格式,多层嵌套。
http://blog.csdn.net/baicp3/article/details/46711067,这个例子虽然是反例,但是引出了JsonArray。方便后续开发。
看完明白上面两个例子后,我们就可以开始了。(注意:没有看懂上面的例子请先看懂,当然,下面的代码复制过去都能用的,最主要是理解)
1.包,请到http://maven.aliyun.com获取,然后复制到pom.xml中
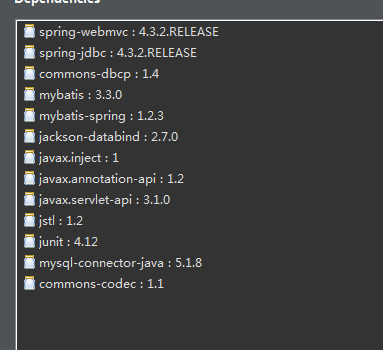
2.配置mybatis.xml,文件放在resource文件夹下,关于数据库的连接就不多讲,照代码中做就是
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd"> <!-- 配置连接mysql -->
<!-- 已测试 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/(数据库名)?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/><!-- localhost:3307 -->
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置MyBatis mapper接口扫描 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:(mapper文件夹名)/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!-- <property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/> -->
<property name="basePackage" value="(项目dao层的位置,如:xxx.xxx.dao)"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.设计实体类(实体类是按照要解析的json数据确定的)
student实体类
package com.bean;
import java.util.Map;
public class Student {
private int age;//年龄
private String gender;//性别,male/female
private String grades;//班级
private String name;//姓名
private Map<String, Double> score;//各科分数
private String scoreId;
private Double weight;//体重
public Student() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(int age, String gender, String grades, String name, String scoreId, Double weight) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.grades = grades;
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
this.scoreId=scoreId;
}
public String getScoreId() {
return scoreId;
}
public void setScoreId(String scoreId) {
this.scoreId = scoreId;
}
public Double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(Double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getGrades() {
return grades;
}
public void setGrades(String grades) {
this.grades = grades;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<String, Double> getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Map<String, Double> score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [age=" + age + ", gender=" + gender + ", grades=" + grades + ", name=" + name + ", score="
+ score + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
Score实体类
package com.bean;
public class Score {
private String scoreId;
private Double Networkprotocol;//网络协议
private Double javaEE;
private Double Computerbasis;//计算机基础
private Double Linuxoperatingsystem;//Linux操作系统
private Double networksecurity;//网络安全
private Double SQLdatabase;//Sql数据库
private Double datastructure;//数据结构
public Score() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Score(String scoreId, Double networkprotocol, Double javaEE, Double computerbasis,
Double linuxoperatingsystem, Double networksecurity, Double sQLdatabase, Double datastructure) {
super();
this.scoreId = scoreId;
Networkprotocol = networkprotocol;
this.javaEE = javaEE;
Computerbasis = computerbasis;
Linuxoperatingsystem = linuxoperatingsystem;
this.networksecurity = networksecurity;
SQLdatabase = sQLdatabase;
this.datastructure = datastructure;
}
public String getScoreId() {
return scoreId;
}
public void setScoreId(String scoreId) {
this.scoreId = scoreId;
}
public Double getNetworkprotocol() {
return Networkprotocol;
}
