rest framework 节流
一、简单节流示例
所谓节流就是控制用户访问频率,这里分为匿名用户(非登录用户)和登录用户的限制。
- 匿名用户:根据其 IP 限制其频率
- 登录用户:IP、用户名都 OK
获取用户请求 IP:request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
需求:一分钟内匿名用户最多只能访问三次
1、app/utils/throttle.py
import time
# 用户保存用户访问时间记录,以用户 IP 为键,值为当前时间组成的列表,最多只能有三个
VISIT_RECORD = {}
# {'127.0.0.1': [1561284634.3823733, 1561284633.0358386, 1561284631.2291381]}
class VisitThrottle(object):
"""节流,限制访问频率"""
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""允许过去的请求"""
# 获取 ip
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime = time.time()
# 第一次访问
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime, ]
return True
# 获取记录
history = VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr]
self.history = history
# 若列表最后一个和当前时间的差大于 1 分钟,就删除最后一个
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
history.pop() # 弹出最后一个
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0, ctime) # 插入到列表第一个位置
return True
def wait(self):
"""剩余计时"""
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
2、app/views.py
from .utils.throttle import VisitThrottle
class UserInfo(APIView):
"""用户个人信息"""
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle, ]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# user_name = request.user.username
# return HttpResponse(user_name)
# self.dispatch
return HttpResponse('UserInfo')
3、访问:http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/info/,这里我以匿名用户身份访问,三次之后:
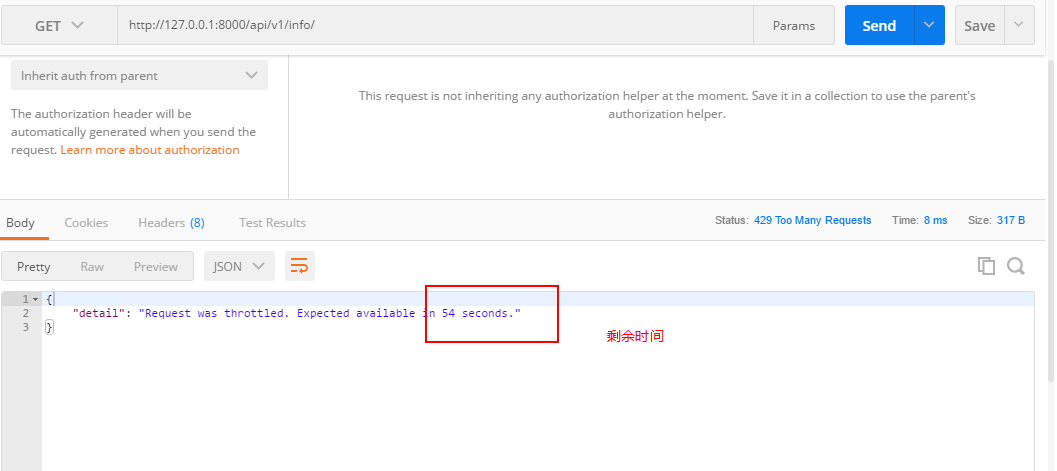
上面是以用户 IP 作为键来限制用户访问频率,若是想要以用户名限制,只需将 IP 更换为用户名即可。
二、全局配置
# 设置全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES": ['app.utils.throttle.VisitThrottle', ],
}
局部设置:
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle, ]
三、内置节流
1、与认证、权限一样,rest framework 也有内置的节流相关实现,一般地自定义节流类需继承 BaseThrottle:
import time
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
VISIT_RECORD = {}
class VisitThrottle(BaseThrottle):
"""节流,限制访问频率"""
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""允许过去的请求"""
# 获取 ip
...
2、类 BaseThrottle 源码:
BaseThrottle 中实现了 allow_request()、get_indent() 以及 wait() 方法,但是除了 get_ident() 方法中获取用户 IP 外,另外两个函数都没有实现其功能。
class BaseThrottle(object):
"""
Rate throttling of requests(对请求进行速率限制).
"""
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
def get_ident(self, request):
"""
Identify the machine making the request by parsing HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR
if present and number of proxies is > 0. If not use all of
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR if it is available, if not use REMOTE_ADDR.
"""
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR') # 获取 IP
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES
if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip()
return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr
def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
3、我们来看看 BaseThrottle 下面的类 SimpleRateThrottle:
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
"""
A simple cache implementation, that only requires `.get_cache_key()`
to be overridden. 一个简单的缓存实现,只需要重写 get_cache_key()方法
The rate (requests / seconds) is set by a `rate` attribute on the View
class. The attribute is a string of the form 'number_of_requests/period'.
速率格式为:request/分钟
Period should be one of: ('s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day')
Previous request information used for throttling is stored in the cache.
用于限制的先前请求信息存储在缓存中
"""
cache = default_cache # Django 内置的缓存
timer = time.time
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES # 从配置文件中加载限制速率
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
self.rate = self.get_rate()
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden.
May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled.
