js数据结构与算法--双向链表的实现
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据节点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,双向链表中的任意一个节点开始,都可以很方便的访问它的前驱节点和后继节点。
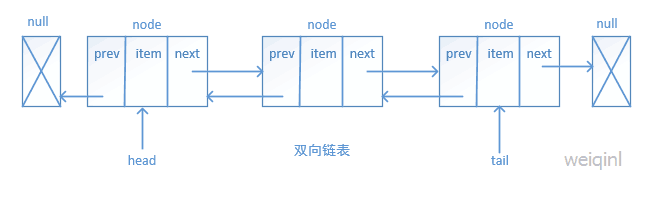
双向链表的实现
linkednode.js ,里面使用了类的继承extends,使用了super函数。
/**
* 链表节点,链表中的项,链表中的节点
*/
export class Node {
constructor(element, next = null) {
this.element = element // 链表中节点的值
this.next = next // 指向列表中下一个节点项的指针
}
}
export class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element, next = null, prev = null) {
super(element, next)
this.prev = prev
}
}
doublyLinkedList.js 双向链表类,实现了各个功能,功能说明,都在代码注释中
import {
DoublyNode
} from './linkednode'
/**
* 双向链表类
*/
export class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
/**
* 链表长度
*/
this.length = 0
/**
* 头指针
*/
this.head = null
/**
* 尾指针
*/
this.tail = null
}
/**
* 在链表末尾添加元素
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
append(element) {
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
this.tail.next = node
node.prev = this.tail
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
return true
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入元素
* @param {Int32Array} position 指定位子
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
insert(position, element) {
// 检查越界值
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
// 实例化一个双向链表的节点
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
// 赋初始值
let current = this.head
let previous
let index = 0 // 位置索引
if (position === 0) { // 在第一个位子添加
if (!this.head) { // 链表无数据的时候,将head和tail都指向新元素
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else { // 链表有数据的时候, head node current
node.next = current
current.prev = node
this.head = node
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 添加到最后一项 current node
current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
} else { // 在列表中间位置添加
// 新链表的节点原型是: previous <---> node <---> current
while (index++ < position) { // 位置索引递增到指定点之前,找出前后两个节点
previous = current // 当前节点设置为新链表中要插入的节点的前一个元素。
current = current.next // 当前节点之后的元素设置为新链表中要插入的节点的当前元素
}
node.next = current
previous.next = node
current.prev = node
node.prev = previous
}
this.length++ // 更新列表的长度
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入元素
* 在链表头,在链表尾,在链表前半段,在链表后半段
* @param {Int32Array} position 指定位置
* @param {*} element 需要插入的元素
*/
insert_up(position, element) {
let node = new DoublyNode(element)
let previous
let current = this.head
if (position > -1 && position <= this.length) {
if (position === 0) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
node.next = current
current.prev = node
this.head = node
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
} else if (position < this.length / 2) { // 目标在链表前半段
let index = 0
// 0 1 2 [] 3 4 5
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = node
node.next = current
node.prev = previous
current.prev = node
} else { // 目标在链表的后半段
// 0 1 2 3 4 | 5 6 [] 7 8 9
let index = this.length
current = this.tail
while (index-- > position) {
previous = current.prev
current = current
}
previous.next = node
node.next = current
node.prev = previous
current.prev = node
}
this.length++
return true
} else {
// 如果超出范围,直接添加到链表末尾
let current = this.tail
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node
this.length++
return true
}
}
/**
* 从任意位置移除元素,返回移除的元素
* 从头部,从尾部,从链表的前半段,从链表的后半段
* @param {*} position 位置索引
*/
removeAt(position) {
let current = this.head // 当前项
let previous // 前一项
let index = 0 // 索引
// 越界检查
if (position > -1 && position < this.length) {
if (position === 0) { // 第一项
this.head = current.next
// 如果是最后一项要删除,将tail置为null,此时head也为null
// 如果非最后一项,则将this.head.prev置为null
if (this.length === 1) { // 只有一项的情况,更新tail
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head.prev = null // 将首项的prev置空 或者 current.next.prev = null
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) { // 最后一项
current = this.tail
previous = current.prev
this.tail = previous
this.tail.next = null
} else if (position <= this.length / 2) { // 索引在链表前半段,分开计算,提升性能
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 将previous与current下一项连起来---跳过current
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
} else { // 索引在链表后半段
index = this.length - 1
current = this.tail
while (index-- > position) {
previous = current
current = current.prev
}
// 将previous与current的上一项连起来--跳过current
previous.prev = current.prev
current.prev.next = previous
}
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
// 超出链表安全长度,链表有数据,则删除末尾元素
if (typeof position === 'number' && this.length > 0) {
let current = this.tail
this.tail = current.prev
this.tail.next = null
this.length--
return current.element
} else {
return null
}
}
}
/**
* 从列表中移除一项
* 先找出元素的索引项,再根据索引移除元素
* @param {*} element 列表中的元素
*/
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
/**
* 返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
* @param {*} element 元素
*/
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head
let index = 0 // 计算位置数
while (current) {
if (element === current.element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
/**
* 判断是否为空链表
* 空链表返回true,非空(链表长度大于0)返回false
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
/**
* 返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似
*/
size() {
return this.length
}
/**
* 获取链表的表头节点
*/
getHead() {
return this.head
}
/**
* 获取链表的尾节点
*/
getTail() {
return this.tail
}
/**
* 输出元素的值
*/
toString() {
let current = this.head
let string = 'null'
while (current) {
string += "<--->" + current.element + (current.next ? '' : '<--->null')
current = current.next
}
return string
}
}
思考
双向链表与单项链表的比较:
双向链表可以双向遍历。从头到尾,或者从尾到头
双向链表可以访问一个特定节点的下一个或者前一个元素,而单链表只能访问下一个元素。
双向链表内存占用比单链表的多
链表还有一个双向循环链表,在需要用到的时候,考虑它们各自的不同,选择合适的链表来操作。
js数据结构与算法--双向链表的实现的更多相关文章
- JS数据结构与算法--双向链表
双向链表中链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向上一个元素,如下图所示: 双向链表结构代码如下: class Node { constructor(element) { this.element ...