public void setNetworkprotocol(Double networkprotocol) {
Networkprotocol = networkprotocol;
}
public Double getJavaEE() {
return javaEE;
}
public void setJavaEE(Double javaEE) {
this.javaEE = javaEE;
}
public Double getComputerbasis() {
return Computerbasis;
}
public void setComputerbasis(Double computerbasis) {
Computerbasis = computerbasis;
}
public Double getLinuxoperatingsystem() {
return Linuxoperatingsystem;
}
public void setLinuxoperatingsystem(Double linuxoperatingsystem) {
Linuxoperatingsystem = linuxoperatingsystem;
}
public Double getNetworksecurity() {
return networksecurity;
}
public void setNetworksecurity(Double networksecurity) {
this.networksecurity = networksecurity;
}
public Double getSQLdatabase() {
return SQLdatabase;
}
public void setSQLdatabase(Double sQLdatabase) {
SQLdatabase = sQLdatabase;
}
public Double getDatastructure() {
return datastructure;
}
public void setDatastructure(Double datastructure) {
this.datastructure = datastructure;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Score [scoreId=" + scoreId + ", Networkprotocol=" + Networkprotocol + ", javaEE=" + javaEE
+ ", Computerbasis=" + Computerbasis + ", Linuxoperatingsystem=" + Linuxoperatingsystem
+ ", networksecurity=" + networksecurity + ", SQLdatabase=" + SQLdatabase + ", datastructure="
+ datastructure + "]";
}
}
4.配置dao,建立dao接口
package company.order.dao; import com.bean.Score;
import com.bean.Student; public interface TestDao {
int addStudent(Student student);
int addScore(Score score);
}
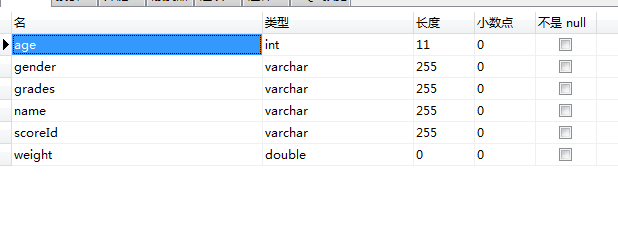
5.设计数据库表结构
student表结构
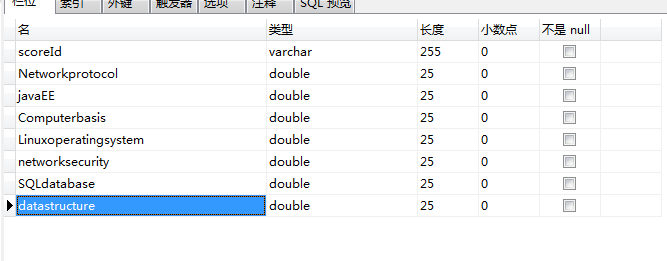
score表结构
6.配置mapper.xml,注意修改路径
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="company.order.dao.TestDao">
<!--测试将json解析的数据存入到数据库 -->
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="com.bean.Student">
insert into student(
age,
gender,
grades,
name,
scoreId,
weight
)values(
#{age},
#{gender},
#{grades},
#{name},
#{scoreId},
#{weight}
)
</insert>
<insert id="addScore" parameterType="com.bean.Score">
insert into score(
scoreId,
Networkprotocol,
javaEE,
Computerbasis,
Linuxoperatingsystem,
networksecurity,
SQLdatabase,
datastructure
)values(
#{scoreId},
#{Networkprotocol},
#{javaEE},
#{Computerbasis},
#{Linuxoperatingsystem},
#{networksecurity},
#{SQLdatabase},
#{datastructure}
)
</insert>
</mapper>
7.上面的准备工作就做好了,然后就是核心业务(模拟的是service业务层)
(1).将json格式字符串解析成想要的数据格式
(2).将数据封装jsonarray
(3).遍历jsonArray,将object数据封装为JSONObject
(4).运用JSONObject.toBean方法,将其封装为实体类对象
(5).写入数据库
import java.util.UUID; import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import company.order.dao.TestDao;
import net.sf.json.JSONArray;
import net.sf.json.JSONObject; public class Domain { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx;
@Before
public void init(){
ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("backstage-mybatis.xml");
} /**
*这个测试的代码相当于service业务层的代码
*/
@Test
public void testJson(){ TestDao dao=ctx. getBean("testDao", TestDao.class);
String jsonstr = "{\"name\":\"三班\",\"students\":[{\"age\":25,\"gender\":\"female\",\"grades\":\"三班\",\"name\":\"露西\",\"score\":{\"网络协议\":98,\"JavaEE\":92,\"计算机基础\":93},\"weight\":51.3},{\"age\":26,\"gender\":\"male\",\"grades\":\"三班\",\"name\":\"杰克\",\"score\":{\"网络安全\":75,\"Linux操作系统\":81,\"计算机基础\":92},\"weight\":66.5},{\"age\":25,\"gender\":\"female\",\"grades\":\"三班\",\"name\":\"莉莉\",\"score\":{\"网络安全\":95,\"Linux操作系统\":98,\"SQL数据库\":88,\"数据结构\":89},\"weight\":55}]}";