On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
self.now = self.timer()
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True
def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False
def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None
return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
4、它继承 BaseThrottle ,并重写了 allow_request() 和 wait() 方法,另外地还设置控制访问速率属性设置。因此我们自定义节流类时,只需继承 SimpleRateThrottle ,并重写 get_cache_key() 方法即可 app/utils/throttle.py:
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle, SimpleRateThrottle
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'Hubery'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request)
5、settings.py
# 设置全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES": ['app.utils.throttle.VisitThrottle', ],
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES": {
"Hubery": '4/m', # 匿名用户设置每分钟只能访问 4 次
}
}
四、匿名用户和登录用户同时限制
1、app/utils/throttle.py:
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
"""匿名用户根据 IP 限制每分钟访问 4 次"""
scope = 'Hubery'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request)
class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
"""登录用户限制每分钟可以访问 10 次"""
scope = 'Jun' # 随便定义
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return request.user.username
2、settings.py
# 设置全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES": ['app.utils.throttle.UserThrottle', ],
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES": {
"Hubery": '4/m', # 匿名用户设置每分钟只能访问 4 次
"Jun": '10/m', # 登录用户设置每分钟只能访问 10 次
}
}
全局设置 登录用户限制(UserThrottle),局部设置 匿名用户限制即可
3、app/views.py
from .utils.throttle import VisitThrottle
class OrderView(APIView):
"""订单管理"""
# authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication, ] # 添加认证
# authentication_classes = []
# permission_classes = [SVIPPermission, ]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None, 'data': None, }
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
print(request.user)
return JsonResponse(ret)
class UserInfo(APIView):
"""用户个人信息"""
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle, ] # 局部设置匿名用户访问频率
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return HttpResponse('UserInfo')
源码流程图
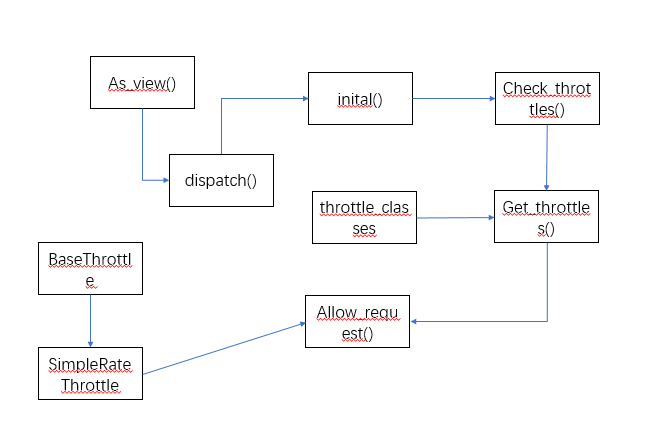
总结
- 自定义节流,须继承
SimpleRateThrottle,并重写get_cache_key()方法 - 可以全局和局部限制,不限制可设置
throttle_classes = []
rest framework 节流的更多相关文章
- windows类书的学习心得
原文网址:http://www.blogjava.net/sound/archive/2008/08/21/40499.html 现在的计算机图书发展的可真快,很久没去书店,昨日去了一下,真是感叹万千 ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django Rest framework 之 节流
RESTful 规范 django rest framework 之 认证(一) django rest framework 之 权限(二) django rest framework 之 节流(三) ...
- 3---Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流 目录 添加节流 自定义节流的方法 限制60s内只能访问3次 (1)API文件夹下面新建throttle.py,代码如下: # u ...
- Django rest framework(3)----节流
目录 Django组件库之(一) APIView源码 Django restframework (1) ----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django res ...
- django的rest framework框架——认证、权限、节流控制
一.登录认证示例 模拟用户登录,获取token,当用户访问订单或用户中心时,判断用户携带正确的token,则允许查看订单和用户信息,否则抛出异常: from django.conf.urls impo ...
- 源码剖析Django REST framework的请求生命周期
学习Django的时候知道,在Django请求的生命周期中,请求经过WSGI和中间件到达路由,不管是FBV还是CBV都会先执行View视图函数中的dispatch方法 REST framework是基 ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(4)----版本
版本 新建一个工程Myproject和一个app名为api (1)api/models.py from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Mo ...
- Django rest framework(7)----分页
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
随机推荐
- c#学习内容
学习winform+DevExpress 界面制作 wpf UIAutomation 控制别的程序 ok c#通过句柄控制别的程序 ok c# 截图 ok c# 多线程 ok c# 数据库myq ...
- Luogu-1381 单词背诵
先将n个单词插入哈希表,记录左右端点,每次右端点往后移动,读入一个新的单词并记录下它的哈希值,如果这个单词之前没出现过那么更新\(ans\)和\(minl\),如果左端点的单词出现了不止一次则可以往右 ...
- 算法(Algorithms)第4版 练习 2.3.17
关键代码: public static void sort(Comparable[] a) { StdRandom.shuffle(a);//eliminate dependence on input ...
- docker仓库及数据卷
docker help rmi, 删除本地镜像 docker run -it --name=centos centos:latest /bin/sh --name的选项可以方便我们以后引用此imag ...
- 3.流程定义的CRUD
表 _re_是仓库的简写 /itcast0711/src/main/java/cn/itcast/b_processDefinition/ProcessDefinitionTest.java pack ...
- 常见SQL函数需要注意的细节
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 这是一位牛人让我们思考的问题,说实话当时真蒙了,函数虽然明白,但细化到这种程度,真的是叫不准啊,下面是几道比较典型的问题,和本人做的实验,不一定准 ...
- JQUERY Uploadify 3.1 C#使用案例
近来因为要做一个上传功能,而firefox又不能直接使用file这样的标签,所以试着用js来写了一个,结果发现代码太多,验证太复杂,而且效果也不理想. 相对的,jquery提供的这一套uploadif ...
- flex与js交互浅析
1.flex调用js方法 调用方法例如:ExternalInterface.call("UploadComplete",oldName,uidName,_dir+"/&q ...
- Python基础-常用模块OS
模块:一个python文件就是一个模块,模块分三种: 1,标准模块,也就是python自带的模块,例如import time,random,string等等 2,第三方模块,这种模块需要自己安装才能 ...
- 基于T4的生成方式
一.什么是T4模板 T4是对“Text Template Transformation Toolkit”(4个T)的简称.是一个基于文本文件转换的工具包.T4的核心是一个基于“文本模板”的转换引擎(以 ...