- JS数据结构与算法——栈
JS数据结构与算法--栈 1.栈结构概念 栈(Stack)是一种先进后出(LIFO Last in First out)的线性表,先进栈的将会比后进栈的先出栈. 栈的限制是仅允许在一端进行插入和删除运 ...
- JS数据结构与算法-概述
JS数据结构与算法概述 数据结构: 计算机存储, 组织数据的方式, 就像锅碗瓢盆 算法: 一系列解决问题的清晰指令, 就像食谱 两者关系: 程序 = 数据结构 + 算法 邂逅数据结构与算法 什么是数据 ...
- JS数据结构及算法(二) 队列
队列是遵循先进先出的一种数据结构,在尾部添加新元素,并从顶部移除元素. 1.普通队列 function Queue() { this.items = []; } Queue.prototype = { ...
- JS数据结构及算法(一) 堆栈
最近在看<学习JavaScript数据结构与算法>这本书,感觉自己又涨知识了 哈哈... 现在将自己看的做个总结,也是巩固理解. 栈:先进后出,新添加和待删除的元素都保存在栈顶.可以用数组 ...
- js数据结构与算法--单链表的实现与应用思考
链表是动态的数据结构,它的每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成. 现实中,有一些链表的例子. 第一个就是寻宝的游戏.你有一条线索,这条线索是指向寻找下一条线 ...
- JS数据结构与算法 - 剑指offer二叉树算法题汇总
❗❗ 必看经验 在博主刷题期间,基本上是碰到一道二叉树就不会碰到一道就不会,有时候一个下午都在搞一道题,看别人解题思路就算能看懂,自己写就呵呵了.一气之下不刷了,改而先去把二叉树的基础算法给搞搞懂,然 ...
- js数据结构与算法存储结构
数据结构(程序设计=数据结构+算法) 数据结构就是关系,没错,就是数据元素相互之间存在的一种或多种特定关系的集合. 传统上,我们把数据结构分为逻辑结构和物理结构. 逻辑结构:是指数据对象中数据元素之间 ...
- JS数据结构与算法-队列结构
队列结构 一.认识队列 受限的线性结构: 我们已经学习了一种受限的线性结构:栈结构. 并且已经知道这种受限的数据结构对于解决某些特定问题,会有特别的 效果. 下面,我们再来学习另外一个受限的数据结构: ...
随机推荐
- HNOI2018寻宝游戏
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4424 题解 我们首先按位考虑. 如果有一位最终的结果为1,那么我们可以把树的序列看成一个二进制数,先出现的在底位,后出 ...
- MATLAB模型预测控制(MPC,Model Predictive Control)
模型预测控制是一种基于模型的闭环优化控制策略. 预测控制算法的三要素:内部(预测)模型.参考轨迹.控制算法.现在一般则更清楚地表述为内部(预测)模型.滚动优化.反馈控制. 大量的预测控制权威性文献都无 ...
- maven私服nexus清理释放磁盘空间
应用背景: 自建的maven私服(或者叫私仓)nexus在使用过程中,因很多服务不断迭代更新上传jar包至nexus中,底层存放在一个叫Blob Stores的存储中,最近发现该存储已增大至好几百G, ...
- MFC:关联变量
1. 对象(控制)变量(control) a. 数据类型:control 只能创建关联一次 b). control 用来操控控件 c). 创建 control 变量:控件 -> 右击 -& ...
- 从线性模型(linear model)衍生出的机器学习分类器(classifier)
1. 线性模型简介 0x1:线性模型的现实意义 在一个理想的连续世界中,任何非线性的东西都可以被线性的东西来拟合(参考Taylor Expansion公式),所以理论上线性模型可以模拟物理世界中的绝大 ...
- python 使用win32com实现对word文档批量替换页眉页脚
最近由于工作需要,需要将70个word文件的页眉页脚全部进行修改,在想到这个无聊/重复/没有任何技术含量的工作时,我的内心是相当奔溃的.就在我接近奔溃的时候我突然想到完全可以用python脚本来实现这 ...
- 【opencv实践】边缘检测
边缘检测: 一.canny算子 Canny边缘检测根据对信噪比与定位乘积进行测度,得到最优化逼近算子,也就是Canny算子.类似与 LoG 边缘检测方法,也属于先平滑后求导数的方法. 二.canny算 ...
- ue4 staticMesh属性记录
Light Map Resolution 光照贴图分辨率 Generate Mesh Distancde Field 生成网格距离场(一种不怎么消耗性能的阴影) http://api.unrealen ...
- 函数语法:原生js判断某个元素是否有指定的class名的几种方法
var aLi = document.querySelectorAll('#tabs li'); for(var i = 0;i <p.length;i++){ //第一种方法,用classLi ...
- Laravel 5.7 使用 PHP artisan migrate 的问题
这是由于Laravel 默认使用 utf8mb4 字符, 包括支持在数据库存储「 表情」 . 如果你正在运行的 MySQL release 版本低于5.7.7 或 MariaDB release版本低 ...