int strstrat=jsonstr.indexOf("[");
int endstrat=jsonstr.lastIndexOf("]")+1;
//将数据分成jsonArray
String jsonStr=jsonstr.substring(strstrat, endstrat);
//System.out.println(jsonStr);
JSONArray jsonArray=new JSONArray();
jsonArray =JSONArray.fromObject(jsonStr);
for (Object object : jsonArray) {
JSONObject jsonObject=JSONObject.fromObject(object);
Student studentData=(Student) JSONObject.toBean(jsonObject, Student.class);
//System.out.println(studentData);
String ScoreId= UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//System.out.println(ScoreId);
studentData.setScoreId(ScoreId);//设计ScoreId方便以后关联查询
Student student=new Student(studentData.getAge(), studentData.getGender(), studentData.getGrades(), studentData.getName(), studentData.getScoreId(), studentData.getWeight());
//System.out.println(student);
int a=dao.addStudent(student);//将学生信息写入到数据库
Map<String,Double> Scores= studentData.getScore();
//遍历Scores,将单个数据存入到数据库
/*map遍历总结
* http://www.cnblogs.com/blest-future/p/4628871.html
* */
Score scoreData=new Score();
for (Map.Entry<String , Double> entry : Scores.entrySet()) {
//Map.entry<Integer,String> 映射项(键-值对) 有几个方法:用上面的名字entry
//entry.getKey() ;entry.getValue(); entry.setValue();
//map.entrySet() 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的 Set视图。
//System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " and value= "+ entry.getValue());
if(entry.getKey().equals("网络协议")){
scoreData.setNetworkprotocol(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("JavaEE")){
scoreData.setJavaEE(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("计算机基础")){
scoreData.setComputerbasis(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("网络安全")){
scoreData.setNetworksecurity(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("Linux操作系统")){
scoreData.setLinuxoperatingsystem(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("SQL数据库")){
scoreData.setSQLdatabase(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
} if(entry.getKey().equals("数据结构")){
scoreData.setDatastructure(Double.parseDouble(entry.getValue()+""));
}
}
Score score=new Score(ScoreId, scoreData.getNetworkprotocol(), scoreData.getJavaEE(), scoreData.getComputerbasis(), scoreData.getLinuxoperatingsystem(), scoreData.getNetworksecurity(), scoreData.getSQLdatabase(), scoreData.getDatastructure());
int b=dao.addScore(score);
System.out.println("学生:"+a+";成绩:"+b);
} //JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.fromObject(jsonStr);
//Grades grades = (Grades) JSONObject.toBean(jsonObject, Grades.class);
//System.out.println(grades);
//System.out.println(grades.getName());
//System.out.println(grades.getStudents()); }
}
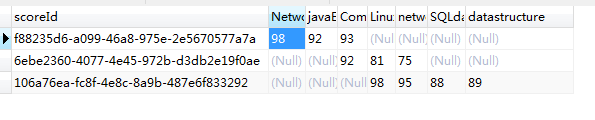
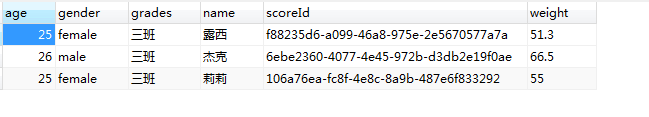
8.结果:
关于json格式字符串解析并用mybatis存入数据库的更多相关文章
- 小白学习Spark系列五:scala解析多级json格式字符串
一.背景 处理json格式的字符串,key值一定为String类型,但value不确定是什么类型,也可能嵌套json字符串,以下是使用 JSON.parseFull 来解析多层json. 二.实例代码 ...
- 在论坛中出现的比较难的sql问题:36(动态行转列 解析json格式字符串)
原文:在论坛中出现的比较难的sql问题:36(动态行转列 解析json格式字符串) 所以,觉得有必要记录下来,这样以后再次碰到这类问题,也能从中获取解答的思路.
- iOS:JSON格式字符串转字典,字典转JSON格式字符串
在iOS开发中,和服务器交互中,经常用到字典和JSON格式字符串相互转换. 代码如下: 1.JSON格式字符串转字典 + (NSDictionary *)dictionaryWithJsonStrin ...
- 关于new Function使用以及将json格式字符串转化为json对象方法介绍
一直对Function()一知半解,今日就Function()的使用做一下总结 一.函数实际是功能完整的对象,用Fucntion()直接创建函数. 语法规则: var 函数名 = new Fun ...
- FastJson对于JSON格式字符串、JSON对象及JavaBean之间的相互转换
fastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了一下三个类: JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换. JSONObject:fas ...
- JSON(五)——同步请求中使用JSON格式字符串进行交互(不太常见的用法)
在同步请求中使用JSON格式进行数据交互的场景并不多,同步请求是浏览器直接与服务器进行数据交互的大多是用jsp的标签jstl和el表达式对请求中的数据进行数据的渲染.我也是在一次开发中要从其它服务器提 ...
- JSON(二)——JavaScript中js对象与JSON格式字符串的相互转换
首先我们来看一下js中JSON格式的字符串 var JSONStr1 = "{\"name\" : \"张三\"}"; 注意以下的写法不是j ...
- C读取json格式字符串
python调用C库时参数太多,约定传json格式字符串,C解析 #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib ...
- FastJson学习:JSON格式字符串、JSON对象及JavaBean之间的相互转换
当前台需要传送一系列相似数据到后端时,可以考虑将其组装成json数组对象,然后转化为json形式的字符串传输到后台 例如: nodes = $('#PmPbsSelect_tree').tree('g ...
随机推荐
- 重新学习MySQL数据库8:MySQL的事务隔离级别实战
重新学习Mysql数据库8:MySQL的事务隔离级别实战 在Mysql中,事务主要有四种隔离级别,今天我们主要是通过示例来比较下,四种隔离级别实际在应用中,会出现什么样的对应现象. Read unco ...
- 基本http服务性能测试(Python vs Golang)
最近学习Golang,总想体验下并发到底有多叼,必我大 python强势多少. 学习了官方教程的http 服务,用性能测试工具wrk测试了下,发现结果很令人惊讶- wrk可以参考我的博客,有基本用法说 ...
- Git 从了解到放弃
1. 简单介绍 1.1. git起源 在1991年linus创建了Linux从此linux成为服务器领域的佼佼者,大部分web服务器.邮件.数据库各种服务器端程序都安装在了linux上面运行,主要是因 ...
- c# out ref 多个返回值问题个人总结
多个返回值可以用ref或者out来实现 如 var b=string.Empty(); var c=string.Empty(); public bool Test(string a, out str ...
- C#常用函数与方法集合
1.DateTime 数字型 System.DateTime currentTime=new System.DateTime(); 1.1 取当前年月日时分秒 ...
- QT中Qtableview视图表格中点击表头进行排序
用QT写了一个小工具,主要是对Excel中大量的数据进行计算和显示. 写了有一段时间,然后断断续续的做一些修改和完善. 因为要显示的数据有多列,很自然的会想到要能够对显示的数据进行排序.如果直接操作m ...
- bzoj1269
题解: splay维护 只不过变成了字符串 代码: #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; +,BS= + ,BN= + ; ,head, ...
- vue.js 源代码学习笔记 ----- 工具方法 option
/* @flow */ import Vue from '../instance/index' import config from '../config' import { warn } from ...
- ThinkPHP 连接数据库
今天在配置连接Mysql 时出现了bool(false)的提示,仔细修改了mysql的密码,还是不对,发现问题应该数据库本身设置了前缀tb_本身的拼写错误和注释掉了 'DB_PREFIX'=>' ...
- 用servlet来提取数据,并作统计,然后用jfreechart画图
指定时间范围的数据提取,并做统计: 用servlet来提取数据,并作统计,然后用jfreechart画图. 使用的话,需要在web.xml里面配置相应的servlet,并且在index.jsp页面做引 ...
